
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word pathology also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue and human cell samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases, and the affix pathy is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment and psychological conditions. A physician practicing pathology is called a pathologist.

A melanocytic nevus is usually a noncancerous condition of pigment-producing skin cells. It is a type of melanocytic tumor that contains nevus cells. Some sources equate the term mole with "melanocytic nevus", but there are also sources that equate the term mole with any nevus form.
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin. It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical doctor who manages diseases related to skin, hair, nails, and some cosmetic problems.
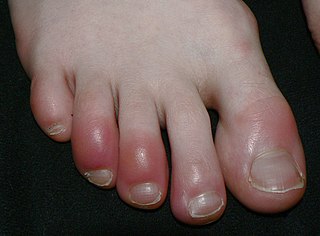
Chilblains, also known as pernio, is a medical condition in which damage occurs to capillary beds in the skin, most often in the hands or feet, when blood perfuses into the nearby tissue, resulting in redness, itching, inflammation, and possibly blisters. It occurs most frequently when predisposed individuals, predominantly women, are exposed to cold and humidity. Ulcerated chilblains are referred to as kibes. Temperature-related chilblains can be prevented by keeping the feet and hands warm in cold weather and avoiding exposing these areas to extreme temperature changes. Once the diagnosis of chilblains is made, first-line treatment includes avoiding cold, damp environments and wearing gloves and warm socks.

A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Dermatoscopy also known as dermoscopy or epiluminescence microscopy, is the examination of skin lesions with a dermatoscope. It is a tool similar to a camera to allow for inspection of skin lesions unobstructed by skin surface reflections. The dermatoscope consists of a magnifier, a light source, a transparent plate and sometimes a liquid medium between the instrument and the skin. Dermatoscope is often handheld, although there are stationary cameras allowing the capture of whole body images in a single shot. When the images or video clips are digitally captured or processed, the instrument can be referred to as a digital epiluminescence dermatoscope. The image is then analyzed automatically and given a score indicating how dangerous it is. This technique is useful to dermatologists and skin cancer practitioners in distinguishing benign from malignant (cancerous) lesions, especially in the diagnosis of melanoma.

Joseph (Josef) Jadassohn was a German dermatologist.
Hans Christian Korting was a German dermatologist and medical researcher specializing in causes and treatment of infectious and non-infectious inflammatory skin diseases as well as non-melanoma skin cancer".

Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) is a chronic autoimmune blistering skin condition, characterised by intensely itchy blisters filled with a watery fluid. DH is a cutaneous manifestation of coeliac disease, although the exact causal mechanism is not known. DH is neither related to nor caused by herpes virus; the name means that it is a skin inflammation having an appearance similar to herpes.

Ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens is a type of familial, autosomal dominant ichthyosis, a rare skin disorder. It is also known as bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma of Siemens or ichthyosis exfoliativa. It is a genetic disorder with no known cure which is estimated to affect about 1 in 500,000 people.
Albert Bernard Ackerman, M.D. was an American dermatologist and pathologist who was "a founding figure in the field of dermatopathology."

Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the sun. Common symptoms in humans and other animals include: red or reddish skin that is hot to the touch or painful, general fatigue, and mild dizziness. Other symptoms include blistering, peeling skin, swelling, itching, and nausea. Excessive UV radiation is the leading cause of (primarily) non-malignant skin tumors, which in extreme cases can be life-threatening. Sunburn is an inflammatory response in the tissue triggered by direct DNA damage by UV radiation. When the cells' DNA is overly damaged by UV radiation, type I cell-death is triggered and the tissue is replaced.
Pseudomelanoma is a cutaneous condition in which melanotic skin lesions clinically resemble a superficial spreading melanoma at the site of a recent shave removal of a melanocytic nevus.
Walter Russell "Nick" Nickel, M.D. was an American dermatologist who was one of the founders of the field of dermatopathology. He was a co-founder and president of four different professional societies and was the founding chairman of the Division of Dermatology at the University of California, San Diego Medical Center.

Alexander Kapp is a German dermatologist and allergist. He was chairman and medical director of the department of dermatology and allergy at the Hannover Medical School until his retirement in 2022. He is known for his work in the field of pathophysiology of inflammatory skin diseases, his research on neuro-immunological interactions in allergic inflammation and on the role of eosinophilic granulocytes in allergy and dermatology.
Clay J. Cockerell is an American physician who works in the field of dermatology and dermatopathology. He is the founder and medical director of Cockerell Dermatopathology, a medical laboratory he operates in Dallas, Texas. He is also a clinical professor of dermatology and dermatopathology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center where he also serves as the director of the dermatopathology division.
Lajos Kemény is a Hungarian dermatologist, venereologist, allergologist, medical researcher, full professor and the Head of the Department of Dermatology and Allergology, the director of the Albert Szent-Györgyi Health Center, Faculty of Medicine, University of Szeged and the Vice-Rector for Science, Research Development and Innovation. He is a notable and respected scientist both in Hungary and around the world.
Thomas Tüting is a German dermatologist and researcher at Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg. He is the clinical director of dermatology and the head of the Laboratory of Experimental Dermatology. His research interests include the identification and characterization of factors responsible for cancer progression and metastasis and resistance to cancer immunotherapy.
Günter Burg is a German dermatologist. Born in Mayen, Germany, he holds German and Swiss citizenship. He has been married to Dr. Doris Burg-Nicklas, a neurologist, since 1968. They have two sons: Andreas and Thomas.

Stephen Ira Katz was an American immunodermatologist who served as the director of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases from 1995 to 2018. He was the Marion B. Sulzberger Professor of Dermatology at the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences from 1989 to 1995.










