Belgica Mountains is an isolated chain of mountains about 10 miles (16 km) long, standing 60 miles (97 km) east-southeast of the Sor Rondane Mountains in Queen Maud Land, in the Antarctic. The chain was discovered by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition (1957-1958) under Gaston de Gerlache, and named after the ship Belgica, commanded by his father, Lt. Adrien de Gerlache, leader of the Belgian Antarctic Expedition of 1897–99.
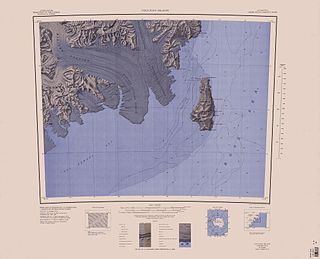
Borchgrevink Glacier is a large glacier in the Victory Mountains, Victoria Land, draining south between Malta Plateau and Daniell Peninsula, and thence projecting into Glacier Strait, Ross Sea, as a floating glacier tongue, the Borchgrevink Glacier Tongue, just south of Cape Jones. It was named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1957–58, for Carsten Borchgrevink, leader of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1898–1900. Borchgrevink visited the area in February 1900 and first observed the seaward portion of the glacier.

The Prince Charles Mountains are a major group of mountains in Mac. Robertson Land in Antarctica, including the Athos Range, the Porthos Range, and the Aramis Range. The highest peak is Mount Menzies, with a height of 3,228 m (10,591 ft). Other prominent peaks are Mount Izabelle and Mount Stinear. These mountains, together with other scattered peaks, form an arc about 420 km (260 mi) long, extending from the vicinity of Mount Starlight in the north to Goodspeed Nunataks in the south.
The Scott Mountains are a large number of isolated peaks lying south of Amundsen Bay in Enderby Land of East Antarctica, Antarctica. Discovered on 13 January 1930 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Sir Douglas Mawson. He named the feature Scott Range after Captain Robert Falcon Scott, Royal Navy. The term mountains is considered more appropriate because of the isolation of its individual features.
Enderby Land is a projecting landmass of Antarctica. Its shore extends from Shinnan Glacier at about 67°55′S44°38′E to William Scoresby Bay at 67°24′S59°34′E, approximately 1⁄24 of the earth's longitude. It was first documented in western and eastern literature in February 1831 by John Biscoe aboard the whaling brig Tula, and named after the Enderby Brothers of London, the ship's owners who encouraged their captains to combine exploration with sealing.
Ironside Glacier is a glacier, about 30 mi (48 km) long, originating at the south side of Mount Minto in the Admiralty Mountains and draining southeast between Mount Whewell and Mount Herschel into Moubray Bay, Victoria Land, Antarctica. At its mouth it is joined by the Honeycomb Glacier flowing in from the north.

Charles Glacier is a small, steep glacier draining the south side of Borg Mountain, in the Borg Massif of Queen Maud Land. It was mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and from air photos by the Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition (NBSAE) (1949–52) and named for Charles W. Swithinbank, a glaciologist with NBSAE.

Norsk Polarinstitutt Glacier is a glacier flowing southwest between Mount Perov and Mount Limburg Stirum in the Belgica Mountains. Discovered by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition, 1957–58, under G. de Gerlache, who named it after the Norsk Polarinstitutt, which at the time was situated in Oslo but today has its headquarters in Tromsø.
Kyle Peak is a peak 2 nautical miles (4 km) northeast of Mount McCarthy, rising to about 2,850 metres (9,350 ft) in the Barker Range of the Victory Mountains, Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee after geologist Philip R. Kyle, who worked in the vicinity of this peak, including in The Pleiades, with the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition, 1971–72, and did further geological work in this area with the United States Antarctic Research Program during the International Northern Victoria Land Project, 1981–82.
Moawhango Névé is a small névé between Mount Camelot and Monte Cassino, in the Freyberg Mountains of Antarctica. It was named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition of 1967–68 in association with a locality of the same name in New Zealand.

Giaever Glacier is a glacier flowing northwest between Mount Kerckhove de Denterghem and Mount Lahaye in the Belgica Mountains of Antarctica. It was discovered by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition, 1957–58, under Gaston de Gerlache, who named it for Norwegian explorer John Schjelderup Giæver, counselor for the expedition, and leader of the Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition, 1949–52.
Mount Harding is the largest mountain in the Grove Mountains of Antarctica, in the south-central part of the range and about 4 nautical miles (7 km) west of Gale Escarpment. It was mapped by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (1956–60) from aerial photographs, and was named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia for N.E. Harding, a topographic draftsman with the Division of National Mapping, Australian Department of National Development, who contributed substantially to the production of Antarctic maps.
Mount Liotard is a mountain having a conspicuous ice-covered peak, 2,225 metres (7,300 ft) high, standing midway between Mount Gaudry and Mount Ditte in the south part of Adelaide Island, Antarctica. It was discovered and first surveyed by the Fourth French Antarctic Expedition in 1909. It was resurveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Andre F. Liotard, a French observer with the FIDS in 1947–48 and the leader of the French Antarctic Expedition, 1949–51.
Mount Tararua is a prominent peak, 2,550 m, surmounting the southwest part of Monteath Hills in the Victory Mountains, Victoria Land. Climbed on January 3, 1963 by the Southern Party of New Zealand Federated Mountain Clubs Antarctic Expedition (NZFMCAE) (1962–63), who named it after their parent mountain club, the Tararua Tramping Club, Wellington, New Zealand.
Salamander Range is a distinctive linear range between the Canham and Black Glacier, in the Freyberg Mountains. Named by the Northern Party of New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE), 1963–64, from the nickname given to Lord Freyberg by Sir Winston Churchill, for the lizard that is untouched by fire.
Skeidshovden Mountain is a mountain rising to 2,730 m at the southwest end of the Wohlthat Mountains in Queen Maud Land. It was first photographed from the air by the German Antarctic Expedition (1938–39). Mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by the Norwegian Antarctic Expedition (1956–60) and named Skeidshovden.
Mount Solvay is a mountain, 2,560 m, close north of Mount Gillet in the Belgica Mountains. Discovered by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition, 1957–58, under Gaston de Gerlache, who named it for Ernest John Solvay, a patron of the expedition.
Mount Kerckhove de Denterghem is a mountain, 2,400 metres (8,000 ft) high, just north of Mount Collard in the Belgica Mountains of Antarctica. It was discovered by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition, 1957–58, under G. de Gerlache, who named it for Count Charles de Kerchove de Denterghem, a patron of the expedition.
Verhaegen is a Dutch-language toponymic surname common in the Belgian provinces of Antwerp and Flemish Brabant. Though, like Verhagen, meaning "from the bushland or hedged lot", at least the name of the noble family of Pierre-Théodore Verhaegen finds its origin in the town of Haacht. Some other variant spellings of the name are Verhaagen, Verhaeghe, Verhaeghen, Verhage, and Verhaghen. People with the name include:
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Mount Verhaegen". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Mount Verhaegen". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey. 


