
The Circus Maximus is an ancient Roman chariot-racing stadium and mass entertainment venue in Rome, Italy. In the valley between the Aventine and Palatine hills, it was the first and largest stadium in ancient Rome and its later Empire. It measured 621 m (2,037 ft) in length and 118 m (387 ft) in width and could accommodate over 150,000 spectators. In its fully developed form, it became the model for circuses throughout the Roman Empire. The site is now a public park.

Mercury is a major god in Roman religion and mythology, being one of the 12 Dii Consentes within the ancient Roman pantheon. He is the god of financial gain, commerce, eloquence, messages, communication, travelers, boundaries, luck, trickery, and thieves; he also serves as the guide of souls to the underworld and the "messenger of the gods".

Venus is a Roman goddess whose functions encompass love, beauty, desire, sex, fertility, prosperity, and victory. In Roman mythology, she was the ancestor of the Roman people through her son, Aeneas, who survived the fall of Troy and fled to Italy. Julius Caesar claimed her as his ancestor. Venus was central to many religious festivals, and was revered in Roman religion under numerous cult titles.
Year 495 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sabinus and Priscus. The denomination 495 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

In ancient Roman religion, Ceres was a goddess of agriculture, grain crops, fertility and motherly relationships. She was originally the central deity in Rome's so-called plebeian or Aventine Triad, then was paired with her daughter Proserpina in what Romans described as "the Greek rites of Ceres". Her seven-day April festival of Cerealia included the popular Ludi Ceriales. She was also honoured in the May lustration (lustratio) of the fields at the Ambarvalia festival: at harvest-time: and during Roman marriages and funeral rites. She is usually depicted as a mature woman.

In Sabine and ancient Roman religion and myth, Luna is the divine embodiment of the Moon. She is often presented as the female complement of the Sun, Sol, conceived of as a god. Luna is also sometimes represented as an aspect of the Roman triple goddess, along with Diana and either Proserpina or Hecate. Luna is not always a distinct goddess, but sometimes rather an epithet that specializes a goddess, since both Diana and Juno are identified as moon goddesses.
Bona Dea was a goddess in ancient Roman religion. She was associated with chastity and fertility among married Roman women, healing, and the protection of the state and people of Rome. According to Roman literary sources, she was brought from Magna Graecia at some time during the early or middle Republic, and was given her own state cult on the Aventine Hill.

The Aventine Hill is one of the Seven Hills on which ancient Rome was built. It belongs to Ripa, the modern twelfth rione, or ward, of Rome.

The Palatine Hill, which relative to the seven hills of Rome is the centremost, is one of the most ancient parts of the city; it has been called "the first nucleus of the Roman Empire". The site is now mainly a large open-air museum whilst the Palatine Museum houses many finds from the excavations here and from other ancient Italian sites.
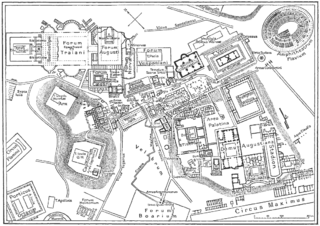
Vicus Tuscus was an ancient street in the city of Rome, running southwest out of the Roman Forum between the Basilica Julia and the Temple of Castor and Pollux towards the Forum Boarium and Circus Maximus via the west side of the Palatine Hill and Velabrum.
Festivals in ancient Rome were a very important part in Roman religious life during both the Republican and Imperial eras, and one of the primary features of the Roman calendar. Feriae were either public (publicae) or private (privatae). State holidays were celebrated by the Roman people and received public funding. Games (ludi), such as the Ludi Apollinares, were not technically feriae, but the days on which they were celebrated were dies festi, holidays in the modern sense of days off work. Although feriae were paid for by the state, ludi were often funded by wealthy individuals. Feriae privatae were holidays celebrated in honor of private individuals or by families. This article deals only with public holidays, including rites celebrated by the state priests of Rome at temples, as well as celebrations by neighborhoods, families, and friends held simultaneously throughout Rome.
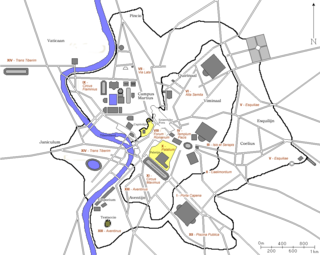
In 7 BC, Augustus divided the city of Rome into 14 administrative regions. These replaced the four regiones—or "quarters"—traditionally attributed to Servius Tullius, sixth king of Rome. They were further divided into official neighborhoods.
The Megalesia, Megalensia, or Megalenses Ludi was a festival celebrated in ancient Rome from April 4 to April 10, in honour of Cybele, whom the Romans called Magna Mater. The name of the festival derives from Greek megalē (μϵγάλη), meaning "great". The festival was one of several on the Roman calendar celebrated with ludi, games and performances.
The Aventine Triad is a modern term for the joint cult of the Roman deities Ceres, Liber and Libera. The cult was established c. 493 BC within a sacred district (templum) on or near the Aventine Hill, traditionally associated with the Roman plebs. Later accounts describe the temple building and rites as "Greek" in style. Some modern historians describe the Aventine Triad as a plebeian parallel and self-conscious antithesis to the Archaic Triad of Jupiter, Mars and Quirinus and the later Capitoline Triad of Jupiter, Minerva and Juno. The Aventine Triad, temple and associated ludi served as a focus of plebeian identity, sometimes in opposition to Rome's original ruling elite, the patricians.

Venus Verticordia was an aspect of the Roman goddess Venus conceived as having the power to convert either virgins or sexually active women from dissolute desire (libido) to sexual virtue (pudicitia). Under this title, Venus was especially cultivated by married women, and on 1 April she was celebrated at the Veneralia festival with public bathing.

The Regio XI Circus Maximus is the eleventh regio of imperial Rome, under Augustus's administrative reform. Regio XI took its name from the Circus Maximus, located in the valley between the Palatine and the Aventine hills.

In Greek and Roman mythology, several goddesses are distinguished by their perpetual virginity. These goddesses included the Greek deities Hestia, Athena, and Artemis, along with their Roman equivalents, Vesta, Minerva, and Diana. In some instances, the inviolability of these goddesses was simply a detail of their mythology, while in other cases virginity was also associated with their worship and religious rites.

The Vallis Murcia was the Latin name of a valley in the city of Rome between the Palatine and the Aventine Hill, where the Circus Maximus was sited. It was historically significant as a communication route and a neutral place of assembly for events, ceremonies, and performances involving harvest, trade, and military exercises. The valley was particularly associated with activities of the plebs and also those bridging the patrician and plebeian divide.
Venus Obsequens was the first Venus for whom a shrine (aedes) was built in ancient Rome. Little is known of her cult beyond the circumstances of her temple founding and a likely connection to the Vinalia Rustica, an August wine festival.













