
Sarasota County is located in Southwest Florida on the Gulf Coast. At the 2020 US census, the population was 434,006. Its county seat is Sarasota and its largest city is North Port. Sarasota County is part of the North Port-Sarasota-Bradenton, FL metropolitan statistical area.

North Port is a city located in Sarasota County, Florida, United States. The population was 74,793 at the 2020 US Census. It is part of the North Port–Bradenton–Sarasota Metropolitan Statistical Area. It was originally developed by General Development Corporation as the northern / Sarasota County portion of its Port Charlotte development, the other portion located in the adjacent Charlotte County. GDC dubbed the city North Port Charlotte, and it was incorporated under that name through a special act of the Florida Legislature in 1959. By referendum in 1974, the city's residents approved a change to its name as North Port, dropping Charlotte from its name to proclaim the city as a separate identity. It is home to the Little Salt Spring, an archaeological and paleontological site owned by the University of Miami.

Lake Jackson Mounds Archaeological State Park (8LE1) is one of the most important archaeological sites in Florida, the capital of chiefdom and ceremonial center of the Fort Walton Culture inhabited from 1050–1500. The complex originally included seven earthwork mounds, a public plaza and numerous individual village residences.

Southwest Florida is the region along the southwest Gulf coast of the U.S. state of Florida. The area is known for its beaches, subtropical landscape, and winter resort economy.

The Windover Archeological Site is a Middle Archaic archaeological site and National Historic Landmark in Brevard County near Titusville, Florida, USA, on the central east coast of the state. Windover is a muck pond where skeletal remains of 168 individuals were found buried in the peat at the bottom of the pond. The skeletons were well preserved because of the characteristics of peat. In addition, remarkably well-preserved brain tissue has been recovered from many skulls from the site. DNA from the brain tissue has been sequenced. The collection of human skeletal remains and artifacts recovered from Windover Pond represent among the largest finds of each type from the Archaic Period. It is considered one of the most important archeological sites ever excavated.
The Weeden Island Cultures are a group of related archaeological cultures that existed during the Late Woodland period of the North American Southeast. The name for this group of cultures was derived from the Weedon Island site in Old Tampa Bay in Pinellas County.

Horr's Island is a significant Archaic period archaeological site located on an island in Southwest Florida formerly known as Horr's Island. Horr's Island is on the south side of Marco Island in Collier County, Florida. The site includes four mounds and a shell ring. It has one of the oldest known mound burials in the eastern United States, dating to about 3400 radiocarbon years Before Present (BP). One of the mounds has been dated to as early as 6700 BP. It was the largest known community in the southeastern United States to have been permanently occupied during the Archaic period.

The Big Mound Key-Boggess Ridge Archeological District is a historic site near Placida, Florida. It is located southeast of Placida, on Big Mound Key. On December 3, 1990, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.

The Fort Walton Mound (8OK6) is an archaeological site located in present-day Fort Walton Beach, Florida, United States. The large platform mound was built about 850 CE by the Pensacola culture, a local form of the Mississippian culture. Because of its significance, the mound was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1964.

The Deptford culture was an archaeological culture in southeastern North America characterized by the appearance of elaborate ceremonial complexes, increasing social and political complexity, mound burial, permanent settlements, population growth, and an increasing reliance on cultigens.
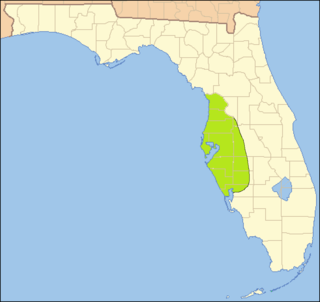
The Safety Harbor culture was an archaeological culture practiced by Native Americans living on the central Gulf coast of the Florida peninsula, from about 900 CE until after 1700. The Safety Harbor culture is defined by the presence of Safety Harbor ceramics in burial mounds. The culture is named after the Safety Harbor Site, which is close to the center of the culture area. The Safety Harbor Site is the probable location of the chief town of the Tocobaga, the best known of the groups practicing the Safety Harbor culture.

The Manasota culture was an archaeological culture that was practiced on the central Gulf coast of the Florida peninsula from about 500 BCE until about 900, when it developed into the Safety Harbor culture. From about 300 to 700 the Manasota culture adopted the ceremonial ceramics and burial practices of the Weeden Island cultures of northern Florida and adjacent Alabama and Georgia.
Lt. Col. William Robert Royal was an American scuba diver in the United States Air Force and amateur archeologist. In the late 1950s, he and other scuba divers found artifacts and human bones from at least seven individuals in Warm Mineral Springs. A partially burned log found in association with some of the human bones was radiocarbon dated to about 10,000 years ago. If the bones were the same age as the log, then the bones were the oldest known evidence of human occupation in Florida at the time.
The Manasota Key Offshore (8SO7030) is an archaeological site under 21 feet (6.4 m) of water in the Gulf of Mexico near the southwest coast of Florida. The site contains remains of multiple humans who were buried in a freshwater pond 7,200 years ago. The pond, which was about 9 feet (2.7 m) above sea level at the time, was subsequently covered by the waters of the Gulf as sea levels rose. The site is about 0.25 miles (0.40 km) from the coast of Manasota Key, near Venice, Florida.

The River Styx archaeological site is the site of a village and burial mound in North Central Florida that was occupied during the development of the Cades Pond culture out of the Deptford culture early in the Current Era (CE).

Gulf Hammock is a wetlands area in the southern end of Levy County, Florida. It extends along the Gulf of Mexico coast from Cedar Key to the Withlacoochee River, and reaches several miles inland. Gulf Hammock includes the largest expanse of hydric hammock in Florida. The area is mostly uninhabited, with the area closest to the Gulf coast in a state park, and the inland areas primarily used for logging and hunting.
Cayo Pelau Archaeological Site is a multi-period aboriginal archaeological site in Charlotte Harbor on the west peninsular Gulf coast of the United States. The island is 3.5 miles directly south of the Big Mound Key-Boggess Ridge Archeological District. It is the only site that lies within two counties, Lee County in the south and Charlotte County, Florida to the north. Neither county has taken responsibility for identifying, protecting or preserving the prehistoric and historical cultural resources on the island.
Aqui Esta Burial Mound (8CH68), also referred to as the Alligator Creek or Punta Gorda Mound, is a prehistoric sand burial mound located in Punta Gorda, Florida, United States.

Myakkahatchee Creek Environmental Park is a 168-acre (68 ha) heavily wooded park in North Port, Florida, north of Interstate 75.












