Related Research Articles

Walkerville is a town in Silver Bow County, Montana, United States, that is an enclave of the consolidated city-county of Butte. The population was 639 at the 2020 census. Walkerville is a suburb of Butte, and the only other incorporated community in the county, as well as the only part of the county that is not part of Butte.

Marcus Daly was an Irish-born American businessman known as one of the four "Copper Kings" of Butte, Montana, United States.

Butte is a consolidated city-county and the county seat of Silver Bow County, Montana, United States. In 1977, the city and county governments consolidated to form the sole entity of Butte-Silver Bow. The city covers 718 square miles (1,860 km2), and, according to the 2020 census, has a population of 34,494, making it Montana's fifth-largest city. It is served by Bert Mooney Airport with airport code BTM.

The Berkeley Pit is a former open pit copper mine in the western United States, located in Butte, Montana. It is one mile (1.6 km) long by one-half mile (800 m) wide, with an approximate maximum depth of 1,780 feet (540 m). It is filled to a depth of about 900 feet (270 m) with water that is acidic, about the acidity of beer or tomatoes. As a result, the pit's water is laden with heavy metals and dissolved metals that leach from the rock in a natural process known as acid rock drainage. The dissolved metals include but are not limited to copper, arsenic, cadmium, zinc, and sulfuric acid.

The Anaconda Copper Mine was a large copper mine in Butte, Montana that closed operations in 1947 and was eventually consumed by the Berkeley Pit, a vast open-pit mine. Originally a silver mine, it was bought for $30,000 in 1881 by an Irish immigrant named Marcus Daly from Michael Hickey, a Civil War veteran, and co-owner Charles X. Larabie. From this beginning Daly, along with partners George Hearst, James Ben Ali Haggin and Lloyd Tevis, created the Anaconda Copper Mining Company, which ultimately became a global mining enterprise that would go on to mine 18 billion pounds of copper over 100 years. At the height of The Anaconda Copper Mining Company, it consisted of the Anaconda and other Butte mines, a smelter at Anaconda, Montana, processing plants in Great Falls, Montana, the American Brass Company, and many other properties spanning multiple countries.

The National Copper Corporation of Chile, abbreviated as Codelco, is a Chilean state-owned copper mining company. It was formed in 1976 from foreign-owned copper companies that were nationalised in 1971.

The Copper Kings were industrialists Marcus Daly, William A. Clark, James Andrew Murray and F. Augustus Heinze. They were known for the epic battles fought in Butte, Montana, and the surrounding region, during the Gilded Age, over control of the local copper mining industry, the fight that had ramifications for not only Montana, but the United States as a whole.

Dennis R. Washington is an American billionaire industrialist who owns, or co-owns controlling interests in, a large consortium of privately held companies collectively known as the Washington Companies and, in Canada, another collection of companies known as the Seaspan Marine Corporation.

Frederick "Fritz" Augustus Heinze was an American businessman, known as one of the three Copper Kings of Butte, Montana, along with William Andrews Clark and Marcus Daly. Contemporary assessments variously described him as an intelligent, charismatic but also devious character. To some people in Montana, he was seen as a hero for standing up to the Amalgamated Copper Company, but he also eventually sold his Butte interests to Amalgamated for a reported $12 million. Thereafter, he played a significant role in the Panic of 1907, for which he was indicted but eventually exonerated. Ultimately, Heinze's flamboyant, hard-drinking lifestyle resulted in a hemorrhage of the stomach thought to be caused by cirrhosis of the liver, and he died in November 1914, aged 44.

The Butte, Anaconda and Pacific Railway is a shortline railroad in the U.S. state of Montana. Founded in 1891, it was the main conduit for ore transport between Butte and Anaconda.

The Bingham Canyon Mine, more commonly known as Kennecott Copper Mine among locals, is an open-pit mining operation extracting a large porphyry copper deposit southwest of Salt Lake City, Utah, in the Oquirrh Mountains. The mine is the largest human-made excavation, and deepest open-pit mine in the world, which is considered to have produced more copper than any other mine in history – more than 19,000,000 short tons. The mine is owned by Rio Tinto Group, a British-Australian multinational corporation. The copper operations at Bingham Canyon Mine are managed through Kennecott Utah Copper Corporation which operates the mine, a concentrator plant, a smelter, and a refinery. The mine has been in production since 1906, and has resulted in the creation of a pit over 0.75 miles (1,210 m) deep, 2.5 miles (4 km) wide, and covering 1,900 acres. It was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1966 under the name Bingham Canyon Open Pit Copper Mine. The mine experienced a massive landslide in April 2013 and a smaller slide in September 2013.
The Anaconda Copper Mining Company, known as the Amalgamated Copper Company from 1899 to 1915, was an American mining company headquartered in Butte, Montana. It was one of the largest trusts of the early 20th century and one of the largest mining companies in the world for much of the 20th century.
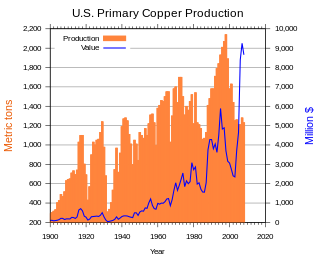
In the United States, copper mining has been a major industry since the rise of the northern Michigan copper district in the 1840s. In 2017, the US produced 1.27 million metric tonnes of copper, worth $8 billion, making it the world's fourth largest copper producer, after Chile, China, and Peru. Copper was produced from 23 mines in the US. Top copper producing states in 2014 were Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, Nevada, and Montana. Minor production also came from Idaho and Missouri. As of 2014, the US had 45 million tonnes of known remaining reserves of copper, the fifth largest known copper reserves in the world, after Chile, Australia, Peru, and Mexico.

The Butte–Anaconda Historic District is a National Historic Landmark (NHL) that spans parts of Walkerville, Butte and Anaconda, Montana, United States. It has the most resources of any U.S. National Historic Landmark District.

The Climax mine, located in Climax, Colorado, United States, is a major molybdenum mine in Lake and Summit counties, Colorado. Shipments from the mine began in 1915. At its highest output, the Climax mine was the largest molybdenum mine in the world, and for many years it supplied three quarters of the world's supply of molybdenum.

Thompson Creek Metals Company Inc. was a full cycle mining company with acquisition, exploration, development, and operation in North America. The corporate office was located in Denver, Colorado. The company primarily produced copper, gold, and molybdenum. Over its history, the Company evolved from being a major primary molybdenum producer to becoming a copper and gold mining company with the construction and development of the Mount Milligan mine and concentrator in British Columbia, Canada. Mount Milligan was Thompson Creek Metals principal operation and the company owned 100% of this property. The company also owned 100% of its Thompson Creek Mine in Idaho. Thompson Creek Metals owned 75% joint venture interest in two other properties, including its Endako Mine in British Columbia, and its Langeloth Metallurgical Facility (roaster) in Pennsylvania. Thompson Creek Metals had additional development projects, including the Berg property in British Columbia.
The Boston and Montana Consolidated Copper and Silver Mining Company was a mining, smelting, and refining company which operated primarily in the state of Montana in the United States. It was established in 1887 and merged with the Amalgamated Copper Company in 1901. The Amalgamated Copper Company changed its name to Anaconda Copper in 1910, and became one of America's largest corporations. Historian Michael P. Malone has written, "Well financed and well managed, the Boston and Montana came to rank among the world's greatest copper companies."
Montana silver mining was a major industry in the 1800s following discovery of numerous silver deposits. Between 1883 and 1891 Montana was second every year to Colorado in silver production, except for 1887 when Montana was number one, producing approximately $15.5 million worth of silver. Major mining districts in Montana included Butte, which was home to many important mines such as the Lexington, Alice, and Moulton mines, and Philipsburg, which housed the Granite Mountain and Bimetallic mines. Other influential, but significantly smaller mines, operated at Helena and the Castle Mountains. The rapid raise and fall of these mines were due to largely geological and economic factors that created favorable conditions for a silver mining boom and subsequent bust. Montana continued to produce considerable silver through most of the 1900s, as a byproduct of copper production at Butte.
Mining in North Korea is important to the country's economy. North Korea is naturally abundant in metals such as magnesite, zinc, tungsten, and iron; with magnesite resources of 6 billion tonnes, particularly in the North and South Hamgyong Provinces, as well as the Chagang Province. However, often these cannot be mined due to the acute shortage of electricity in the country, as well as the lack of proper tools to mine these materials and an antiquated industrial base. Coal, iron ore, limestone, and magnesite deposits are larger than other mineral commodities. Mining joint ventures have occurred with other countries include China, Canada, Egypt, and South Korea.

Butte is a city in southwestern Montana established as a mining camp in the 1860s in the northern Rocky Mountains straddling the Continental Divide. Butte became a hotbed for silver and gold mining in its early stages, and grew exponentially upon the advent of electricity in the late-nineteenth century due to the land's large natural stores of copper. In 1888 alone, mining operations in Butte had generated an output of $23 million. The arrival of several magnates in the area around this time, later known as the "Copper Kings," marked the beginning of Butte's establishment as a boomtown.
References
- ↑ Jim Robbins, "Reopening of Anaconda mine bittersweet," Denver Post, 24 August 1986, p.5B.
- ↑ Associated Press, "Anaconda will close Butte operation," Denver Post, 1 August 1983.
- ↑ Gallagher, Susan (July 11, 2004). "Mine reopening lifts battered Butte". Deseret News. Archived from the original on March 30, 2017. Retrieved 2011-11-11.
- ↑ Steve J. Czehura, "Butte: a world-class ore deposit," Mining Engineering, September 2006, p.18.