This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations .(January 2015) |
Murage was a medieval toll for the building or repair of town walls in England, Wales and Ireland.
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations .(January 2015) |
Murage was a medieval toll for the building or repair of town walls in England, Wales and Ireland.
The term murage, while having this specific meaning, could also refer to other aid for walls or to the walls themselves. It is generally applied to defensive town walls but can also refer to flood defences and sea walls. The tax was taken in many towns in Ireland and in English possessions in France. [1]
This was granted by the king by letters patent for a limited term, but the walls were frequently not completed within the term, so the grant was periodically renewed. Such grants sometimes specifically state that they were to be taken for the repair and maintenance of walls. In the later Middle Ages, many places had a vested[ clarification needed ] collection of murage.
The earliest grant was for Shrewsbury in 1218. (Actually, the grant is dated 26 June 1220.) [2] Other towns receiving early grants included Bridgnorth, Stafford, Worcester, Oxford, Gloucester, and Bristol. Many of these places were in the west of England, and were particularly at risk from Welsh incursions.
Since the king's writ did not run in Wales, it is perhaps surprising that several Welsh towns also obtained murage grants. The first was for Hay on Wye in 1232, the year after the town was burnt by Llywelyn the Great. Other towns in Wales or the Welsh Marches having such grants included Oswestry, Radnor, Abergavenny, Carmarthen, Monmouth, Knighton, Montgomery, and Clun. Clun is now fully in England and Knighton partly so. However few such grants were made after 1283, after the completion of the Edward I's Conquest of Wales.
Some of the walls for which murage was granted were probably enclosing towns for the first time. Others, such as at Worcester, were extensions to walls in order to bring suburbs inside the town, or to fund the repair of existing walls, as was the case at Canterbury, to which murage was granted in 1378, 1379, 1385, 1399 and 1402.
In the Lordship of Ireland, murage was used to build walls around Dublin (1221), Galway (1270), Trim (1289–90), Fethard (1292), Castledermot (1275), Kilkenny, Drogheda, Youghal, Dundalk, Naas and many other places; as much of Ireland was not under royal control, cities loyal to the King needed walls to protect them from Gaelic Irish raiders. [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] In Dublin there was a major scandal over murage in 1311–12, when it emerged that none of the funds collected for murage had actually been spent on repairs to the city walls.
"Ye Olde Murenger House", a public house in High Street, Newport, South Wales, dated to about 1530, takes its name from the collector of this toll. [8]

Eleanor de Montfort, Princess of Wales and Lady of Snowdon was an English noble and Welsh Princess. She was the daughter of Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester and Eleanor of England. She was also the second woman who can be shown to have used the title Princess of Wales.

Kington is a market town, electoral ward and civil parish in Herefordshire, England. The ward had a population of 3,240, while the 2011 Census registered a population of 2,626.

Knighton is a market town and community on the River Teme, straddling the border between Powys, Wales and Shropshire, England. It lies in the traditional county of Radnorshire. Originally an Anglo-Saxon settlement, Knighton is located on Offa's Dyke, the ancient earthwork that divided the two countries. It later became a Norman defensive border town.

New Radnor is a village in Powys, Wales, to the south of Radnor Forest, and was the county town of Radnorshire.

Clun Castle is a medieval ruined castle in Clun, Shropshire, England. Clun Castle was established by the Norman lord Robert de Say after the Norman invasion of England and went on to become an important Marcher lord castle in the 12th century, with an extensive castle-guard system. Owned for many years by the Fitzalan family, Clun played a key part in protecting the region from Welsh attack until it was gradually abandoned as a property in favour of the more luxurious Arundel Castle. The Fitzalans converted Clun Castle into a hunting lodge in the 14th century, complete with pleasure gardens, but by the 16th century the castle was largely ruined. Slighted in 1646 after the English Civil War, Clun remained in poor condition until renovation work in the 1890s.
John Fitzalan, 3rd Lord of Clun and Oswestry (1200–1240) in the Welsh Marches in the county of Shropshire.

Monnow Bridge, in Monmouth, Wales, is the only remaining fortified river bridge in Great Britain with its gate tower standing on the bridge. Such bridge towers were common across Europe from medieval times, but many were destroyed due to urban expansion, diminishing defensive requirements and the increasing demands of traffic and trade. The historical and architectural importance of the bridge and its rarity are reflected in its status as a scheduled monument and a Grade I listed building. The bridge crosses the River Monnow 500 metres (1,600 ft) above its confluence with the River Wye.

Buildwas Abbey was a Cistercian monastery located on the banks of the River Severn, at Buildwas in Shropshire, England - today about 2 miles (3.2 km) west of Ironbridge. Founded by the local bishop in 1135, it was sparsely endowed at the outset but enjoyed several periods of growth and increasing wealth: notably under Abbot Ranulf in the second half of the 12th century and again from the mid-13th century, when large numbers of acquisitions were made from the local landed gentry. Abbots were regularly used as agents by Plantagenet in their attempts to subdue Ireland and Wales and the abbey acquired a daughter house in each country.

Fulk FitzWarin, variant spellings, the third, was a prominent representative of a marcher family associated especially with estates in Shropshire and at Alveston in Gloucestershire. In young life, early in the reign of King John (1199–1216), he won notoriety as the outlawed leader of a roving force striving to recover his familial right to Whittington Castle in Shropshire, which John had granted away to a Welsh claimant. Progressively rehabilitated, and enjoying his lordship, he endured further setbacks in 1215–1217.
Muragh was a tax levied historically in Britain and Ireland for the construction or maintenance of town walls. The term derived from Old French, ultimately from Latin murus meaning a wall. Muragh, also referred to as murage, was generally a term used for the tax meant for the repairs of the defensive walls that enclosed towns in historical England, Wales, Ireland. Beginning as a defence against Viking raids, the tax continued through the Middle Ages before declining in the 17th century, as many town walls ceased to be regarded as important militarily after the English Civil War.

The Old Dee Bridge in Chester, Cheshire, England, is the oldest bridge in the city. It crosses the River Dee carrying the road that leads from the bottom of Lower Bridge Street and the Bridgegate to Handbridge. A bridge on this site was first built in the Roman era, and the present bridge is largely the result of a major rebuilding in 1387. It is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade I listed building, and is a scheduled monument.
Pavage was a medieval toll for the maintenance or improvement of a road or street in medieval England, Wales and Ireland. The king by letters patent granted the right to collect it to an individual, or the corporation of a town, or to the "bailiffs and good men" of a neighbouring village.

Pontage was a toll levied for the building or repair of bridges dating to the medieval era in England, Wales and Ireland.
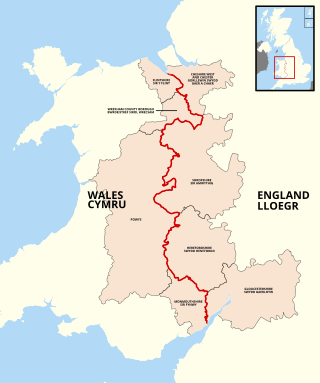
The England–Wales border, sometimes referred to as the Wales–England border or the Anglo-Welsh border, runs for 160 miles (260 km) from the Dee estuary, in the north, to the Severn estuary in the south, separating England and Wales.
Isabella Mortimer, Lady of Clun and Oswestry was a noblewoman and a member of an important and powerful Welsh Marcher family. Although often overshadowed in modern historiography by her better-known parents, she is now known to have played an important part in her family's struggles against Llywelyn ap Gruffudd and to have helped to secure the frontline at Shropshire in the run-up to English conquest of Wales. She was the wife and widow of John III FitzAlan, baron of Clun and Oswestry and de jure earl of Arundel. After a lengthy widowhood, she married for a second time and largely disappeared from the records.

Worcester's city walls are a sequence of defensive structures built around the city of Worcester in England between the 1st and 17th centuries. The first walls to be built around Worcester were constructed by the Romans. These early walls lasted beyond the fall of the Empire, and the defences encouraged several early Christian foundations to establish themselves in Worcester during the troubled 6th and 7th centuries. The Anglo-Saxons expanded Worcester in the 890s, forming a new walled, planned city, called a burh. The burh utilised the southern stretches of the old Roman walls, but pushed further north to enclose a much larger area. The Anglo-Saxon city walls were maintained by a share of taxes on a local market and streets, in an agreement reinforced by a royal charter.

The Monmouth town walls and defences comprise the defensive system of town walls and gates built in Monmouth, Wales between 1297 and the early part of the following century. Wye Bridge Gate, East Gate, Monk's Gate, and Monnow Bridge Gate were access points to the town. West Gate, across Monnow Street, also provided access. Only the Monnow Bridge Gatehouse survives intact, albeit in a substantially modified version from the original.
William Devereux (1219–1265) was an important Marcher Lord who held Lyonshall Castle controlling a strategically vital approach to the border of Wales. The castle's significance was heightened by the rebellion of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, Prince of Wales. With strong family ties to the politically powerful families of Cantilupe and Giffard, his support was strongly sought after by Henry III and Simon de Montfort throughout the Second Barons' War.

Ye Olde Murenger House is a 19th-century pub with a mock Tudor front on High Street, Newport, Wales. It replaced a 17th-century pub, the Fleur de Lys, on the same site. It is named after the medieval job of a murenger, a person who collected tolls for the repair of the town walls, and is Grade II listed due to its historic interest to the immediate area.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)