Related Research Articles
An economic indicator is a statistic about an economic activity. Economic indicators allow analysis of economic performance and predictions of future performance. One application of economic indicators is the study of business cycles. Economic indicators include various indices, earnings reports, and economic summaries: for example, the unemployment rate, quits rate, housing starts, consumer price index, Inverted yield curve, consumer leverage ratio, industrial production, bankruptcies, gross domestic product, broadband internet penetration, retail sales, price index, and changes in credit conditions.

The price–earnings ratio, also known as P/E ratio, P/E, or PER, is the ratio of a company's share (stock) price to the company's earnings per share. The ratio is used for valuing companies and to find out whether they are overvalued or undervalued.
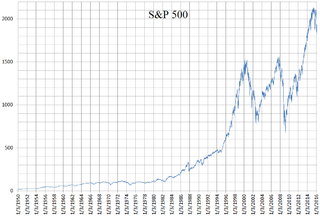
The Standard and Poor's 500, or simply the S&P 500, is a stock market index tracking the stock performance of 500 of the largest companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States. It is one of the most commonly followed equity indices and includes approximately 80% of the total market capitalization of U.S. public companies, with an aggregate market cap of more than $43 trillion as of January 2024.

Inventory or stock refers to the goods and materials that a business holds for the ultimate goal of resale, production or utilisation.

Financial accounting is a branch of accounting concerned with the summary, analysis and reporting of financial transactions related to a business. This involves the preparation of financial statements available for public use. Stockholders, suppliers, banks, employees, government agencies, business owners, and other stakeholders are examples of people interested in receiving such information for decision making purposes.
Year-to-date (YTD) is a period, starting from the beginning of the current year and continuing up to the present day.

XBRL is a freely available and global framework for exchanging business information. XBRL allows the expression of semantics commonly required in business reporting. The standard was originally based on XML, but now additionally supports reports in JSON and CSV formats, as well as the original XML-based syntax. XBRL is also increasingly used in its Inline XBRL variant, which embeds XBRL tags into an HTML document. One common use of XBRL is the exchange of financial information, such as in a company's annual financial report. The XBRL standard is developed and published by XBRL International, Inc. (XII).
The return on equity (ROE) is a measure of the profitability of a business in relation to its equity; where:
Market timing is the strategy of making buying or selling decisions of financial assets by attempting to predict future market price movements. The prediction may be based on an outlook of market or economic conditions resulting from technical or fundamental analysis. This is an investment strategy based on the outlook for an aggregate market rather than for a particular financial asset.
In finance, return is a profit on an investment. It comprises any change in value of the investment, and/or cash flows which the investor receives from that investment over a specified time period, such as interest payments, coupons, cash dividends and stock dividends. It may be measured either in absolute terms or as a percentage of the amount invested. The latter is also called the holding period return.
Year-ending is a 12-month period used for financial and other seasonal reporting.
Same-store sales is a business term that refers to the difference in revenue generated by a retail chain's existing outlets over a certain period, compared to an identical period in the past, usually in the previous year. By comparing sales data from existing outlets that is, by excluding new outlets or outlets which have since closed, the comparison is like-to-like, and avoids comparing fundamentally incomparable data. This financial and operational metric is expressed as a percentage.

Socially responsible investing (SRI) is any investment strategy which seeks to consider financial return alongside ethical, social or environmental goals. The areas of concern recognized by SRI practitioners are often linked to environmental, social and governance (ESG) topics. Impact investing can be considered a subset of SRI that is generally more proactive and focused on the conscious creation of social or environmental impact through investment. Eco-investing is SRI with a focus on environmentalism.
The Springfield ARCA 100 is an ARCA Menards Series stock car race held annually on the Illinois State Fairgrounds Racetrack during the Illinois State Fair.
Quarter-to-date (QTD) is a period starting at the beginning of the current quarter and ending at the current date. Quarter-to-date is used in many contexts, mainly for recording results of an activity in the time between a date and the beginning of either the calendar or fiscal quarter.
Return on investment (ROI) or return on costs (ROC) is the ratio between net income and investment. A high ROI means the investment's gains compare favourably to its cost. As a performance measure, ROI is used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment or to compare the efficiencies of several different investments. In economic terms, it is one way of relating profits to capital invested.

In finance, a stock index, or stock market index, is an index that measures the performance of a stock market, or of a subset of a stock market. It helps investors compare current stock price levels with past prices to calculate market performance.
The Barron's 400 Index or B400 is a stock market index of 400 public companies in the United States, as selected by editors and associates of Barron's magazine. Established in 2007, the Barron's 400 has tended to outperform certain other major indexes at least through the first half of 2013.
References
- ↑ Pound, Samantha Subin,Jesse. "Dow closes lower on Monday, but still posts best month since 1976". CNBC. Retrieved 2023-10-07.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Nikhilesh (2016-08-24). "Generate Month to Date using SQL". Helical IT Solutions Pvt Ltd. Retrieved 2023-10-07.