Related Research Articles

Unemployment, according to the OECD, is people above a specified age not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the reference period.

The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics and statistics and serves as a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System. The BLS collects, processes, analyzes, and disseminates essential statistical data to the American public, the U.S. Congress, other Federal agencies, State and local governments, business, and labor representatives. The BLS also serves as a statistical resource to the United States Department of Labor, and conducts research measuring the income levels families need to maintain a satisfactory quality of life.
An economic indicator is a statistic about an economic activity. Economic indicators allow analysis of economic performance and predictions of future performance. One application of economic indicators is the study of business cycles. Economic indicators include various indices, earnings reports, and economic summaries: for example, the unemployment rate, quits rate, housing starts, consumer price index, Inverted yield curve, consumer leverage ratio, industrial production, bankruptcies, gross domestic product, broadband internet penetration, retail sales, price index, and changes in credit conditions.

In economics, a discouraged worker is a person of legal employment age who is not actively seeking employment or who has not found employment after long-term unemployment, but who would prefer to be working. This is usually because an individual has given up looking, hence the term "discouraged".
Freelance, freelancer, or freelance worker, are terms commonly used for a person who is self-employed and not necessarily committed to a particular employer long-term. Freelance workers are sometimes represented by a company or a temporary agency that resells freelance labor to clients; others work independently or use professional associations or websites to get work.

Monster.com is a global employment website that was established in 1999 as a result of the merger between The Monster Board and Online Career Centre.

Nonfarm payroll employment is a compiled name for goods, construction and manufacturing companies in the US. Approximately 80% of the workforce is accounted for nonfarm payrolls and it excludes farm workers, private household employees, actively serving military or non-profit organization employees. Approximately 131,000 businesses and government agencies, which amounts to around 670,000 worksites, are surveyed on a monthly basis.
Consumer confidence is an economic indicator that measures the degree of optimism that consumers feel about the overall state of the economy and their personal financial situation. If the consumer has confidence in the immediate and near future economy and his/her personal finance, then the consumer will spend more than save.

The Conference Board, Inc. is a 501(c)(3) non-profit business membership and research group organization. It counts over 1,000 public and private corporations and other organizations as members, encompassing 60 countries.
CareerBuilder is an American employment website founded in 1995 that operates in the United States, Canada, Europe, and Asia. In 2008, it had the largest market share among online employment websites in the United States. CareerBuilder provides talent management software and other recruitment related services. The company is majority-owned by Apollo Global Management.

An employment agency is an organization which matches employers to employees. In developed countries, there are multiple private businesses which act as employment agencies and a publicly funded employment agency.
An employment website is a website that deals specifically with employment or careers. Many employment websites are designed to allow employers to post job requirements for a position to be filled and are commonly known as job boards. Other employment sites offer employer reviews, career and job-search advice, and describe different job descriptions or employers. Through a job website, a prospective employee can locate and fill out a job application or submit resumes over the Internet for the advertised position.

A farmworker, farmhand or agricultural worker is someone employed for labor in agriculture. In labor law, the term "farmworker" is sometimes used more narrowly, applying only to a hired worker involved in agricultural production, including harvesting, but not to a worker in other on-farm jobs, such as picking fruit.
Green jobs are, according to the United Nations Environment Program, "work in agricultural, manufacturing, research and development (R&D), administrative, and service activities that contribute(s) substantially to preserving or restoring environmental quality. Specifically, but not exclusively, this includes jobs that help to protect ecosystems and biodiversity; reduce energy, materials, and water consumption through high efficiency strategies; de-carbonize the economy; and minimize or altogether avoid generation of all forms of waste and pollution." The environmental sector has the dual benefit of mitigating environmental challenges as well as helping economic growth.
Bill Warren was a corporate human resource executive with Rockwell International and former President of Monster.com. He received the 1997 Employment Management Association’s Pericles Pro Meritus Award for being the founder of online recruiting on the Internet.

The International Labor Comparisons Program (ILC) of the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) adjusts economic statistics to a common conceptual framework in order to make data comparable across countries. Its data can be used to evaluate the economic performance of one country relative to that of other countries and to assess international competitiveness.
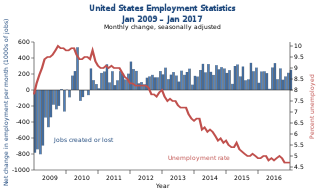
Unemployment in the United States discusses the causes and measures of U.S. unemployment and strategies for reducing it. Job creation and unemployment are affected by factors such as economic conditions, global competition, education, automation, and demographics. These factors can affect the number of workers, the duration of unemployment, and wage levels.
Job losses caused by the Great Recession refers to jobs that have been lost worldwide within people since the start of the Great Recession. In the US, job losses have been going on since December 2007, and it accelerated drastically starting in September 2008 following the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers. By February 2010, the American economy was reported to be more shaky than the economy of Canada. Many service industries have reported dropping their prices in order to maximize profit margins. This is an era in which employment is becoming unstable, and in which being either underemployed or unemployed is a common part of life for many people.
Statistics on unemployment in India had traditionally been collected, compiled and disseminated once every ten years by the Ministry of Labour and Employment (MLE), primarily from sample studies conducted by the National Sample Survey Office. Other than these 5-year sample studies, India had historically not collected monthly, quarterly or yearly nationwide employment and unemployment statistics on a routine basis. In 2016, the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy, a non-governmental entity based in Mumbai, started sampling and publishing monthly unemployment in India statistics.
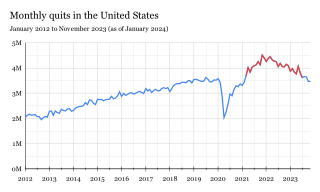
The Great Resignation, also known as the Big Quit and the Great Reshuffle, was a mainly American economic trend in which employees voluntarily resigned from their jobs en masse, beginning in early 2021 during the COVID-19 pandemic. Among the most cited reasons for resigning included wage stagnation amid rising cost of living, limited opportunities for career advancement, hostile work environments, lack of benefits, inflexible remote-work policies, and long-lasting job dissatisfaction. Most likely to quit were workers in hospitality, healthcare, and education. In addition, many of the resigning workers were retiring Baby Boomers, who are one of the largest demographic cohorts in the United States.
References
- 1 2 "Monster Employment Index (MEI) Discontinued". Data Stream. Thomson Reuters.
- ↑ "Jobsearch portal Monster rebranded as Foundit, becomes talent management portal". The Economic Times. 2022-11-23. ISSN 0013-0389 . Retrieved 2024-07-02.
- ↑ Hopkins, Matthew (Jan 14, 2013). "Discontinued Data: U.S. - Monster Employment Index". Data Buffet. Moody's Analytics.