The Capital Regional District (CRD) is a local government administrative district encompassing the southern tip of Vancouver Island and the southern Gulf Islands in the Canadian province of British Columbia. The CRD is one of several regional districts in British Columbia and had an official population of 415,451 as of the Canada 2021 Census.

Greater Victoria is located in British Columbia, Canada, on the southern tip of Vancouver Island. It is usually defined as the thirteen municipalities of the Capital Regional District (CRD) on Vancouver Island as well as some adjacent areas and nearby islands.

The Taconic Mountains are a 150-mile-long sub-range of the Appalachian Mountains lying on the eastern border of New York State and adjacent New England. The range, which played a role in the history of geological science, is separated from the Berkshires and Green Mountains to the east by a series of valleys, principally those of the Housatonic River, Battenkill River and Otter Creek. The Taconics' highest point is Mount Equinox in Vermont at 3,840 feet (1,170 m); among many other summits are Dorset Mountain, Mount Greylock and Mount Everett.

Langford is a city on southern Vancouver Island in the province of British Columbia, Canada. Langford is one of the 13 component municipalities of Greater Victoria and is within the Capital Regional District. Langford was incorporated in 1992 and has a population of over 40,000 people. Its municipal neighbours are Colwood to the southeast, Highlands to the north, Metchosin to the southwest, and View Royal to the northeast.

Mont Saint-Hilaire is a mountain, 414 m (1,358 ft) high, in the Montérégie region of southern Quebec. It is about thirty kilometres east of Montreal, and immediately east of the Richelieu River. It is one of the Monteregian Hills. Around the mountains are the towns of Mont-Saint-Hilaire and Saint-Jean-Baptiste. Other nearby towns include Otterburn Park, Beloeil and McMasterville.


Mount Taylor is a prominent hill with an elevation of 856 metres (2,808 ft) AHD that is located between the Woden Valley, Weston Creek district and Tuggeranong Valley, in Canberra, within the Australian Capital Territory, Australia. Mount Taylor is part of the Canberra Nature Park and is surrounded by the suburbs of Kambah, Fisher, Waramanga, Chifley, Pearce, and Torrens. There are walking tracks to the peak. While there is no public road access to the peak there is a fire trail up the mountain from the end of Waldock St, Chifley where there is also a car park and picnic tables. The fire trail is normally closed to public vehicular access by locked gates, but the gates contain access points for walkers. The trail is especially popular with families and older walkers as it provides the easiest and most leisurely access to the peak. Originally a dirt road, it was partially sealed in 2009 on the steeper grades to make it safer for walkers and mountain bike riders.

The North Shore Mountains are a mountain range overlooking Vancouver in British Columbia, Canada. Their southernmost peaks are visible from most areas in Vancouver and form a distinctive backdrop for the city.

The Illawarra escarpment, or officially the Illawarra Range, is the fold-created cliffs and plateau-eroded outcrop mountain range west of the Illawarra coastal plain south of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. The range encloses the Illawarra region which stretches from Stanwell Park in the north to Kiama, Gerringong and the Shoalhaven River in the south.

Sooke Potholes Provincial Park is a 7.28 hectare provincial park in British Columbia, Canada. It is adjacent to the Sooke River and Sooke Potholes Regional Park, near Victoria, B.C. Intended primarily to provide access to the Sooke River and the associated potholes, it also offers wildlife viewing and other day-use activities.
Sooke Potholes Regional Park is a 63.5-hectare (157-acre) nature park along the Sooke River, near Sooke, British Columbia. It is known for its rocky pools and canyon-like features and is a popular destination for hiking and swimming.

The Metacomet-Monadnock Trail is a 114-mile-long (183 km) hiking trail that traverses the Metacomet Ridge of the Pioneer Valley region of Massachusetts and the central uplands of Massachusetts and southern New Hampshire. Although less than 70 miles (110 km) from Boston and other large population centers, the trail is considered remarkably rural and scenic and includes many areas of unique ecologic, historic, and geologic interest. Notable features include waterfalls, dramatic cliff faces, exposed mountain summits, woodlands, swamps, lakes, river floodplain, farmland, significant historic sites, and the summits of Mount Monadnock, Mount Tom and Mount Holyoke. The Metacomet-Monadnock Trail is maintained largely through the efforts of the Berkshire Chapter of the Appalachian Mountain Club (AMC). Much of the trail is a portion of the New England National Scenic Trail.

Lamentation Mountain, or Mount Lamentation, 720 feet (220 m), is a traprock mountain located 2.5 miles (4.0 km) north of Meriden, Connecticut. It is part of the narrow, linear Metacomet Ridge that extends from Long Island Sound near New Haven, Connecticut, north through the Connecticut River Valley of Massachusetts to the Vermont border. Lamentation Mountain is known for its scenic vistas, extensive cliff faces, unique microclimate ecosystems, and rare plant communities. It rises steeply 550 feet (170 m) above the city of Meriden to the south with west-facing cliffs of 200 feet (61 m) or more. The cliff line, described by the Connecticut Forest and Park Association as "perhaps the most scenic traprock ridge walk in the state" is a prominent landscape feature visible for miles. The mountain is traversed by the 50-mile (80 km) Mattabesett Trail.

The Metacomet Ridge, Metacomet Ridge Mountains, or Metacomet Range of southern New England is a narrow and steep fault-block mountain ridge known for its extensive cliff faces, scenic vistas, microclimate ecosystems, and rare or endangered plants. The ridge is an important recreation resource located within 10 miles (16 km) of more than 1.5 million people, offering four long-distance hiking trails and over a dozen parks and recreation areas, including several historic sites. It has been the focus of ongoing conservation efforts because of its natural, historic, and recreational value, involving municipal, state, and national agencies and nearly two dozen non-profit organizations.

Brace Mountain is the peak of a ridge in the southern Taconic Mountains, near the tripoint of the U.S. states of New York, Connecticut and Massachusetts. Its 2,311-foot (704 m) main summit is located in New York; it is the highest point in that state's Dutchess County.
Humpback Rocks is a massive greenstone outcropping near the peak of Humpback Mountain in the Blue Ridge Mountains of Augusta County and Nelson County, Virginia, United States, with a summit elevation of 3,080 feet (940 m). The rock formation is so named for the visual effect of a "hump" it creates on the western face of the mountain.

The Sooke Flowline is an abandoned 44-kilometre (27 mi) concrete aqueduct that snakes through the Sooke Hills from Sooke Lake to the Humpback Reservoir near Mt. Wells Regional Park. From this reservoir, a buried, riveted steel pressure main transported water to Victoria. Between 1994 and 2007, this main was replaced since it was long past its useful life. The flowline was vital to the continued growth of the City of Victoria as it provided a reliable water supply. While the flowline remains, Victoria's water supply is now carried via Kapoor tunnel. Leigh Hodgetts, CRD Waterworks superintendent, reported that the westernmost section of the flowline is still used to carry Sooke's water supply, via a 16-inch interconnecting pipe feeding the Sooke distribution system from Charters Creek to Sooke River Road.

The Tunxis Trail is a 79-mile (127 km) Blue-Blazed hiking trail "system" that traverses the western ridge of the central Connecticut Valley. The mainline trail is not completely contiguous, notably there are two gaps of several miles.
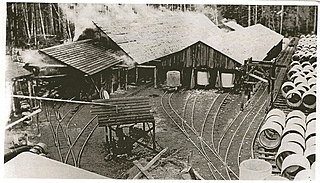
The water supply system for Victoria, British Columbia, Canada, now operated by the Capital Regional District (CRD), served in 2010 over 330,000 people with clean drinking water from a catchment area of 11,025 hectares centered on its main reservoir at Sooke Lake. The CRD’s ownership and complete control of its entire watershed assures its customers of a supply that is secure in both quantity and quality. The main reservoir and its subsidiary reservoirs are estimated to contain 93 billion litres of water, enough to meet the needs of its customers for two years without any rainfall. The history of this remarkable system is sketched below.

The Sea to Sea Green Blue Belt is a 62 kilometre long greenbelt surrounding the Greater Victoria metropolitan area in Canada. The greenbelt includes green space, forests, farms, and wetlands stretching from Sooke to Salt Spring Island. It also includes the "blue spaces" of Sooke Basin and Saanich Inlet.


















