
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a packet oriented mobile data standard on the 2G and 3G cellular communication network's global system for mobile communications (GSM). GPRS was established by European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) in response to the earlier CDPD and i-mode packet-switched cellular technologies. It is now maintained by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a signaling protocol used for initiating, maintaining, and terminating real-time sessions that include voice, video and messaging applications. SIP is used for signaling and controlling multimedia communication sessions in applications of Internet telephony for voice and video calls, in private IP telephone systems, in instant messaging over Internet Protocol (IP) networks as well as mobile phone calling over LTE (VoLTE).
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), also called IP telephony, is a method and group of technologies for the delivery of voice communications and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, such as the Internet. The terms Internet telephony, broadband telephony, and broadband phone service specifically refer to the provisioning of communications services over the Internet, rather than via the public switched telephone network (PSTN), also known as plain old telephone service (POTS).

A media gateway is a translation device or service that converts media streams between disparate telecommunications technologies such as POTS, SS7, Next Generation Networks or private branch exchange (PBX) systems. Media gateways enable multimedia communications across packet networks using transport protocols such as Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) and Internet Protocol (IP).
Customized Applications for Mobile networks Enhanced Logic (CAMEL) is a set of standards designed to work on either a GSM core network or the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) network. The framework provides tools for operators to define additional features for standard GSM services/UMTS services. The CAMEL architecture is based on the Intelligent Network (IN) standards, and uses the CAP protocol. The protocols are codified in a series of ETSI Technical Specifications.
The IP Multimedia Subsystem or IP Multimedia Core Network Subsystem (IMS) is a standardised architectural framework for delivering IP multimedia services. Historically, mobile phones have provided voice call services over a circuit-switched-style network, rather than strictly over an IP packet-switched network. Alternative methods of delivering voice (VoIP) or other multimedia services have become available on smartphones, but they have not become standardized across the industry. IMS is an architectural framework that provides such standardization.
A session border controller (SBC) is a network element deployed to protect SIP based voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) networks.
PacketCable network is a technology specification defined by the industry consortium CableLabs for using Internet Protocol (IP) networks to deliver multimedia services, such as IP telephony, conferencing, and interactive gaming on a cable television infrastructure.
The next-generation network (NGN) is a body of key architectural changes in telecommunication core and access networks. The general idea behind the NGN is that one network transports all information and services by encapsulating these into IP packets, similar to those used on the Internet. NGNs are commonly built around the Internet Protocol, and therefore the term all IP is also sometimes used to describe the transformation of formerly telephone-centric networks toward NGN.

A VoIP phone or IP phone uses voice over IP technologies for placing and transmitting telephone calls over an IP network, such as the Internet. This is in contrast to a standard phone which uses the traditional public switched telephone network (PSTN).
Generic Access Network (GAN) is a protocol that extends mobile voice, data and multimedia applications over IP networks. Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA) is the commercial name used by mobile carriers for external IP access into their core networks. The latest generation system is named Wi-Fi Calling or VoWiFi by a number of handset manufacturers, including Apple and Samsung, a move that is being mirrored by carriers like T-Mobile US and Vodafone. The service is dependent on IMS, IPsec, IWLAN and ePDG.
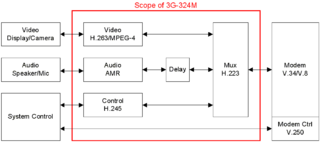
3G-324M is the 3GPP umbrella protocol for video telephony in 3G mobile networks.
Mobile VoIP or simply mVoIP is an extension of mobility to a voice over IP network. Two types of communication are generally supported: cordless telephones using DECT or PCS protocols for short range or campus communications where all base stations are linked into the same LAN, and wider area communications using 3G or 4G protocols.
Text over IP is a means of providing a real-time text (RTT) service that operates over IP-based networks. It complements Voice over IP (VoIP) and Video over IP.
The 3GPP has defined the Voice Call Continuity (VCC) specifications in order to describe how a voice call can be persisted, as a mobile phone moves between circuit switched and packet switched radio domains.
System Architecture Evolution (SAE) is the core network architecture of mobile communications protocol group 3GPP's LTE wireless communication standard.

Video Share is an IP Multimedia System (IMS) enabled service for mobile networks that allows users engaged in a circuit switch voice call to add a unidirectional video streaming session over the packet network during the voice call. Any of the parties on the voice call can initiate a video streaming session. There can be multiple video streaming sessions during a voice call, and each of these streaming sessions can be initiated by any of the parties on the voice call. The video source can either be the camera on the phone or a pre-recorded video clip.
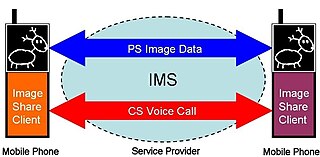
Image Share is a service for sharing images between users during a mobile phone call. It has been specified for use in a 3GPP-compliant cellular network by the GSM Association in the PRD IR.79 Image Share Interoperability Specification.
In intelligent networks (IN) and cellular networks, service layer is a conceptual layer within a network service provider architecture. It aims at providing middleware that serves third-party value-added services and applications at a higher application layer. The service layer provides capability servers owned by a telecommunication network service provider, accessed through open and secure Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) by application layer servers owned by third-party content providers. The service layer also provides an interface to core networks at a lower resource layer. The lower layers may also be named control layer and transport layer.
IMS is a set of specifications to offer multimedia services through IP protocol. This makes it possible to incorporate all kinds of services, such as voice, multimedia and data, on an accessible platform through any Internet connection.





