Related Research Articles
A day is the time period of a full rotation of the Earth with respect to the Sun. On average, this is 24 hours. As a day passes at a given location it experiences morning, noon, afternoon, evening, and night. This daily cycle drives circadian rhythms in many organisms, which are vital to many life processes.

Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the local mean time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, counted from midnight. At different times in the past, it has been calculated in different ways, including being calculated from noon; as a consequence, it cannot be used to specify a particular time unless a context is given. The term GMT is also used as one of the names for the time zone UTC+00:00 and, in UK law, is the basis for civil time in the United Kingdom.

A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it is convenient for areas in frequent communication to keep the same time.
The International Meridian Conference was a conference held in October 1884 in Washington, D.C., in the United States, to determine a prime meridian for international use. The conference was held at the request of U.S. President Chester A. Arthur. The subject to discuss was the choice of "a meridian to be employed as a common zero of longitude and standard of time reckoning throughout the world". It resulted in the recommendation of the Greenwich Meridian as the international standard for zero degrees longitude.

Japan Standard Time, or Japan Central Standard Time, is the standard time zone in Japan, 9 hours ahead of UTC (UTC+09:00). Japan does not observe daylight saving time, though its introduction has been debated on several occasions. During World War II, the time zone was often referred to as Tokyo Standard Time.

The International Date Line (IDL) is the line between the South and North Poles that is the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific Ocean, roughly following the 180.0° line of longitude and deviating to pass around some territories and island groups. Crossing the date line eastbound decreases the date by one day, while crossing the date line westbound increases the date.
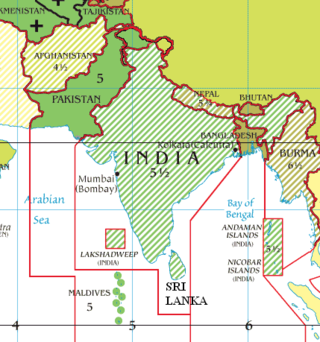
Indian Standard Time (IST), sometimes also called India Standard Time, is the time zone observed throughout the Republic of India, with a time offset of UTC+05:30. India does not observe daylight saving time or other seasonal adjustments. In military and aviation time, IST is designated E* ("Echo-Star"). It is indicated as Asia/Kolkata in the IANA time zone database.
Time in New Zealand is divided by law into two standard time zones. The main islands use New Zealand Standard Time (NZST), 12 hours in advance of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) / military M (Mike), while the outlying Chatham Islands use Chatham Standard Time (CHAST), 12 hours 45 minutes in advance of UTC / military M^ (Mike-Three).

Moscow Time is the time zone for the city of Moscow, Russia, and most of western Russia, including Saint Petersburg. It is the second-westernmost of the eleven time zones of Russia. It has been set to UTC+03:00 without DST since 26 October 2014; before that date it had been set to UTC+04:00 year-round on 27 March 2011.
UTC+11:30 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +11:30.

Sri Lankan Standard Time (SLST) is the time zone for Sri Lanka. It is 5 hours and 30 minutes ahead of GMT/UTC (UTC+05:30) as observed since 15 April 2006.
The UTC offset is the difference in hours and minutes between Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and local solar time, at a particular place. This difference is expressed with respect to UTC and is generally shown in the format ±[hh]:[mm], ±[hh][mm], or ±[hh]. So if the time being described is two hours ahead of UTC, the UTC offset would be "+02:00", "+0200", or simply "+02".
UTC+00:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +00:00. This time zone is the basis of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and all other time zones are based on it. In ISO 8601, an example of the associated time would be written as 2069-01-01T12:12:34+00:00. It is also known by the following geographical or historical names:
Madras Time was a time zone established in 1802 by John Goldingham, the first official astronomer of the British East India Company in British India when he determined the longitude of Madras as 5 hours, 21 minutes and 14 seconds ahead of Greenwich Mean Time. It has been described as 8 minutes and 46 seconds from UTC+05:30 and 32 minutes and 6 seconds behind Calcutta Time which puts it at (UTC+05:21:14). Before India's independence, it was the closest precursor to Indian Standard Time which is derived from the location of the observatory at 82.5°E longitude in Shankargarh Allahabad in Uttar Pradesh.

Bangladesh Standard Time is the time zone of Bangladesh. It is offset six hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time, and observed as a national standard throughout the country. Bangladesh briefly observed daylight saving time (DST) in 2009 to cope with the ongoing electricity crisis, but in 2010 the decision was cancelled by the government of Bangladesh.

India uses only one time zone across the whole nation and all its territories, called Indian Standard Time (IST), which equates to UTC+05:30, i.e. five and a half hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). India does not currently observe daylight saving time.
Venezuela uses the UTC−04:00 time offset, and they had previously used UTC−04:30 from 9 December 2007 until 30 April 2016. The time is commonly called Venezuelan Standard Time (VET), and legally referred to as Hora Legal de Venezuela (HLV) or Venezuela's Legal Time. The HLV is administered by the Navigation and Hydrography Service, in the Cagigal Naval Observatory, Caracas.

Finland uses Eastern European Time (EET) during the winter as standard time and Eastern European Summer Time (EEST) during the summer as daylight saving time. EET is two hours ahead of coordinated universal time (UTC+02:00) and EEST is three hours ahead of coordinated universal time (UTC+03:00). Finland adopted EET on 30 April 1921, and has observed daylight saving time in its current alignment since 1981 by advancing the clock forward one hour at 03:00 EET on the last Sunday in March and back at 04:00 EET on the last Sunday in October, doing so an hour earlier for the first two years.

Various proposals have been made to replace the system of time zones with Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) as a local time.

Iceland observes UTC±00:00 year-round, known as Greenwich Mean Time or Western European Time. UTC±00:00 was adopted on 7 April 1968 – in order for Iceland to be in sync with Europe – replacing UTC−01:00, which had been the standard time zone since 16 November 1907. Iceland previously observed daylight saving time, moving the clock forward one hour, between 1917 and 1921, and 1939 and 1968. The start and end dates varied, as decided by the government. Between 1941 and 1946, daylight saving time commenced on the first Sunday in March and ended in late October, and between 1947 and 1967 it commenced on the first Sunday in April, in all instances since 1941 occurring and ending at 02:00. Since 1994, there have been an increasing number of proposals made to the Althing to reintroduce daylight saving time for a variety of reasons, but all such proposals and resolutions have been rejected.
References
- ↑ "Let's Have More Sunlight - Let's Move India Forward". MoreSunlight.in.
- ↑ "Let there be more light: Advance India's clocks by half an hour for big economic, social and health benefits". 30 June 2017.
- ↑ "Shifting India's Time-Zone by 30 Minutes Will Have Economic, Social, Health and Environmental Benefits: Faisal Farooqui".
- ↑ "It's darkest before an early dawn".
- ↑ Sengupta, D. P.; Ahuja, Dilip R. (16 May 2012). "Advance Indian Standard Time by half an hour". The Hindu. Retrieved 2018-06-20.
- ↑ "Article" (PDF). www.currentscience.ac.in.