Mount Fuji, located on Honshū, is the highest volcano in Japan at 3,776.24 m (12,389 ft), 2nd-highest peak of an island (volcanic) in Asia, and 7th-highest peak of an island in the world. It is a dormant stratovolcano that last erupted in 1707–1708. Mount Fuji lies about 100 kilometers (60 mi) south-west of Tokyo, and can be seen from there on a clear day. Mount Fuji's exceptionally symmetrical cone, which is snow-capped for about 5 months a year, is a well-known symbol of Japan and it is frequently depicted in art and photographs, as well as visited by sightseers and climbers.

Akaishi Mountains is a mountain range in central Honshū, Japan, bordering Nagano, Yamanashi and Shizuoka prefectures. It is also called the Southern Alps, as it joins with the Hida Mountains and the Kiso Mountains to form the Japanese Alps.

The Hida Mountains, or Northern Alps, is a Japanese mountain range which stretches through Nagano, Toyama and Gifu prefectures. A small portion of the mountains also reach into Niigata Prefecture. William Gowland coined the phrase "Japanese Alps" during his time in Japan, but he was only referring to the Hida Mountains when he used that name. The Kiso and Akaishi mountains received the name in the ensuing years.

Yushan, also known as Mount Yu and by other names, is the highest mountain on Taiwan Island at 3,952 m (12,966 ft) above sea level, giving Taiwan the 4th-highest maximum elevation of any island in the world. It is the highest point in the western Pacific region outside of the Kamchatka Peninsula. Yushan and surrounding mountains belong to Yushan Range. The area was once in the ocean; it rose to its current height because of the Eurasian Plate's movement over the Philippine Sea Plate.

Purple Mountain or Zijin Shan is located on the eastern side of Nanjing in Jiangsu province, China. It is 448.2 m (1467 ft) high, with the lowest point 30 m (98 ft). Its peaks are often found enveloped in mysterious purple and golden clouds at dawn and dusk, hence its name.

100 Famous Japanese Mountains is a book composed in 1964 by mountaineer and author Kyūya Fukada. The list became famous when Crown Prince Naruhito took note of it. The list has been the topic of NHK documentaries, and other hiking books.
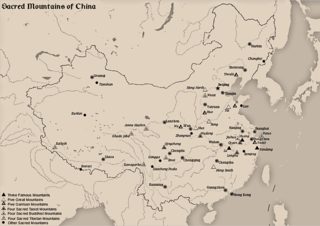
The Sacred Mountains of China are divided into several groups. The Five Great Mountains refers to five of the most renowned mountains in Chinese history, and they were the subjects of imperial pilgrimage by emperors throughout ages. They are associated with the supreme God of Heaven and the five main cosmic deities of Chinese traditional religion. The group associated with Buddhism is referred to as the Four Sacred Mountains of Buddhism, and the group associated with Taoism is referred to as the Four Sacred Mountains of Taoism.

Mount Myōkō is an active stratovolcano in Honshu, Japan. It is situated at the southwest of Myōkō city, Niigata Prefecture, and a part of Jōshin'etsu-kōgen National Park. Mount Myōkō is listed as one of 100 Famous Japanese Mountains, and together with Mount Yahiko, it is well known as the "famous mountain" of Niigata Prefecture.

Pinneshiri is a mountain located in the Hidaka Mountains, Hokkaidō, Japan. The mountain is made from ultramafic rock of unknown age.

Mount Haku, or Mount Hakusan, is a dormant volcano. The stratovolcano is located on the borders of Gifu and Ishikawa prefectures in Japan. It is thought to have first been active 300,000 to 400,000 years ago, with the most recent eruption occurring in 1659. Along with Mount Tate and Mount Fuji, it is one of Japan's "Three Holy Mountains".
The Ryōhaku Mountains are a mountain range spanning Gifu, Toyama, Ishikawa, Fukui and Shiga prefectures in Japan. It is divided into the Kaetsu Mountains, whose major peak is Mount Haku, and the Etsumi Mountains, whose major peak is Mount Nōgōhaku. The range derives its name from the two major peaks, which both have "haku" in their names. Most of the Ryōhaku Mountains are within Hakusan National Park.

Suzuka Mountains are a mountain range running through Mie Prefecture and along the borders of Gifu and Shiga prefectures in central Japan. The tallest peak in the range is Mount Oike at 1,247 m (4,091 ft). In spite of its height, Mount Oike is not the most visited mountain; that distinction belongs to Mount Gozaisho because of its Gozaisho Ropeway, making reaching the peak much easier.

Mount Amagi is a range of volcanic mountains in central Izu Peninsula in Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan, forming the border between Izu City and Higashi-Izu Town. It is also referred to as the Amagi Mountain Range.

Mount Yao, formerly Mount Shiren, is located in west of Pingdingshan, Henan Province. It lies east of the Funiu Mountains. It stands in the middle area of inner land, near to the National Way 311, 207, closing to the Zhijiao Railway. The Spring Temple Buddha is in this mountain.

Mount Azumaya is one of the 100 Famous Japanese Mountains. The 2,354-metre-high (7,723 ft) peak lies on the border of Nagano Prefecture and Gunma Prefecture. There exist alternative spellings of the mountain's name, like: 吾妻山 and 吾嬬山 which is read as "Agatsuma-yama". In the village Tsumagoi, the mountain is spelled 吾妻山.

Mashike Mountains are a group mountains on the western coast of Hokkaidō. The mountain range is divided into two regions by the Hamamasu River. The northern region is a group of volcanic mountains called Shokanbetsudake Mountains. The southern region is known as the Kabato Mountains. The Mashike mountains lie between the Teshio Mountains to the north and the Ishikari Plain to the south. Mashikie mountains includes part of Shokanbetsu-Teuri-Yagishiri Quasi-National Park.

Mount Kamuishiri is a mountain located in the Kabato Mountains of Tōbetsu, Hokkaidō, Japan. Pinneshiri, Mount Kamuishiri, and Mount Machine are together known as The Three Mountains of Kabato.

Pinneshiri (ピンネシリ) is a mountain located in the Kabato Mountains on the border of Tōbetsu and Shintotsukawa, Hokkaidō, Japan. Pinneshiri derives its name from the Ainu language pinne-sir, meaning "male land". The name of neighboring Mount Machine means "female land". Pinneshiri, Mount Kamuishiri, and Mount Machine are together known as The Three Mountains of Kabato.
Pinneshiri may refer to one of the following mountains in Japan: