
Adams Morgan is a neighborhood in Northwest Washington, D.C., centered at the intersection of 18th Street NW and Columbia Road, about 1.5 miles (2.54 km) north of the White House. Known for its broad mix of cultures and activities, Adams Morgan contains together both residential and entertainment areas, and has a vibrant nightlife with numerous bars and restaurants, particularly along 18th Street NW. Columbia Road also holds a busy stretch of shops and businesses. As a distinct, named area, Adams Morgan came into being in the late 1950s, when it drew together several smaller and older neighborhoods that were first developed in the latter 19th and early 20th centuries. It is today composed primarily of well-made rowhouses; and classically-styled mid-rise apartment buildings, many of which are now co-ops and condos; along with various commercial structures.

Mount Pleasant is a neighborhood in the northwestern quadrant of Washington, D.C. It is bounded by Rock Creek Park to the north and west; Harvard Street NW to the south; and 16th Street NW to the east. It is north of Adams Morgan and west of Columbia Heights. It is home to approximately 10,000 people.

Rajshahi Medical College (RMC) is a public medical school located in Rajshahi, Bangladesh. The college is affiliated with Rajshahi Medical University. It was the second such institution in erstwhile East Pakistan after Dhaka Medical College. It has a large hospital which is the central provider for advanced health care in the northern part of Bangladesh.

Massachusetts Avenue is a major diagonal transverse road in Washington, D.C., and the Massachusetts Avenue Historic District is a historic district that includes part of it.
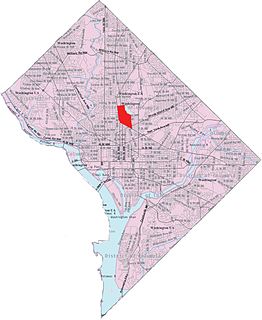
Pleasant Plains is a neighborhood in central Washington, D.C. largely occupied by Howard University. For this reason it is also sometimes referred to as Howard Town or, less frequently, Howard Village.

Lincoln Park is the largest urban park located in the Capitol Hill neighborhood of Washington, D.C. It was known historically as Lincoln Square. From 1862 to 1865, it was the site of the largest hospital in Washington, DC: Lincoln Hospital.

Washington, D.C., during the American Civil War was the center of the Union war effort, which rapidly turned it from a small city into a major capital with full civic infrastructure and strong defenses.

Jefferson General Hospital was the third-largest hospital during the American Civil War, located at Port Fulton, Indiana and was active between February 21, 1864 and December 1866. The land was owned by U.S. Senator from Indiana Jesse D. Bright. Bright was sympathetic to the Confederates, and was expelled from his position as Senator in 1862. Union authorities took the property without compensation, similar to what happened at Arlington National Cemetery.

The Herbert C. Hoover Building is the Washington, D.C. headquarters of the United States Department of Commerce.

The Park Centre for Mental Health is a heritage-listed psychiatric hospital at 60 Grindle Road, Wacol, City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. It is one of the largest psychiatric hospitals in Australia. The hospital provides a range of mental health services, including extended inpatient care, mental health research, education and a high security psychiatric unit. It was designed by Kersey Cannan and built from 1866 to 1923. It is also known as Goodna Hospital for the Insane, Goodna Mental Hospital, Woogaroo Lunatic Asylum, and Wolston Park Hospital Complex. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 21 October 1992.

The Grant Road Historic District is located in the Tenleytown neighborhood of Washington, D.C.. The two-block historic district is what remains of a former settlement in rural Washington County in the District of Columbia. It includes 13 contributing buildings and the road itself, a narrow remnant of a country road that was used by soldiers in the Civil War. Following the war, the road was named after Civil War general and President Ulysses S. Grant. Grant Road developed into a residential street lined with mostly small, two-story homes for working-class people.

The Ellis Island Immigrant Hospital was a United States Public Health Service hospital on Ellis Island in New York Harbor, which operated from 1902 to 1951. The hospital is part of the Statue of Liberty National Monument. While the monument is managed by the National Park Service as part of the National Parks of New York Harbor office, the south side of Ellis Island, including the hospital, is managed by the non-profit Save Ellis Island Foundation and has been off-limits to the general public since its closing in 1954.

Graylands Hospital is Western Australia's largest mental health inpatient facility, and the only public stand-alone psychiatric teaching hospital. It is located on a 10-hectare (25-acre) site in Mount Claremont, in a suburb formerly known as Graylands, after which the hospital was named. The hospital has 178 beds, including 30 beds in the Frankland Centre, and 320 nurses on staff.

Rocky Creek World War Two Hospital Complex is a heritage-listed military hospital at Kennedy Highway, Tolga, Tablelands Region, Queensland, Australia. It was initially built in October 1942, with further construction continuing over the course of much of World War II. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 25 February 2000.

St James' Hospital was a healthcare facility in Balham, London that existed between 1910 and 1988. The hospital buildings occupied sites within the boundary of Ouseley Road, Sarsfield Road and St James's Drive Balham London SW12.

The Armory Square Hospital formally known as the District Armory or Armory of the District of Columbia was a military hospital for the Union Army located on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., which operated from 1862 to 1865. It stood at the intersection of 6th Street SW and B Street SW between the Smithsonian Castle and the Capitol. The 12 wards extended across the Mall, all the way to the Canal. Today, the National Air and Space Museum stands in its place.

Finley General Hospital was a Union Army hospital which operated near Washington, D.C., during the Civil War. It operated from 1862 to 1865.

Harewood General Hospital was one of several purpose-built pavilion style hospitals operating in the Washington, D.C., area during the Civil War which rendered care to Union military personnel. A purpose-built pavilion style hospital, it was in use from September 4, 1862, to May 5, 1866.
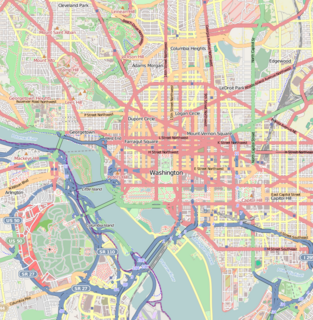
Campbell General Hospital was a Union Civil War hospital which operated from September 1862 to July 20, 1865, in northwest Washington, D.C..

Victoria Hospital was a hospital in Hong Kong. Previously called Victoria Jubilee Hospital, the hospital was named to commemorate the jubilee of Queen Victoria. The foundation stone for the hospital was laid on 22 June 1897. Operation commenced on 7 November 1903 and in December 1947. The hospital buildings were severely damaged during the Second World War and it was decided that the buildings should be demolished to make way for civil servant housing.























