
Transport in Spain is characterised by a network of roads, railways, trams, air routes, and ports. Its geographic location makes it an important link between Europe, Africa, and the Americas. Major forms of transit generally radiate from the capital, Madrid, located in the centre of the country, to link with the capitals of the autonomous communities.

Rail transport in Spain operates on four rail gauges and services are operated by a variety of private and public operators. Total railway length in 2020 was 15,489 km. The Spanish high-speed rail network is the longest HSR network in Europe with 3,966 km and the second longest in the world, after China's.

Madrid Atocha, also named Madrid Puerta de Atocha–Almudena Grandes, is the first major railway station in Madrid. It is the largest station serving commuter trains (Cercanías), regional trains from the south and southeast, intercity trains from Navarre, Cádiz and Huelva (Andalusia) and La Rioja, and the AVE high speed trains from Girona, Tarragona and Barcelona (Catalonia), Huesca and Zaragoza (Aragon), Sevilla, Córdoba, Málaga and Granada (Andalusia), Valencia, Castellón and Alicante. These train services are run by Spain's national rail company, Renfe. As of 2019, this station has daily services to Marseille, France.

Alta Velocidad Española (AVE) is a high-speed rail service operated by Renfe, the Spanish State railway company.

The Alicante Tram, trademarked as Alicante Metropolitan TRAM, operates in the Spanish city of Alicante and its surrounding area. Like other narrow gauge railways in the Valencian Community, it is run by Ferrocarrils de la Generalitat Valenciana (FGV). It was inaugurated on 15 August 2003 replacing narrow-gauge diesel trains between Alicante and El Campello.
High-speed railways in Spain are in operation since 1992 when the first line was opened connecting the cities of Madrid, Córdoba and Seville. Unlike the rest of the Iberian broad gauge network, the Spanish High-speed network mainly uses standard gauge. This permits direct connections to outside Spain through the link to the French network at the Perthus Tunnel. High-speed trains run on a network of high-speed rail track owned and managed by ADIF, where the dominant service is AVE while other high speed services such as Avant, Alvia, Avlo, Euromed, Ouigo España and Iryo, as well as mid-speed (Altaria) services also operate.

Sagrera railway station is a major through station under construction in the Barcelona districts of Sant Andreu and Sant Martí, in Catalonia, Spain. It is intended to serve as the central station for northern and eastern Barcelona, with Sants serving as the central station for southern and western Barcelona. Together with El Prat de Llobregat and Sants, currently the only high-speed rail stations in the Barcelona area, it will be on the Madrid–Barcelona high-speed rail line. It will also be on the conventional Barcelona–Cerbère and Barcelona–Mataró–Maçanet-Massanes railways. Once fully completed, it will be a major public transport hub, with dedicated stations on Barcelona Metro lines 4 and 9/10, as well as a bus station. The complex will be fully underground excepting for the station building, with two levels of platforms, accounting for a total of 18 railway tracks.

Alicante Terminal is the central railway station of Alicante, Spain. Commonly referred locally as the RENFE station, the station is part of Adif system, and is a terminal station.

Cercanías Murcia/Alicante is a commuter rail service (cercanías) in the provinces of Alicante and Murcia. The line connects Alicante and Murcia with San Vicente del Raspeig, Elche, Orihuela, Totana, Lorca, and Águilas. It runs through 200 km of railways with a total of 26 stations.

The Madrid–Asturias high-speed rail line connects the city of Madrid with the autonomous community of Asturias and was inaugurated on 29 November 2023. The line is built to standard gauge and gauge changers are provided at strategic points to allow interchange with older Spanish railways which were built to Iberian gauge.
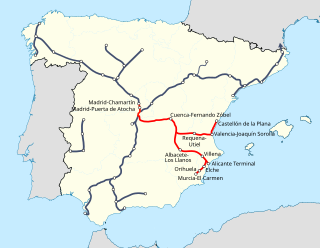
The Madrid–Levante high-speed network is a network of high-speed rail lines that connects Madrid with the Mediterranean coast of the Levante Region, specifically with Castilla-La Mancha, the Valencian Community and the Murcia Region autonomous communities.

The Madrid–Galicia high-speed rail line is a high-speed railway line in Spain that links the city of Madrid with the region of Galicia via the cities of Olmedo, Zamora, Ourense and Santiago de Compostela. The line also connects the Atlantic Axis high-speed rail line to the rest of the Spanish AVE high-speed network. The Madrid–Galicia high-speed rail line is constructed as double electrified line and is designed for trains running at speeds up to 350 kilometres per hour (220 mph).

Avlo is a low-cost high-speed rail service operated by Spanish national rail company Renfe, offering services connecting major Spanish cities such as Madrid, Zaragoza, Barcelona, Valencia, Alicante and others on specific high-speed lines.

Albacete-Los Llanos railway station is a railway station serving the Spanish city of Albacete, Castilla–La Mancha.

Antequera-Santa Ana railway station is a railway station at a railway junction near the Spanish town of Antequera, Málaga in Andalusia. It is located 17 kilometres (11 mi) from the town centre. It was created principally to serve passengers on the developing AVE high-speed rail system. However, the station has access to Iberian gauge lines for conventional services.

Valencia-Joaquín Sorolla railway station is a railway station in Valencia, Spain, opened in 2010. Along with Estació del Nord, it is a city centre terminus station, primarily serving AVE high-speed rail services, with Estació del Nord serving all other passenger rail traffic.

Ciudad Real railway station is the main railway station of the Spanish city of Ciudad Real, Castilla–La Mancha. Located on the AVE high-speed rail line from Madrid Atocha to Seville-Santa Justa and Málaga María Zambrano, travel to Madrid can be achieved in under an hour.
The Murcia–Almería high-speed rail line is an under-construction railway in the Region of Murcia and Andalusia in Spain.

Cartagena railway station Cartagena is a railway terminal station located in the Spanish municipality of Cartagena, in the region of Murcia. It has medium and long distance services operated by Renfe. The Art Nouveau building was built between 1903, when the foundation work began, and 1908, when the central or main building was finished. The design of the building was the joint work of architect Emilio Antón Hernández along with engineers José Cebada Ruiz and José Moreno Rodríguez, all of them being directed and supervised by the engineer Ramón Peironcely.

Almería railway station is the main railway station of the Spanish city of Almería, Andalusia.


















