Related Research Articles

Holography is a technique that enables a wavefront to be recorded and later reconstructed. It is best known as a method of generating real three-dimensional images, but also has a wide range of other applications. In principle, it is possible to make a hologram for any type of wave.

The State Russian Museum, formerly the Russian Museum of His Imperial Majesty Alexander III, on Arts Square in Saint Petersburg, is the world's largest depository of Russian fine art. It is also one of the largest art museums in the world with total area over 30 hectares. In 2022 it attracted 2,651,688 visitors, ranking twelfth on list of most-visited art museums in the world.

The Houston Museum of Natural Science is a natural history museum located on the northern border of Hermann Park in Houston, Texas, United States. The museum was established in 1909 by the Houston Museum and Scientific Society, an organization whose goals were to provide a free institution for the people of Houston focusing on education and science. The museum complex consists of a central facility with four floors of natural science halls and exhibits, the Burke Baker Planetarium, the Cockrell Butterfly Center, and the Wortham Giant Screen Theatre. In 2022 the museum received 1,520,000 visitors, making it seventh on the List of most-visited museums in the United States, and was the third most-visited U.S. science museum. Much of the museum's popularity is attributed to its large number of special or guest exhibits.

Yuri Nikolayevich Denisyuk was a Russian physicist and one of the founders of optical holography in the former Soviet Union. He is known for his great contribution to holography, in particular for the so-called "Denisyuk hologram". He was a full member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, doctor of physical and mathematical sciences, professor (1980).

ITMO University is a state-supported university in Saint Petersburg and is one of Russia's National Research Universities. ITMO University is one of 15 Russian universities that were selected to participate in Russian Academic Excellence Project 5-100 by the government of the Russian Federation to improve their international standing among the world's research and educational centers.

The Polytechnic Museum is one of the oldest science museums in the world and is located in Moscow. It showcases Russian and Soviet technology and science, as well as modern inventions. It was founded in 1872 after the first All-Russian Technical Exhibition on the bicentennial anniversary of the birth of Peter the Great at the initiative of the Society of Devotees of Natural Science, Anthropology, and Ethnography. The first stage of the museum was designed by Ippolit Monighetti and completed in 1877. The north wing was added in 1896 and the south wing in 1907.

Stephen Anthony Benton was the E. Rudge ('48) and Nancy Allen Professor of Media & Sciences, and the Director for Center for Advanced Visual Studies (CAVS) at Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He was the inventor of the rainbow hologram and a pioneer in medical imaging and fine arts holography. Benton held 14 patents in optical physics and photography, and taught media arts and sciences at MIT.

The Russian State Arctic and Antarctic Museum is a museum in St. Petersburg, Russia. It was established in November 1930 as part of the Soviet Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute, but was not opened until six years later.

The Memorial Museum of Cosmonautics, also known as the Memorial Museum of Astronautics or Memorial Museum of Space Exploration, is a museum in Moscow, Russia, dedicated to space exploration. It is located within the base of the Monument to the Conquerors of Space in the north-east of the city. The museum contains a wide variety of Soviet and Russian space-related exhibits and models which explore the history of flight; astronomy; space exploration; space technology; and space in the arts. According to the Russian tourist board, the museum's collection holds approximately 85,000 different items and receives approximately 300,000 visitors yearly.



Central Naval Museum is a naval museum in St Petersburg, Russia, reflecting the development of Russian naval traditions and the history of the Russian Navy. The museum’s permanent display includes such relics as the Botik of Peter the Great, Catherine II’s marine throne, trophies captured in sea battles, and the personal belongings of prominent Russian and Soviet naval commanders. The collection includes paintings by Ivan Aivazovsky, Alexey Bogolyubov, Lev Lagorio and other marine artists, ship sculpture, navigational instruments, naval equipment and machinery from the 17th to 20th centuries and numerous models of ships.

Petrogradsky Island or Petrograd Island is the third-largest island in the Neva River delta in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Along with Zayachy Island, Aptekarsky Island, and Petrovsky Island, it constitutes the Petrogradskaya Side. It is the administrative center of the Petrogradsky District and hosts a number of universities and research centers, as well as cultural, historical, and recreational facilities.

Saint Petersburg Toy Museum is a non-state cultural establishment.

The Russian Museum of Ethnography is a museum in St. Petersburg that houses a collection of about 500,000 items relating to the ethnography, or cultural anthropology, of peoples of the former Russian Empire and the Soviet Union.
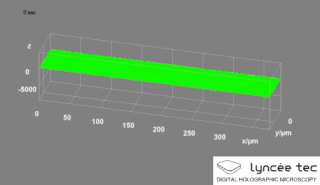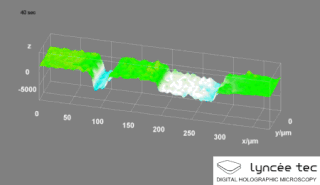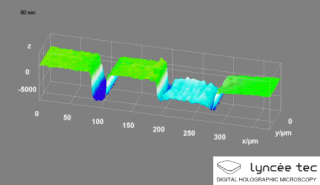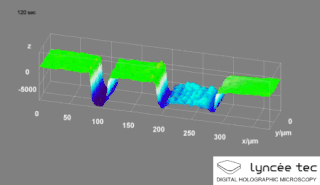
Digital holographic microscopy (DHM) is digital holography applied to microscopy. Digital holographic microscopy distinguishes itself from other microscopy methods by not recording the projected image of the object. Instead, the light wave front information originating from the object is digitally recorded as a hologram, from which a computer calculates the object image by using a numerical reconstruction algorithm. The image forming lens in traditional microscopy is thus replaced by a computer algorithm. Other closely related microscopy methods to digital holographic microscopy are interferometric microscopy, optical coherence tomography and diffraction phase microscopy. Common to all methods is the use of a reference wave front to obtain amplitude (intensity) and phase information. The information is recorded on a digital image sensor or by a photodetector from which an image of the object is created (reconstructed) by a computer. In traditional microscopy, which do not use a reference wave front, only intensity information is recorded and essential information about the object is lost.

The Museum of Soviet Arcade Machines is a private historical interactive museum that keeps a collection of arcade machines that were produced in the USSR from the mid-1970s. April 13, 2007 is considered to be the foundation day of the museum. Visitors of the museum are given 15-kopeck coins at the entrance to get the arcade machines started. The ticket price also includes an excursion.


The Nature Museum of the Republic of Kazakhstan is a natural history museum of the National Academy of Sciences of Kazakhstan, located in the Gylym Ordasy complex in Almaty.

The Almaty Museum is a history museum in Almaty, Kazakhstan, located in the former building of the Vernensky Children's Orphanage. It features exhibits on the history of the city.
References
- ↑ Интерактивный "Музей оптики" познакомит с жизнью голограмм и астролябий [Interactive "the optics Museum" will acquaint with a life of holograms and astrolabes] (in Russian). Piter Info site. 2008-12-16. Archived from the original on 2011-10-08. Retrieved 2009-08-20.