Related Research Articles

A bumblebee is any of over 250 species in the genus Bombus, part of Apidae, one of the bee families. This genus is the only extant group in the tribe Bombini, though a few extinct related genera are known from fossils. They are found primarily in higher altitudes or latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere, although they are also found in South America, where a few lowland tropical species have been identified. European bumblebees have also been introduced to New Zealand and Tasmania. Female bumblebees can sting repeatedly, but generally ignore humans and other animals.

Behavioral ecology, also spelled behavioural ecology, is the study of the evolutionary basis for animal behavior due to ecological pressures. Behavioral ecology emerged from ethology after Niko Tinbergen outlined four questions to address when studying animal behaviors: What are the proximate causes, ontogeny, survival value, and phylogeny of a behavior?

The speckled wood is a butterfly found in and on the borders of woodland areas throughout much of the Palearctic realm. The species is subdivided into multiple subspecies, including Pararge aegeria aegeria, Pararge aegeria tircis, Pararge aegeria oblita, and Pararge aegeria insula. The color of this butterfly varies between subspecies. The existence of these subspecies is due to variation in morphology down a gradient corresponding to a geographic cline. The background of the wings ranges from brown to orange, and the spots are either pale yellow, white, cream, or a tawny orange. The speckled wood feeds on a variety of grass species. The males of this species exhibit two types of mate locating behaviors: territorial defense and patrolling. The proportion of males exhibiting these two strategies changes based on ecological conditions. The monandrous female must choose which type of male can help her reproduce successfully. Her decision is heavily influenced by environmental conditions.

A spermatophore or sperm ampulla is a capsule or mass containing spermatozoa created by males of various animal species, especially salamanders and arthropods, and transferred in entirety to the female's ovipore during reproduction. Spermatophores may additionally contain nourishment for the female, in which case it is called a nuptial gift, as in the instance of bush crickets. In the case of the toxic moth Utetheisa ornatrix, the spermatophore includes sperm, nutrients, and pyrrolizidine alkaloids which prevent predation because it is poisonous to most organisms. However, in some species such as the Edith's checkerspot butterfly, the "gift" provides little nutrient value. The weight of the spermatophore transferred at mating has little effect on female reproductive output.
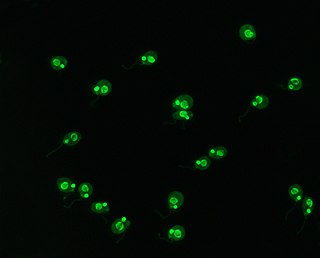
Crithidia is a genus of trypanosomatid Euglenozoa. They are parasites that exclusively parasitise arthropods, mainly insects. They pass from host to host as cysts in infective faeces and typically, the parasites develop in the digestive tracts of insects and interact with the intestinal epithelium using their flagellum. They display very low host-specificity and a single parasite can infect a large range of invertebrate hosts. At different points in its life-cycle, it passes through amastigote, promastigote, and epimastigote phases; the last is particularly characteristic, and similar stages in other trypanosomes are often called crithidial.

Bombus terrestris, the buff-tailed bumblebee or large earth bumblebee, is one of the most numerous bumblebee species in Europe. It is one of the main species used in greenhouse pollination, and so can be found in many countries and areas where it is not native, such as Tasmania. Moreover, it is a eusocial insect with an overlap of generations, a division of labor, and cooperative brood care. The queen is monandrous which means she mates with only one male. B. terrestris workers learn flower colors and forage efficiently.

Haplodiploidy is a sex-determination system in which males develop from unfertilized eggs and are haploid, and females develop from fertilized eggs and are diploid. Haplodiploidy is sometimes called arrhenotoky.

The Apinae are the subfamily that includes the majority of bees in the family Apidae. It includes the familiar "corbiculate" bees—bumblebees, honey bees, orchid bees, stingless bees, and the extinct genus Euglossopteryx. It also includes all but two of the groups that were previously classified in the family Anthophoridae.

The gyne is the primary reproductive female caste of social insects. Gynes are those destined to become queens, whereas female workers are typically sterile and cannot become queens. A colony with multiple queens is said to be a polygyne form, whereas with only one is a monogyne form.

Drosophila pseudoobscura is a species of fruit fly, used extensively in lab studies of speciation. It is native to western North America.

The early bumblebee or early-nesting bumblebee is a small bumblebee with a wide distribution in most of Europe and parts of Asia. It is very commonly found in the UK and emerges to begin its colony cycle as soon as February which is earlier than most other species, hence its common name. There is even some evidence that the early bumblebee may be able to go through two colony cycles in a year. Like other bumblebees, Bombus pratorum lives in colonies with queen and worker castes. Bombus pratorum queens use aggressive behavior rather than pheromones to maintain dominance over the workers!

The tree bumblebee or new garden bumblebee is a species of bumblebee common in the European continent and parts of Asia. Since the start of the twenty-first century, it has spread to the United Kingdom and Iceland. These bumblebees prefer habitats that others do not, allowing them to pollinate flowers in areas that many other species do not get to.
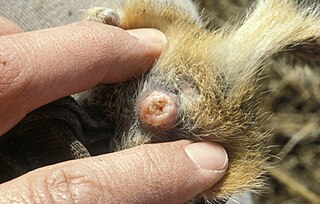
A mating plug, also known as a copulation plug, sperm plug, vaginal plug, sement or sphragis, is gelatinous secretion used in the mating of some species. It is deposited by a male into a female genital tract, such as the vagina, and later hardens into a plug or glues the tract together. While females can expel the plugs afterwards, the male's sperm still gets a time advantage in getting to the egg, which is often the deciding factor in fertilization.

Trigona spinipes is a species of stingless bee. It occurs in Brazil, where it is called arapuá, aripuá, irapuá, japurá or abelha-cachorro ("dog-bee"). The species name means "spiny feet" in Latin. Trigona spinipes builds its nest on trees, out of mud, resin, wax, and assorted debris, including dung. Therefore, its honey is not fit for consumption, even though it is reputed to be of good quality by itself, and is used in folk medicine. Colonies may have from 5,000 to over 100,000 workers.

Bombus muscorum, commonly known as the large carder bee or moss carder bee, is a species of bumblebee in the family Apidae. The species is found throughout Eurasia in fragmented populations, but is most commonly found in the British Isles. B. muscorum is a eusocial insect. The queen is monandrous, mating with only one male after leaving a mature nest to found its own. Males mate territorially and the species is susceptible to inbreeding and bottlenecks. The species builds its nests on or just under the ground in open grassland and forages very close to the nest. In recent years, populations have significantly declined due to loss of natural habitat. B. muscorum is currently listed as vulnerable in Europe by the European Red List of Bees.

Bombus terricola, the yellow-banded bumblebee, is a species of bee in the genus Bombus. It is native to southern Canada and the east and midwest of the United States. It possesses complex behavioral traits, such as the ability to adapt to a queenless nest, choose which flower to visit, and regulate its temperature to fly during cold weather. It was at one time a common species, but has declined in numbers since the late 1990s, likely due to urban development and parasite infection. It is a good pollinator of wild flowers and crops such as alfalfa, potatoes, raspberries, and cranberries.

Plebeia remota is a species of stingless bee that is in the family Apidae and tribe Meliponini. Bees of the species are normally found in a few states in southern Brazil and their nests can be found in tree cavities. Depending on the region, P. remota may have a different morphology and exhibit different behaviors. The bee's diet consists of nectar and pollen that are collected intensely from a few sources. Researchers have conducted a multitude of studies analyzing the changes that occur in the colony during reproductive diapause and what happens during the provisioning and oviposition process or POP.
Nannotrigona testaceicornis is a eusocial stingless bee species of the order Hymenoptera and the genus Nannotrigona. Its local common name is abelhas iraí. This species has a large geographic distribution and occupies different biomes, including urban areas, around Neotropical America. The bees of this species nest in trees or artificial cavities because of this broad distribution. N. testaceicornis is important for agriculture because it will pollinate a vast number of plant species year round.

Bombus ignitus is a species of bumblebee in the family Apidae. It is mainly distributed in Eastern Asia, commonly found in China, Japan, and Korea. It is used in China and Japan commercially as a pollinator. B. ignitus is a eusocial insect with a queen that is monandrous - mating with only one male in the late summer before hibernating until the following spring. It builds its nest out of a mass of pollen and lays its eggs after completion. Due to numerous conflicts between queens and fertile workers, some surviving queens are badly injured, described by some as living corpses.

Bombus morio is one of the few bumblebee species found in South America. These bees reside mainly in the forests of Brazil, nesting on the surface of the ground. They are one of the biggest species of bumblebee and are important pollinators. They are one of the few species of bees that exhibit buzz pollination to collect pollen from the flowers.
References
- ↑ John V. Freudenstein and Finn N. Rasmussen (1999). "What does morphology tell us about orchid relationships?—a cladistic analysis". American Journal of Botany. Botanical Society of America. 86 (2): 225–248. doi: 10.2307/2656939 . JSTOR 2656939. PMID 21680361.
- ↑ Kenneth M. Cameron; et al. (1999). "A phylogenetic analysis of the Orchidaceae: evidence from rbcL nucleotide sequences". American Journal of Botany. Botanical Society of America. 86 (2): 208–224. doi:10.2307/2656938. JSTOR 2656938. PMID 21680360.
- ↑ Lauwers, K.; Van Dyck, H. (2006). "The Cost of Mating with a Non-Virgin Male in a Monandrous Butterfly: Experimental Evidence from the Speckled Wood, Pararge aegeria". Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 60 (1): 69–76. doi:10.1007/s00265-005-0142-4.
- ↑ Baer, B. and P. Schmid-Hempel (2001). "Unexpected consequences of polyandry for parasitism and fitness in the bumblebee, Bombus terrestris". Evolution. 55 (8): 1639–1643. doi:10.1554/0014-3820(2001)055[1639:ucopfp]2.0.co;2. PMID 11580023.
- ↑ Alves, D.A.; Imperatriz-Fonseca, V.L.; Santos-Filho, P.S. (2009). "Production of workers, queens and males in Plebeia remota colonies (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Meliponini), a stingless bee with reproductive diapause". Genetics and Molecular Research. 8 (2): 672–683. doi: 10.4238/vol8-2kerr030 . PMID 19554766.
- ↑ Holman, L.; Freckleton, R. P.; Snook, R. R. (2008). "What use is an infertile sperm? A comparative study of sperm-heteromorphic Drosophila". Evolution. 62 (2): 374–85. doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2007.00280.x. PMID 18053077.
| This botany article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |