
A forklift is a powered industrial truck used to lift and move materials over short distances. The forklift was developed in the early 20th century by various companies, including Clark, which made transmissions, and Yale & Towne Manufacturing, which made hoists. Since World War II, the use and development of the forklift truck have greatly expanded worldwide. Forklifts have become an indispensable piece of equipment in manufacturing and warehousing. In 2013, the top 20 manufacturers worldwide posted sales of $30.4 billion, with 944,405 machines sold.

A crane is a type of machine, generally equipped with a hoist rope, wire ropes or chains, and sheaves, that can be used both to lift and lower materials and to move them horizontally. It is mainly used for lifting heavy things and transporting them to other places. The device uses one or more simple machines to create mechanical advantage and thus move loads beyond the normal capability of a human. Cranes are commonly employed in the transport industry for the loading and unloading of freight, in the construction industry for the movement of materials, and in the manufacturing industry for the assembling of heavy equipment.

A garbage truck is a truck specially designed to collect municipal solid waste and transport it to a solid waste treatment facility, such as a landfill, recycling center or transfer station. Other common names for this type of truck include trash truck in the United States, and refuse truck, dustcart, rubbish truck, junk truck, bin wagon, dustbin lorry, bin lorry or bin van elsewhere. Technical names include waste collection vehicle and refuse collection vehicle (RCV). These trucks are a common sight in most urban areas.
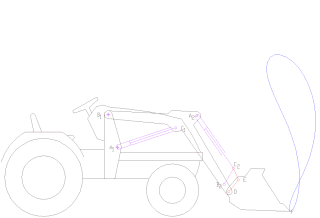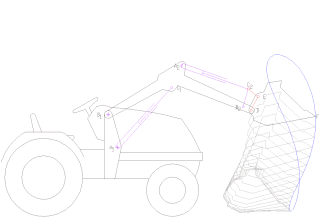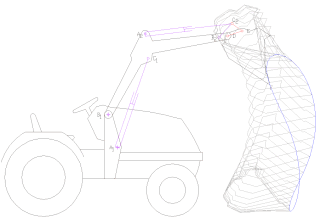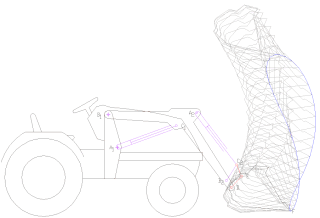
A loader is a heavy equipment machine used in construction to move or load materials such as soil, rock, sand, demolition debris, etc. into or onto another type of machinery.

A dump truck, known also as a dumper truck or tipper truck, is used for transporting dumps for construction as well as coal. A typical dump truck is equipped with an open-box bed, which is hinged at the rear and equipped with hydraulic rams to lift the front, allowing the material in the bed to be deposited ("dumped") on the ground behind the truck at the site of delivery. In the UK, Australia, South Africa and India the term applies to off-road construction plant only, and the road vehicle is known as a tipper lorry, tip-truck, tip-trailer, tipper truck, or tipper.

A distribution center for a set of products is a warehouse or other specialized building, often with refrigeration or air conditioning, which is stocked with products (goods) to be redistributed to retailers, to wholesalers, or directly to consumers. A distribution center is a principal part, the order processing element, of the entire order fulfillment process. Distribution centers are usually thought of as being demand driven. A distribution center can also be called a warehouse, a DC, a fulfillment center, a cross-dock facility, a bulk break center, and a package handling center. The name by which the distribution center is known is commonly based on the purpose of the operation. For example, a "retail distribution center" normally distributes goods to retail stores, an "order fulfillment center" commonly distributes goods directly to consumers, and a cross-dock facility stores little or no product but distributes goods to other destinations.

Bulk material handling is an engineering field that is centered on the design of equipment used for the handling of dry materials. Bulk materials are those dry materials which are powdery, granular or lumpy in nature, and are stored in heaps. Examples of bulk materials are minerals, ores, coal, cereals, woodchips, sand, gravel, clay, cement, ash, salt, chemicals, grain, sugar, flour and stone in loose bulk form. It can also relate to the handling of mixed wastes. Bulk material handling is an essential part of all industries that process bulk ingredients, including: food, beverage, confectionery, pet food, animal feed, tobacco, chemical, agricultural, polymer, plastic, rubber, ceramic, electronics, metals, minerals, paint, paper, textiles and more.

A bucket-wheel excavator (BWE) is a large heavy equipment machine used in surface mining.

A silo is a structure for storing bulk materials. Silos are used in agriculture to store grain or fermented feed known as silage. Silos are commonly used for bulk storage of grain, coal, cement, carbon black, woodchips, food products and sawdust. Three types of silos are in widespread use today: tower silos, bunker silos, and bag silos.

An automated guided vehicle or automatic guided vehicle (AGV) is a portable robot that follows along marked long lines or wires on the floor, or uses radio waves, vision cameras, magnets, or lasers for navigation. They are most often used in industrial applications to transport heavy materials around a large industrial building, such as a factory or warehouse. Application of the automatic guided vehicle broadened during the late 20th century.

A semi-trailer is a trailer without a front axle. In the United States, the term is also used to refer to the combination of a truck and a semi-trailer, a tractor-trailer.

Ground support equipment (GSE) is the support equipment found at an airport, usually on the apron, the servicing area by the terminal. This equipment is used to service the aircraft between flights. As the name suggests, ground support equipment is there to support the operations of aircraft whilst on the ground. The role of this equipment generally involves ground power operations, aircraft mobility, and cargo/passenger loading operations.
Automated Truck Loading Systems - ATLS has been commonly used in the material handling industry to refer to the automation of loading or unloading trucks and trailers with product either on or without pallets, slip sheets, racks, containers, using several different types of automated guided vehicle systems (AGV) or engineered conveyor belt systems that are integrated into vehicles, automating the shipping / receiving and logistics operations.
Hydraulic hooklift hoists are mounted on heavy duty trucks to enable hauliers to change out flatbeds, dumpster bodies, and similar containers. Primarily used in conjunction with tilt frame bodies and specialised containers, generally designed for the transportation of materials in the waste, recycling, scrap and demolition industries.

Pallet rack is a material handling storage aid system designed to store materials on pallets. Although there are many varieties of pallet racking, all types allow for the storage of palletized materials in horizontal rows with multiple levels. Forklift trucks are usually required to place the loaded pallets onto the racks for storage. Since the Second World War, pallet racks have become a ubiquitous element of most modern warehouses, manufacturing facilities, retail centers, and other storage and distribution facilities. All types of pallet racking increase storage density of the stored goods. Costs associated with the racking increases with increasing storage density.
Material handling equipment (MHE) is mechanical equipment used for the movement, storage, control and protection of materials, goods and products throughout the process of manufacturing, distribution, consumption and disposal. The different types of handling equipment can be classified into four major categories: transport equipment, positioning equipment, unit load formation equipment, and storage equipment.

A live bottom trailer is a semi-trailer used for hauling loose material such as asphalt, grain, potatoes, sand and gravel. A live bottom trailer is the alternative to a dump truck or an end dump trailer. The typical live bottom trailer has a conveyor belt on the bottom of the trailer tub that pushes the material out of the back of the trailer at a controlled pace. Unlike the conventional dump truck, the tub does not have to be raised to deposit the materials.

Material handling involves short-distance movement within the confines of a building or between a building and a transportation vehicle. It uses a wide range of manual, semi-automated, and automated equipment and includes consideration of the protection, storage, and control of materials throughout their manufacturing, warehousing, distribution, consumption, and disposal. Material handling can be used to create time and place utility through the handling, storage, and control of waste, as distinct from manufacturing, which creates form utility by changing the shape, form, and makeup of material.
A specialized set of jargon describe the tools, equipment, and employment sectors used in the trucking industry in the United States. Some terms may be used within other English-speaking countries, or within the freight industry in general. For example, shore power is a term borrowed from shipping terminology, in which electrical power is transferred from shore to ship, instead of the ship relying upon idling its engines. Drawing power from land lines is more efficient than engine idling and eliminates localized air pollution. Another borrowed term is "landing gear", which refers to the legs which support the front end of a semi-trailer when it is not connected to a semi-truck. Some nicknames are obvious wordplay, such as "portable parking lot", in reference to a truck that carries automobiles.

Open wagons form a large group of railway goods wagons designed primarily for the transportation of bulk goods that are not moisture-retentive and can usually be tipped, dumped or shovelled. The International Union of Railways (UIC) distinguishes between ordinary wagons and special wagons (F/6). Open wagons often form a significant part of a railway company's goods wagon fleet; for example, forming just under 40% of the Deutsche Bahn's total goods wagon stock in Germany.

















