Related Research Articles
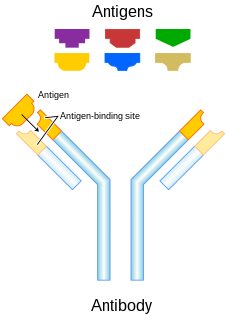
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can tag a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly.
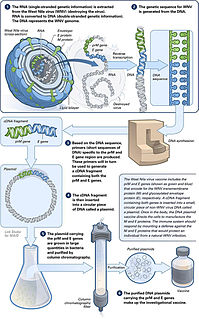
A DNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that transfects a specific antigen-coding DNA sequence into the cells of an organism as a mechanism to induce an immune response.
A monoclonal antibody is an antibody produced from a cell line made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.

In biochemistry, immunostaining is any use of an antibody-based method to detect a specific protein in a sample. The term "immunostaining" was originally used to refer to the immunohistochemical staining of tissue sections, as first described by Albert Coons in 1941. However, immunostaining now encompasses a broad range of techniques used in histology, cell biology, and molecular biology that use antibody-based staining methods.
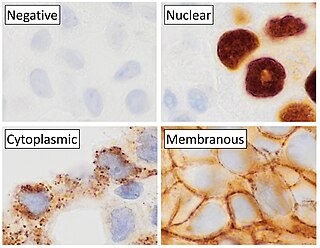
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno", in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and "histo", meaning tissue. Albert Coons conceptualized and first implemented the procedure in 1941.
Polyclonal antibodies (pAbs) are antibodies that are secreted by different B cell lineages within the body. They are a collection of immunoglobulin molecules that react against a specific antigen, each identifying a different epitope.

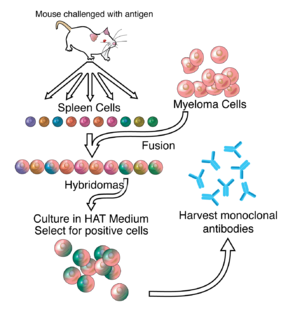
Hybridoma technology is a method for producing large numbers of identical antibodies. This process starts by injecting a mouse with an antigen that provokes an immune response. A type of white blood cell, the B cell, produces antibodies that bind to the injected antigen. These antibody producing B-cells are then harvested from the mouse and, in turn, fused with immortal B cell cancer cells, a myeloma, to produce a hybrid cell line called a hybridoma, which has both the antibody-producing ability of the B-cell and the longevity and reproductivity of the myeloma. The hybridomas can be grown in culture, each culture starting with one viable hybridoma cell, producing cultures each of which consists of genetically identical hybridomas which produce one antibody per culture (monoclonal) rather than mixtures of different antibodies (polyclonal). The myeloma cell line that is used in this process is selected for its ability to grow in tissue culture and for an absence of antibody synthesis. In contrast to polyclonal antibodies, which are mixtures of many different antibody molecules, the monoclonal antibodies produced by each hybridoma line are all chemically identical.

Epitope mapping is the process of experimentally identifying the binding site, or "epitope", of an antibody on its target antigen. Identification and characterization of antibody binding sites aid in the discovery and development of new therapeutics, vaccines, and diagnostics. Epitope characterization can also help elucidate the mechanism of binding for an antibody and can strengthen intellectual property (patent) protection. Experimental epitope mapping data can be incorporated into robust algorithms to facilitate in silico prediction of B-cell epitopes based on sequence and/or structural data. Epitopes are generally divided into three classes: linear, conformational and discontinuous. Linear epitopes are formed by a continuous sequence of amino acids in a protein. In Conformational epitopes the binding residues are contained within certain key protein structural conformations, such as in helices, loops or beta sheets. The conformation of the epitope is important for bringing binding residues in the correct positions. Finally, discontinuous epitopes consist of parts of the antigen that are not close in the protein sequence but are brought together by three-dimensional protein folding. Discontinuous epitopes can harbour linear and conformational parts. B-cell epitope mapping studies suggest that most interactions between antigens and antibodies, particularly autoantibodies and protective antibodies, rely on binding to discontinuous epitopes.

A single-domain antibody (sdAb), also known as a nanobody, is an antibody fragment consisting of a single monomeric variable antibody domain. Like a whole antibody, it is able to bind selectively to a specific antigen. With a molecular weight of only 12–15 kDa, single-domain antibodies are much smaller than common antibodies which are composed of two heavy protein chains and two light chains, and even smaller than Fab fragments and single-chain variable fragments.
Immunogenicity is the ability of a foreign substance, such as an antigen, to provoke an immune response in the body of a human or other animal. It may be wanted or unwanted:

Protein A is a 42 kDa surface protein originally found in the cell wall of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is encoded by the spa gene and its regulation is controlled by DNA topology, cellular osmolarity, and a two-component system called ArlS-ArlR. It has found use in biochemical research because of its ability to bind immunoglobulins. It is composed of five homologous Ig-binding domains that fold into a three-helix bundle. Each domain is able to bind proteins from many mammalian species, most notably IgGs. It binds the heavy chain within the Fc region of most immunoglobulins and also within the Fab region in the case of the human VH3 family. Through these interactions in serum, where IgG molecules are bound in the wrong orientation, the bacteria disrupts opsonization and phagocytosis.

Monoclonal antibody therapy is a form of immunotherapy that uses monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to bind monospecifically to certain cells or proteins. The objective is that this treatment will stimulate the patient's immune system to attack those cells. Alternatively, in radioimmunotherapy a radioactive dose localizes a target cell line, delivering lethal chemical doses. Antibodies have been used to bind to molecules involved in T-cell regulation to remove inhibitory pathways that block T-cell responses. This is known as immune checkpoint therapy.
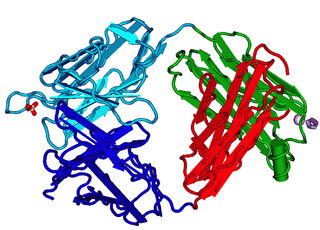
The fragment antigen-binding region is a region on an antibody that binds to antigens. It is composed of one constant and one variable domain of each of the heavy and the light chain. The variable domain contains the paratope, comprising a set of complementarity-determining regions, at the amino terminal end of the monomer. Each arm of the Y thus binds an epitope on the antigen.
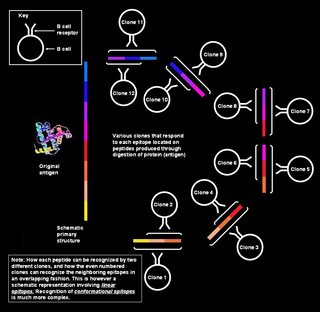
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.

Immunolabeling is a biochemical process that enables the detection and localization of an antigen to a particular site within a cell, tissue, or organ. Antigens are organic molecules, usually proteins, capable of binding to an antibody. These antigens can be visualized using a combination of antigen-specific antibody as well as a means of detection, called a tag, that is covalently linked to the antibody. If the immunolabeling process is meant to reveal information about a cell or its substructures, the process is called immunocytochemistry. Immunolabeling of larger structures is called immunohistochemistry.
Small modular immunopharmaceuticals, or SMIPs for short, are artificial proteins that are intended for use as pharmaceutical drugs. They are largely built from parts of antibodies (immunoglobulins), and like them have a binding site for antigens that could be used for monoclonal antibody therapy. SMIPs have similar biological half-life and, being smaller than antibodies, are reasoned to have better tissue penetration properties. They were invented by Trubion and are now being developed by Emergent BioSolutions, which acquired Trubion in 2010.
A bispecific monoclonal antibody is an artificial protein that can simultaneously bind to two different types of antigen or two different epitopes on the same antigen. Naturally occurring antibodies typically only target one antigen. BsAbs can be manufactured in several structural formats. BsAbs can be designed to recruit and activate immune cells, to interfere with receptor signaling and inactivate signaling ligands, and to force association of protein complexes. BsAbs have been explored for cancer immunotherapy, drug delivery, and Alzeimer's disease.
2F5 is a broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibody (mAb) that has been shown to bind to and neutralize HIV-1 in vitro, making it a potential candidate for use in vaccine synthesis. 2F5 recognizes an epitope in the membrane-proximal external region (MPER) of HIV-1 gp41. 2F5 then binds to this epitope and its constant region interacts with the viral lipid membrane, which neutralizes the virus.
Recombinant antibodies are antibody fragments produced by using recombinant antibody coding genes. They mostly consist of a heavy and light chain of the variable region of immunoglobulin. Recombinant antibodies have many advantages in both medical and research applications, which make them a popular subject of exploration and new production against specific targets. The most commonly used form is the single chain variable fragment (scFv), which has shown the most promising traits exploitable in human medicine and research. In contrast to monoclonal antibodies produced by hybridoma technology, which may lose the capacity to produce the desired antibody over time or the antibody may undergo unwanted changes, which affect its functionality, recombinant antibodies produced in phage display maintain high standard of specificity and low immunogenicity.
Passive antibody therapy, also called serum therapy, is a subtype of passive immunotherapy that administers antibodies to target and kill pathogens or cancer cells. It is designed to draw support from foreign antibodies that are donated from a person, extracted from animals, or made in the laboratory to elicit an immune response instead of relying on the innate immune system to fight disease. It has a long history from the 18th century for treating infectious diseases and is now a common cancer treatment. The mechanism of actions include: antagonistic and agonistic reaction, complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC).
References
- ↑ Larsson K, Wester K, Nilsson P, Uhlén M, Hober S, Wernérus H (2006). "Multiplexed PrEST immunization for high-throughput affinity proteomics". J. Immunol. Methods. 315 (1–2): 110–20. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2006.07.014. PMID 16949094.
- ↑ Labrijn, Aran F; Buijsse, Antonio Ortiz; van den Bremer, Ewald T J; Verwilligen, Annemiek Y W; Bleeker, Wim K; Thorpe, Susan J; Killestein, Joep; Polman, Chris H; Aalberse, Rob C; Schuurman, Janine; van de Winkel, Jan G J; Parren, Paul W H I (2009). "Therapeutic IgG4 antibodies engage in Fab-arm exchange with endogenous human IgG4 in vivo". Nature Biotechnology. 27 (8): 767–771. doi:10.1038/nbt.1553. ISSN 1087-0156. PMID 19620983. S2CID 205274286.