A regulatory sequence is a segment of a nucleic acid molecule which is capable of increasing or decreasing the expression of specific genes within an organism. Regulation of gene expression is an essential feature of all living organisms and viruses.

In molecular biology, a riboswitch is a regulatory segment of a messenger RNA molecule that binds a small molecule, resulting in a change in production of the proteins encoded by the mRNA. Thus, an mRNA that contains a riboswitch is directly involved in regulating its own activity, in response to the concentrations of its effector molecule. The discovery that modern organisms use RNA to bind small molecules, and discriminate against closely related analogs, expanded the known natural capabilities of RNA beyond its ability to code for proteins, catalyze reactions, or to bind other RNA or protein macromolecules.
The 5′ untranslated region is the region of a messenger RNA (mRNA) that is directly upstream from the initiation codon. This region is important for the regulation of translation of a transcript by differing mechanisms in viruses, prokaryotes and eukaryotes. While called untranslated, the 5′ UTR or a portion of it is sometimes translated into a protein product. This product can then regulate the translation of the main coding sequence of the mRNA. In many organisms, however, the 5′ UTR is completely untranslated, instead forming a complex secondary structure to regulate translation.
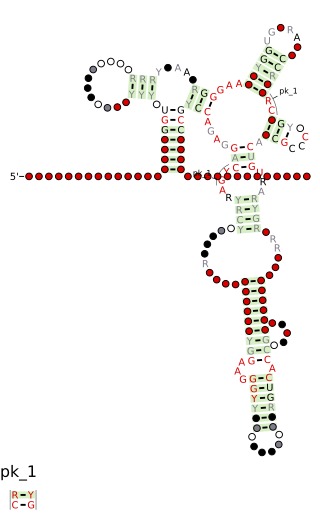
Cobalamin riboswitch is a cis-regulatory element which is widely distributed in 5' untranslated regions of vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) related genes in bacteria.

The SAM riboswitch is found upstream of a number of genes which code for proteins involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis in Gram-positive bacteria. Two SAM riboswitches in Bacillus subtilis that were experimentally studied act at the level of transcription termination control. The predicted secondary structure consists of a complex stem-loop region followed by a single stem-loop terminator region. An alternative and mutually exclusive form involves bases in the 3' segment of helix 1 with those in the 5' region of helix 5 to form a structure termed the anti-terminator form. When SAM is unbound, the anti-terminator sequence sequesters the terminator sequence so the terminator is unable to form, allowing the polymerase to read-through the downstream gene. When S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) is bound to the aptamer, the anti-terminator is sequestered by an anti-anti-terminator; the terminator forms and terminates the transcription. However, many SAM riboswitches are likely to regulate gene expression at the level of translation.

The ykkC/yxkD leader is a conserved RNA structure found upstream of the ykkC and yxkD genes in Bacillus subtilis and related genes in other bacteria. The function of this family is unclear for many years although it has been suggested that it may function to switch on efflux pumps and detoxification systems in response to harmful environmental molecules. The Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis sequence AE013027 overlaps with that of purine riboswitch suggesting that the two riboswitches may work in conjunction to regulate the upstream gene which codes for TTE0584 (Q8RC62), a member of the permease family.

The c4 antisense RNA is a non-coding RNA used by certain phages that infect bacteria. It was initially identified in the P1 and P7 phages of E. coli. The identification of c4 antisense RNAs solved the mystery of the mechanism for regulation of the ant gene, which is an anti-repressor.

The Downstream-peptide motif refers to a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics in the cyanobacterial genera Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus and one phage that infects such bacteria. It was also detected in marine samples of DNA from uncultivated bacteria, which are presumably other species of cyanobacteria.

The glutamine riboswitch is a conserved RNA structure that was predicted by bioinformatics. It is present in a variety of lineages of cyanobacteria, as well as some phages that infect cyanobacteria. It is also found in DNA extracted from uncultivated bacteria living in the ocean that are presumably species of cyanobacteria.
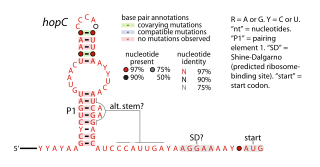
The hopC RNA motif is a predicted cis-regulatory element identified by a bioinformatic screen for conserved RNA secondary structures. hopC RNAs are exclusively found within bacteria classified within the genus Helicobacter, some of which are human pathogens that infect the stomach and can cause ulcers.

The L17 downstream element RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified in bacteria by bioinformatics. All known L17 downstream elements were detected immediately downstream of genes encoding the L17 subunit of the ribosome, and therefore might be in the 3' untranslated regions of these genes. The element is found in a variety of lactic acid bacteria and in the genus Listeria.

The manA RNA motif refers to a conserved RNA structure that was identified by bioinformatics. Instances of the manA RNA motif were detected in bacteria in the genus Photobacterium and phages that infect certain kinds of cyanobacteria. However, most predicted manA RNA sequences are derived from DNA collected from uncultivated marine bacteria. Almost all manA RNAs are positioned such that they might be in the 5' untranslated regions of protein-coding genes, and therefore it was hypothesized that manA RNAs function as cis-regulatory elements. Given the relative complexity of their secondary structure, and their hypothesized cis-regulatory role, they might be riboswitches.

The pan RNA motif defines a conserved RNA structure that was identified using bioinformatics. pan motif RNAs are present in three phyla: Chloroflexota, Bacillota, and Pseudomonadota, although within the latter phylum they are only known in deltaproteobacteria. A pan RNA is present in the Firmicute Bacillus subtilis, which is one of the most extensively studied bacteria.

The pfl RNA motif refers to a conserved RNA structure present in some bacteria and originally discovered using bioinformatics. pfl RNAs are consistently present in genomic locations that likely correspond to the 5' untranslated regions of protein-coding genes. This arrangement in bacteria is commonly associated with cis-regulatory elements. Moreover, they are in presumed 5' UTRs of multiple non-homologous genes, suggesting that they function only in these locations. Additional evidence of cis-regulatory function came from the observation that predicted rho-independent transcription terminators overlap pfl RNAs. This overlap suggests that the alternate secondary structures of pfl RNA and the transcription terminator stem-loops compete with each other, and this is a common mechanism for cis gene control in bacteria.

The psaA RNA motif describes a class of RNAs with a common secondary structure. psaA RNAs are exclusively found in locations that presumably correspond to the 5' untranslated regions of operons formed of psaA and psaB genes. For this reason, it was hypothesized that psaA RNAs function as cis-regulatory elements of these genes. The psaAB genes encode proteins that form subunits in the photosystem I structure used for photosynthesis. psaA RNAs have been detected only in cyanobacteria, which is consistent with their association with photosynthesis.

The Pseudomon-Rho RNA motif refers to a conserved RNA structure that was discovered using bioinformatics. The RNAs that conform to this motif are found in species within the genus Pseudomonas, as well as the related Azotobacter vinelandii. They are consistently located in what could be the 5' untranslated regions of genes that encode the Rho factor protein, and this arrangement in bacteria suggested that Pseudomon-Rho RNAs might be cis-regulatory elements that regulate concentrations of the Rho protein.

The rmf RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was originally detected using bioinformatics. rmf RNAs are consistently foundwithin species classified into the genus Pseudomonas, and is located potentially in the 5′ untranslated regions of rmf genes. These genes encodes the ribosome modulation factor protein, which affects the translation of genes by modifying ribosome structure in response to stress such as starvation. This ribosome modulation is a part of the stringent response in bacteria. The likely biological role of rmf RNAs is ambiguous. Since the RNA could be in the 5′ UTRs of protein-coding genes, it was hypothesized that it functions as a cis-regulatory element. This hypothesis is bolstered by the observation that ribosome modulation factor binds ribosomal RNA, and many cis-regulatory RNAs called ribosomal protein leaders participate in a feedback regulation mechanism by binding to proteins that normally bind to ribosomal RNA. However, since rmf RNAs are not very close to the rmf genes, they might function as non-coding RNAs.
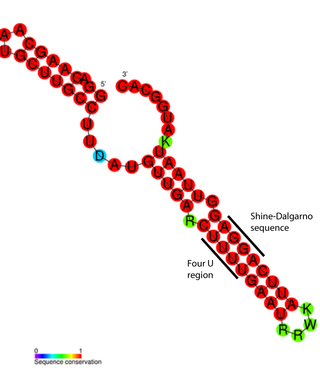
An RNA thermometer is a temperature-sensitive non-coding RNA molecule which regulates gene expression. Its unique characteristic it is that it does not need proteins or metabolites to function, but only reacts to temperature changes. RNA thermometers often regulate genes required during either a heat shock or cold shock response, but have been implicated in other regulatory roles such as in pathogenicity and starvation.
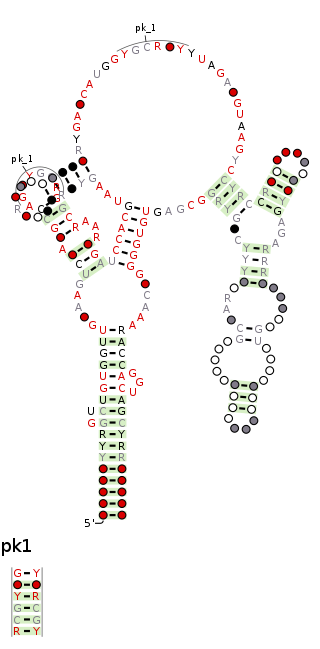
The raiA RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. raiA motif RNAs are found in Actinomycetota and Bacillota, and have many conserved features—including conserved nucleotide positions, conserved secondary structures and associated protein-coding genes—in both of these phyla. Some conserved features of the raiA RNA motif suggest that they function as cis-regulatory elements, but other aspects of the motif suggest otherwise.

The uup RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. uup motif RNAs are found in Bacillota and Gammaproteobacteria.


















