
Centaurus is a bright constellation in the southern sky. One of the largest constellations, Centaurus was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. In Greek mythology, Centaurus represents a centaur; a creature that is half human, half horse. Notable stars include Alpha Centauri, the nearest star system to the Solar System, its neighbour in the sky Beta Centauri, and V766 Centauri, one of the largest stars yet discovered. The constellation also contains Omega Centauri, the brightest globular cluster as visible from Earth and the largest identified in the Milky Way, possibly a remnant of a dwarf galaxy.
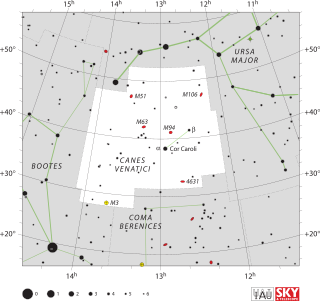
Canes Venatici is one of the 88 constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for 'hunting dogs', and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the Herdsman, a neighboring constellation.

Coma Berenices is an ancient asterism in the northern sky, which has been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is in the direction of the fourth galactic quadrant, between Leo and Boötes, and it is visible in both hemispheres. Its name means "Berenice's Hair" in Latin and refers to Queen Berenice II of Egypt, who sacrificed her long hair as a votive offering. It was introduced to Western astronomy during the third century BC by Conon of Samos and was further corroborated as a constellation by Gerardus Mercator and Tycho Brahe. It is the only modern constellation named for a historic person.

Boris Aleksandrovich Vorontsov-Velyaminov was a Russian astrophysicist. His name is sometimes given as Vorontsov-Vel'yaminov.
NGC 1 is an intermediate spiral galaxy of the morphological type Sbc, located in the constellation of Pegasus. It was discovered on 30 September 1861 by Heinrich d'Arrest.

NGC 2 is an intermediate spiral galaxy with the morphological type of Sab, located in the constellation of Pegasus. NGC 2 was discovered by Lawrence Parsons, 4th Earl of Rosse on 20 August 1873."

NGC 3 is a lenticular galaxy with the morphological type of S0, located in the constellation of Pisces. Other sources classify NGC 3 as a barred spiral galaxy as a type of SBa. It was discovered on November 29, 1864, by Albert Marth.

The Principal Galaxies Catalogue (PGC) is an astronomical catalog published in 1989 that lists B1950 and J2000 equatorial coordinates and cross-identifications for 73,197 galaxies. It is based on the Lyon-Meudon Extragalactic Database (LEDA), which was originally started in 1983. 40,932 coordinates (56%) have standard deviations smaller than 10″. A total of 131,601 names from the 38 most common sources are listed. Available mean data for each object are given:
Vorontsov-Vel'yaminov Interacting Galaxies are those included in the Atlas and Catalogue of Interacting Galaxies, by B.A. Vorontsov-Vel'yaminov, R.I. Noskova and V.P. Arkhipova. It was published by the Astronomical Council of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR.

MCG+07-33-027 is an isolated spiral galaxy located about 330 million light-years away in the constellation Hercules. It has a very high rate of star formation which would make it a starburst galaxy. Normally, starburst galaxies are triggered by the collision of another galaxy. However most galaxies are in groups or clusters, while MCG+07-33-027 is solitary. Therefore, the cause of the starburst was not due to a collision or by the passing of a nearby galaxy and so the cause of the activity remains unknown.

NGC 965 is a spiral galaxy approximately 294 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Cetus. It was discovered by American astronomer Ormond Stone in 1886 with the 26" refractor at Leander McCormick Observatory.

NGC 502, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5034 or UGC 922, is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 113 million light-years from the Solar System and was discovered on 25 September 1862 by German astronomer Heinrich Louis d'Arrest. When the Morphological Catalogue of Galaxies was published between 1962 and 1974, the identifications of NGC 502 and NGC 505 were reversed. In reality, NGC 502 is equal to MGC +01-04-041 and not MCG +01-04-043 as noted in the catalogue.

NGC 1282 is an elliptical galaxy located about 230 million light-years away in the constellation Perseus. It was discovered by astronomer Guillaume Bigourdan on October 23, 1884. NGC 1282 is a member of the Perseus Cluster.

NGC 1283 is an elliptical galaxy located about 250 million light-years away in the constellation Perseus. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer Guillaume Bigourdan on October 23, 1884 and is a member of the Perseus Cluster. It also contains an active galactic nucleus.

NGC 1293 is an elliptical galaxy located about 215 million light-years away in the constellation Perseus. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on October 17, 1786. NGC 1293 is a member of the Perseus Cluster.

NGC 1294 is a lenticular galaxy located about 285 million light-years away in the constellation Perseus. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on October 17, 1786 and is a member of the Perseus Cluster.

NGC 4513 is a lenticular galaxy and a ring galaxy located about 110 million light-years away in the constellation Draco. It was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on October 16, 1866.

MCG+01-02-015 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is an example of a void galaxy, and noted to be one of the loneliest galaxies spotted, with no other galaxy around 100 million light-years in all directions.

NGC 3006 is an edge-on spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It has an apparent magnitude of 15. It was discovered by the astronomer Bindon Stoney on January 25, 1851.

ESO 383-76 is an elongated, X-ray luminous supergiant elliptical galaxy, residing as the dominant, brightest cluster galaxy (BCG) of the Abell 3571 galaxy cluster, the sixth-brightest in the sky at X-ray wavelengths. It is located at the distance of 200.6 megaparsecs from Earth, and is possibly a member of the large Shapley Supercluster. With a diameter of about 540.89 kiloparsecs, it is one of the largest galaxies known.



















