
The Warsaw Ghetto was the largest of the Nazi ghettos during World War II and the Holocaust. It was established in November 1940 by the German authorities within the new General Government territory of occupied Poland. At its height, as many as 460,000 Jews were imprisoned there, in an area of 3.4 km2 (1.3 sq mi), with an average of 9.2 persons per room, barely subsisting on meager food rations. From the Warsaw Ghetto, Jews were deported to Nazi concentration camps and mass-killing centers. In the summer of 1942, at least 254,000 ghetto residents were sent to the Treblinka extermination camp during Großaktion Warschau under the guise of "resettlement in the East" over the course of the summer. The ghetto was demolished by the Germans in May 1943 after the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising had temporarily halted the deportations. The total death toll among the prisoners of the ghetto is estimated to be at least 300,000 killed by bullet or gas, combined with 92,000 victims of starvation and related diseases, the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising, and the casualties of the final destruction of the ghetto.

Yad Vashem is Israel's official memorial to the victims of the Holocaust. It is dedicated to preserving the memory of the Jews who were murdered; echoing the stories of the survivors; honoring Jews who fought against their Nazi oppressors and gentiles who selflessly aided Jews in need; and researching the phenomenon of the Holocaust in particular and genocide in general, with the aim of avoiding such events in the future. Yad Vashem's vision, as stated on its website, is: "To lead the documentation, research, education and commemoration of the Holocaust, and to convey the chronicles of this singular Jewish and human event to every person in Israel, to the Jewish people, and to every significant and relevant audience worldwide."

Szmul Mordko Zygielbojm was a Polish socialist politician, Bund trade-union activist, and member of the National Council of the Polish government-in-exile.

Yitzhak Zuckerman, also known by his nom de guerre "Antek", was one of the leaders of the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising in 1943 against Nazi Germany during World War II.

The Ghetto Fighters' House, is a Holocaust museum founded in 1949 by members of Kibbutz Lohamei Hagetaot.

Lubartów Ghetto was established by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland during World War II, and existed officially from 1941 until October 1942. The Polish Jews of the town of Lubartów were confined there initially. The ghetto inmates also included Jews deported from other cities in the vicinity including Lublin and Ciechanów and the rest of German-occupied Europe for the total of 3,500 Jews in its initial stages including 2,000 Jews from Slovakia. In May 1942 additional transport from Slovakia with 2,421 Jews arrived.

POLIN Museum of the History of Polish Jews is a museum on the site of the former Warsaw Ghetto. The Hebrew word Polin in the museum's English name means either "Poland" or "rest here" and relates to a legend about the arrival of the first Jews to Poland. Construction of the museum in designated land in Muranów, Warsaw's prewar Jewish quarter, began in 2009, following an international architectural competition won by Finnish architects Rainer Mahlamäki and Ilmari Lahdelma.

The Będzin Ghetto was a World War II ghetto set up by Nazi Germany for the Polish Jews in the town of Będzin in occupied south-western Poland. The formation of the 'Jewish Quarter' was pronounced by the German authorities in July 1940. Over 20,000 local Jews from Będzin, along with additional 10,000 Jews expelled from neighbouring communities, were forced to subsist there until the end of the ghetto history during the Holocaust. Most of the able-bodied poor were forced to work in German military factories before being transported aboard Holocaust trains to the nearby concentration camp at Auschwitz where they were exterminated. The last major deportation of the ghetto inmates by the German SS – men, women and children – between 1 and 3 August 1943 was marked by the ghetto uprising by members of the Jewish Combat Organization.

The Brześć Ghetto or the Ghetto in Brest on the Bug, also: Brześć nad Bugiem Ghetto, and Brest-Litovsk Ghetto was a Nazi ghetto created in occupied Western Belarus in December 1941, six months after the German troops had invaded the Soviet Union in June 1941. Less than a year after the creation of the ghetto, around October 15–18, 1942, most of approximately 20,000 Jewish inhabitants of Brest (Brześć) were murdered; over 5,000 were executed locally at the Brest Fortress on the orders of Karl Eberhard Schöngarth; the rest in the secluded forest of the Bronna Góra extermination site, sent there aboard Holocaust trains under the guise of 'resettlement'.

Henio Zytomirski was a Polish Jew, who was murdered at the age of 9 in a gas chamber at Majdanek concentration camp during the German Nazi occupation of Poland. Henio became an icon of the Holocaust, not only in Lublin but all over Poland. His life story became a part of the curriculum taught in the general education system in Poland. The "Letters to Henio" project has been held in Lublin since 2005. Henio Zytomirski is one of the heroes of "The Primer" permanent exhibition at barrack 53 of the Majdanek Museum, an exhibition dedicated to children held in the camp.

The Monument to the Ghetto Heroes is a monument in Warsaw, Poland, commemorating the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising of 1943 during the Second World War. It is located in the area which was formerly a part of the Warsaw Ghetto, at the spot where the first armed clash of the uprising took place.

The Warsaw Ghetto boundary markers are memorial plaques and boundary lines that mark the maximum perimeter of the former ghetto established by Nazi Germany in 1940 in occupied Warsaw, Poland.
The history of the Jews in Łęczna, Poland is first recorded and dated to 1501. The Jewish community of the town was evident and stable until the holocaust, after which it ceased to exist. The Glincman family from Wlodawa sent some family members to live there in the late 1800s to widen their business to surrounding towns. Nowadays monuments and buildings are still visible and commemorated in town.

The Tarnopol Ghetto was a Jewish World War II ghetto established in 1941 by the Schutzstaffel (SS) in the prewar Polish city of Tarnopol.
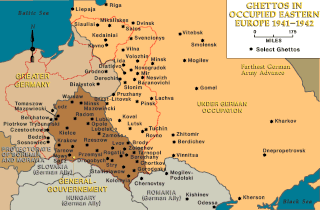
Brzesko Ghetto was a Nazi ghetto during World War II in occupied Poland. The ghetto was created by the Third Reich in 1941 in the Polish town of Brzesko located in the Kraków District about 40 miles from Kraków. The ghetto was open when it was first created. In 1942, walls were put up and the ghetto became a closed ghetto. An estimated 4,000 Jewish people lived there but another 2,000 moved there by 1942, many arriving from Kraków and the surrounding area. The Jewish people living within Brzesko were sent to the Bełżec extermination camp and Auschwitz extermination camp. After the exterminations, the camp was closed end of 1942.

The Warsaw Ghetto Museum is a historical museum in Warsaw currently under construction.

In the best-known photograph taken during the 1943 Warsaw Ghetto Uprising, a boy holds his hands over his head while SS-Rottenführer Josef Blösche points a submachine gun in his direction. The boy and others hid in a bunker during the final liquidation of the ghetto, but they were caught and forced out by German troops. After the photograph was taken, all of the Jews in the photograph were marched to the Umschlagplatz and deported to Majdanek extermination camp or Treblinka. The exact location and the photographer are not known, and Blösche is the only person in the photograph who can be identified with certainty. The image is one of the most famous photographs of the Holocaust, and the boy came to represent children in the Holocaust, as well as all Jewish victims.
The American Memorial to Six Million Jews of Europe, also referred to as the Warsaw Ghetto Memorial, is a public Holocaust memorial situated at Warsaw Ghetto Memorial Plaza in Riverside Park, within the Upper West Side of Manhattan, New York City. It is a monument to the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising and the six million Jews who were murdered in the Holocaust. Dedicated on October 19, 1947, it is one of the first memorials to the Holocaust in the United States.

















