
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. Ecuador also includes the Galápagos Islands in the Pacific, about 1,000 kilometers (621 mi) west of the mainland. The country's capital is Quito and its largest city is Guayaquil.

This article describes the diplomatic affairs, foreign policy and international relations of Ecuador

Quito, officially San Francisco de Quito, is the capital of Ecuador, with an estimated population of 2.8 million in its metropolitan area. It is also the capital of the province of Pichincha. Quito is located in a valley on the eastern slopes of Pichincha, an active stratovolcano in the Andes.

Cuenca, officially Santa Ana de los Ríos de Cuenca, is an Ecuadorian city, head of the canton of the same name and capital of the province of Azuay, as well as its largest and most populated city. It is crossed by the Tomebamba, Tarqui, Yanuncay and Machángara rivers, in the south-central inter-Andean region of Ecuador, in the Paute river basin, at an altitude of 2,538 meters above sea level and with a temperate Andean climate averaging 16.3 °C.

The president of Ecuador, officially called the constitutional president of the Republic of Ecuador, serves as the head of state and head of government of Ecuador. It is the highest political office in the country as the head of the executive branch of government. Per the current constitution, the president can serve two four-year terms. Prior to that, the president could only serve one four-year term.

Loja, formerly Loxa and fully City of the Immaculate Conception of Loja, is the capital of Ecuador's Loja Province. It is located in the Cuxibamba valley in the south of the country, sharing borders with the provinces of Zamora-Chinchipe and other cantons of the province of Loja. Loja holds a rich tradition in the arts, and for this reason is known as the Music and Cultural Capital of Ecuador. The city is home to two major universities.

San Isidro is an upscale district of the Lima Province in Peru. It is located in the west center of the city, it has a few meters of coastline. Officially created on April 24, 1931, San Isidro, along with Orrantia and Country Club neighbourhoods, was separated from Miraflores.

The Second Ecuadorian–Peruvian War, known locally as the War of '41, was a South American border war fought between 5–31 July 1941. It was the first of three military conflicts between Ecuador and Peru during the 20th century.

The Ciudad Mitad del Mundo is a tract of land owned by the prefecture of the province of Pichincha, Ecuador. It is located at San Antonio parish of the canton of Quito, 26 km (16 mi) north of the center of Quito. The grounds contain the Monument to the Equator, which highlights the exact location of the Equator and commemorates the eighteenth-century Franco-Spanish Geodesic Mission which fixed its approximate location; they also contain the Museo Etnográfico Mitad del Mundo, Ethnographic Museum Middle of the Earth, a museum about the indigenous people ethnography of Ecuador.
The Cantons of Ecuador are the second-level subdivisions of Ecuador, below the provinces. There are 221 cantons in the country, of which three are not in any province. The cantons are further sub-divided into parishes, which are classified as either urban or rural. Below is a list of cantons by province.

The Ecuadorian–Peruvian territorial dispute was a territorial dispute between Ecuador and Peru, which, until 1928, also included Colombia. The dispute had its origins on each country's interpretation of what Real Cedulas Spain used to precisely define its colonial territories in the Americas. After independence, all of Spain's colonial territories signed and agreed to proclaim their limits in the basis of the principle of uti possidetis juris, which regarded the Spanish borders of 1810 as the borders of the new republics. However, conflicting claims and disagreements between the newly formed countries eventually escalated to the point of armed conflicts on several occasions.

ALBA or ALBA–TCP, formally the Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America or the Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America – Peoples' Trade Treaty, is an intergovernmental organization based on the idea of political and economic integration of Latin American and Caribbean countries.

The Asociación de Scouts del Ecuador, the national Scouting organization of Ecuador, was founded in 1920, and became a member of the World Organization of the Scout Movement in 1922. The coeducational Asociación de Scouts del Ecuador has 3,220 members as of 2011.
The French Geodesic Mission to the Equator, also called the French Geodesic Mission to Peru and the Spanish-French Geodesic Mission, was an 18th-century expedition to what is now Ecuador carried out for the purpose of performing an arc measurement, measuring the length of a degree of latitude near the Equator, by which the Earth's radius can be inferred. The mission was one of the first geodesic missions carried out under modern scientific principles, and the first major international scientific expedition.

Lenín Boltaire Moreno Garcés is an Ecuadorian politician who served as the 46th president of Ecuador, from 2017 to 2021. Moreno was vice president from 2007 to 2013, serving under President Rafael Correa.

Alausí Canton is a canton in the Chimborazo Province in Ecuador. Its seat is Alausí. The canton is being promoted as a tourist region, and was named a Pueblo Mágico by the Ecuadorian Ministry of Tourism (MINTUR) in 2019.

The National Police of Ecuador is the national police force and the main civil law enforcement agency of Ecuador. It is commanded by the Commanding General and subordinate to the Ministry of the Interior.
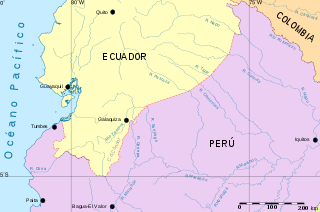
The Brasilia Presidential Act, also known as the Fujimori–Mahuad Treaty, is an international treaty signed in Brasilia by the then President of Ecuador, Jamil Mahuad and then President of Peru, Alberto Fujimori, which effectively put an end to the Ecuadorian–Peruvian territorial dispute.

Ecuador is a nation in northwest South America known as the Republic of Ecuador. Hundreds of thousands of kinds of plants and animals can be found there as a result of the diversity of its four zones. There are roughly 1640 bird species there. Along with the 4,500 kinds of butterflies, there are also 345 reptiles, 358 amphibians, and 258 mammals. Ecuador is regarded as one of the 17 nations with the highest concentration of biodiversity on Earth. The majority of its animals and plants are found in 26 state-protected areas. It also provides gastronomy, a range of cultures and customs, and historical attractions like Quito.
Latin American and Caribbean Space Agency is an international space exploration organization based in Mexico, comprising several countries in Latin America and the Caribbean region. It was established in 2021 as part of the Latin American space race. According to its charter, its objective is to coordinate the space cooperation activities of Latin American and Caribbean countries for the peaceful use and exploration of outer space, the Moon and other celestial bodies.
























