
A bacteriophage, also known informally as a phage, is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν, meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm.

Enterobacteria phage λ is a bacterial virus, or bacteriophage, that infects the bacterial species Escherichia coli. It was discovered by Esther Lederberg in 1950. The wild type of this virus has a temperate life cycle that allows it to either reside within the genome of its host through lysogeny or enter into a lytic phase, during which it kills and lyses the cell to produce offspring. Lambda strains, mutated at specific sites, are unable to lysogenize cells; instead, they grow and enter the lytic cycle after superinfecting an already lysogenized cell.
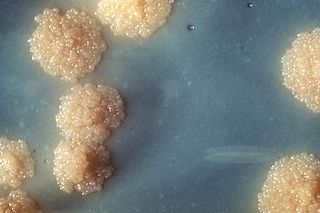
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, M. tuberculosis has an unusual, waxy coating on its cell surface primarily due to the presence of mycolic acid. This coating makes the cells impervious to Gram staining, and as a result, M. tuberculosis can appear weakly Gram-positive. Acid-fast stains such as Ziehl–Neelsen, or fluorescent stains such as auramine are used instead to identify M. tuberculosis with a microscope. The physiology of M. tuberculosis is highly aerobic and requires high levels of oxygen. Primarily a pathogen of the mammalian respiratory system, it infects the lungs. The most frequently used diagnostic methods for tuberculosis are the tuberculin skin test, acid-fast stain, culture, and polymerase chain reaction.

Mycobacterium is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis and leprosy in humans. The Greek prefix myco- means 'fungus', alluding to this genus' mold-like colony surfaces. Since this genus has cell walls with a waxy lipid-rich outer layer that contains high concentrations of mycolic acid, acid-fast staining is used to emphasize their resistance to acids, compared to other cell types.

Mycobacterium smegmatis is an acid-fast bacterial species in the phylum Actinomycetota and the genus Mycobacterium. It is 3.0 to 5.0 μm long with a bacillus shape and can be stained by Ziehl–Neelsen method and the auramine-rhodamine fluorescent method. It was first reported in November 1884 by Lustgarten, who found a bacillus with the staining appearance of tubercle bacilli in syphilitic chancres. Subsequent to this, Alvarez and Tavel found organisms similar to that described by Lustgarten also in normal genital secretions (smegma). This organism was later named M. smegmatis.
Recombineering is a genetic and molecular biology technique based on homologous recombination systems, as opposed to the older/more common method of using restriction enzymes and ligases to combine DNA sequences in a specified order. Recombineering is widely used for bacterial genetics, in the generation of target vectors for making a conditional mouse knockout, and for modifying DNA of any source often contained on a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC), among other applications.

A mycobacteriophage is a member of a group of bacteriophages known to have mycobacteria as host bacterial species. While originally isolated from the bacterial species Mycobacterium smegmatis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative agent of tuberculosis, more than 4,200 mycobacteriophage have since been isolated from various environmental and clinical sources. 2,042 have been completely sequenced. Mycobacteriophages have served as examples of viral lysogeny and of the divergent morphology and genetic arrangement characteristic of many phage types.

Mycobacteroides abscessus is a species of rapidly growing, multidrug-resistant, nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) that is a common soil and water contaminant. Although M. abscessus most commonly causes chronic lung infection and skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI), it can also cause infection in almost all human organs, mostly in patients with suppressed immune systems. Amongst NTM species responsible for disease, infection caused by M. abscessus complex are more difficult to treat due to antimicrobial drug resistance.

Rajan Sankaranarayanan is an Indian structural biologist and a group leader at the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) in Hyderabad. He is known for his research in the field of protein translation, especially for his contribution in chiral proofreading during protein biosynthesis. In 2020, Sankaranarayanan was awarded the Infosys Prize in life sciences, the most prestigious award that recognizes achievements in science and research, in India.
Giles is a bacteriophage that infects Mycobacterium smegmatis bacteria. The genome of this phage is very different from that of other mycobacteriophages and is highly mosaic. More than half of its predicted genes are novel and are not seen in other species.
Mycobacterium virus L5 is a bacteriophage known to infect bacterial species of the genus Mycobacterium.
Gordonia is a genus of gram-positive, aerobic, catalase-positive bacterium in the Actinomycetota, closely related to the Rhodococcus, Mycobacterium, Skermania, and Nocardia genera. Gordonia bacteria are aerobic, non-motile, and non-sporulating. Gordonia is from the same lineage that includes Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The genus was discovered by Tsukamura in 1971 and named after American bacteriologist Ruth Gordon. Many species are often found in the soil, while other species have been isolated from aquatic environments. Some species have been associated with problems like sludge bulking and foaming in wastewater treatment plants. Gordonia species are rarely known to cause infections in humans.
Mycobacterium virus Patience, also called Patience, is a bacteriophage that infects Mycobacterium smegmatis bacteria. The large difference between the GC content of this virus's genome (50.3%) and that of its host (67.4%) indicate Patience likely evolved among bacteria of lower GC content but was able to infect M. smegmatis as well. It is the only species of the genus Patiencevirus.
Mycobacterium virus D29 (D29) is a cluster A mycobacteriophage belonging to the Siphoviridae family of viruses, it was discovered in 1954 by S. Froman. D29 is notable for its ability to infect M. tuberculosis. D29 is a double stranded DNA mycobacteriophage. It is a lytic phage, this means that D29 takes the lytic pathway of infection instead of the lysogenic pathway of infection. There are no human associated diseases associated with mycobacterium virus D29.

The Actinobacteriophage database, more commonly known as PhagesDB, is a website and database that gathers and shares information related to the discovery, characterization and genomics of viruses that prefer to infect Actinobacterial hosts. It is used to compare phages and their genomic annotations. The database provides information on more than 8,000 bacteriophages, including over 1,600 with already sequenced genomes.
SEA-PHAGES stands for Science Education Alliance-Phage Hunters Advancing Genomics and Evolutionary Science; it was formerly called the National Genomics Research Initiative. This was the first initiative launched by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) Science Education Alliance (SEA) by their director Tuajuanda C. Jordan in 2008 to improve the retention of Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) students. SEA-PHAGES is a two-semester undergraduate research program administered by the University of Pittsburgh's Graham Hatfull's group and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute's Science Education Division. Students from over 100 universities nationwide engage in authentic individual research that includes a wet-bench laboratory and a bioinformatics component.

Graham F. Hatfull is the Eberly Family Professor of Biotechnology at the University of Pittsburgh, where he studies bacteriophages. He has been an HHMI professor since 2002, and is the creator of their SEA-PHAGES program. In 2024, he was elected as a permanent member of the National Academy of Sciences.

Heather Hendrickson is a microbiologist and an Associate Professor in the School of Biological Sciences at the University of Canterbury in Christchurch, New Zealand. She previously worked at Massey University, Auckland, New Zealand. Her research is focussed on the evolution of bacterial cell shape, and the discovery of bacteriophages that can attack antibiotic-resistant bacteria and the bee disease American foulbrood.

François Balloux is the director of the UCL Genetics Institute, and a professor of computational biology at University College London.

Microbacterium virus MuffinTheCat is a species of bacteriophage in the family Tectiviridae. It was collected and identified by Darcy Reimer on 1 October 2019. It is part of the Microbacterium testaceum NRRL B-24232 viral strand and the GE viral cluster. Microbacterium of the Microbacterium testaceum species serve as natural hosts. Microbacterium virus MuffinTheCat is morphologically almost indistinguishable from its sibling species in the Tectiviridae family, but it along with its sibling species in the GE cluster are different enough from other Tectiviridae members that the GE cluster may soon be identified as a new genus. Microbacterium virus MuffinTheCat is identified from other GE cluster members by its genome differences.












