Related Research Articles

A fibroblast is a type of biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (stroma) for animal tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of connective tissue in animals.

Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues.

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix (ICM), is a network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.
Polyomaviridae is a family of viruses whose natural hosts are primarily mammals and birds. As of 2020, there are six recognized genera and 117 species, five of which are unassigned to a genus. 14 species are known to infect humans, while others, such as Simian Virus 40, have been identified in humans to a lesser extent. Most of these viruses are very common and typically asymptomatic in most human populations studied. BK virus is associated with nephropathy in renal transplant and non-renal solid organ transplant patients, JC virus with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, and Merkel cell virus with Merkel cell cancer.
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. After cells of interest have been isolated from living tissue, they can subsequently be maintained under carefully controlled conditions. They need to be kept at body temperature (37 °C) in an incubator. These conditions vary for each cell type, but generally consist of a suitable vessel with a substrate or rich medium that supplies the essential nutrients (amino acids, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals), growth factors, hormones, and gases (CO2, O2), and regulates the physio-chemical environment (pH buffer, osmotic pressure, temperature). Most cells require a surface or an artificial substrate to form an adherent culture as a monolayer (one single-cell thick), whereas others can be grown free floating in a medium as a suspension culture. This is typically facilitated via use of a liquid, semi-solid, or solid growth medium, such as broth or agar. Tissue culture commonly refers to the culture of animal cells and tissues, with the more specific term plant tissue culture being used for plants. The lifespan of most cells is genetically determined, but some cell-culturing cells have been 'transformed' into immortal cells which will reproduce indefinitely if the optimal conditions are provided.

Uterine fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas or fibroids, are benign smooth muscle tumors of the uterus. Most women with fibroids have no symptoms while others may have painful or heavy periods. If large enough, they may push on the bladder, causing a frequent need to urinate. They may also cause pain during penetrative sex or lower back pain. A woman can have one uterine fibroid or many. Occasionally, fibroids may make it difficult to become pregnant, although this is uncommon.
Matrigel is the trade name for the solubilized basement membrane matrix secreted by Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm (EHS) mouse sarcoma cells produced by Corning Life Sciences. Matrigel resembles the laminin/collagen IV-rich basement membrane extracellular environment found in many tissues and is used by cell biologists as a substrate for culturing cells.
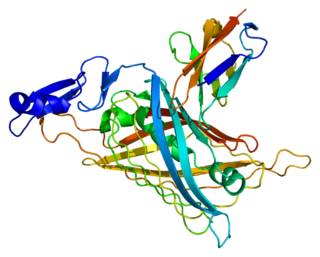
Perlecan (PLC) also known as basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein (HSPG) or heparan sulfate proteoglycan 2 (HSPG2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HSPG2 gene. The HSPG2 gene codes for a 4,391 amino acid protein with a molecular weight of 468,829. It is one of the largest known proteins. The name perlecan comes from its appearance as a "string of pearls" in rotary shadowed images.

72 kDa type IV collagenase also known as matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and gelatinase A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MMP2 gene. The MMP2 gene is located on chromosome 16 at position 12.2.

Secreted frizzled-related protein 1, also known as SFRP1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SFRP1 gene.

Matrix metalloproteinase-26 also known as matrilysin-2 and endometase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MMP26 gene.

Stromelysin-3 (SL-3) also known as matrix metalloproteinase-11 (MMP-11) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MMP11 gene.

Periostin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POSTN gene. Periostin functions as a ligand for alpha-V/beta-3 and alpha-V/beta-5 integrins to support adhesion and migration of epithelial cells.

WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 2, or WISP-2 is a matricellular protein that in humans is encoded by the WISP2 gene.

Matrix metalloproteinase 28 also known as epilysin is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MMP28 gene.

In medicine, desmoplasia is the growth of fibrous connective tissue. It is also called a desmoplastic reaction to emphasize that it is secondary to an insult. Desmoplasia may occur around a neoplasm, causing dense fibrosis around the tumor, or scar tissue (adhesions) within the abdomen after abdominal surgery.

The tumor microenvironment is a complex ecosystem surrounding a tumor, composed of cancer cells, stromal tissue and the extracellular matrix. Mutual interaction between cancer cells and the different components of the tumor microenvironment support its growth and invasion in healthy tissues which correlates with tumor resistance to current treatments and poor prognosis. The tumor microenvironment is in constant change because of the tumor's ability to influence the microenvironment by releasing extracellular signals, promoting tumor angiogenesis and inducing peripheral immune tolerance, while the immune cells in the microenvironment can affect the growth and evolution of cancerous cells.
A 3D cell culture is an artificially created environment in which biological cells are permitted to grow or interact with their surroundings in all three dimensions. Unlike 2D environments, a 3D cell culture allows cells in vitro to grow in all directions, similar to how they would in vivo. These three-dimensional cultures are usually grown in bioreactors, small capsules in which the cells can grow into spheroids, or 3D cell colonies. Approximately 300 spheroids are usually cultured per bioreactor.
Patient derived xenografts (PDX) are models of cancer where the tissue or cells from a patient's tumor are implanted into an immunodeficient or humanized mouse. It is a form of xenotransplantation. PDX models are used to create an environment that allows for the continued growth of cancer after its removal from a patient. In this way, tumor growth can be monitored in the laboratory, including in response to potential therapeutic options. Cohorts of PDX models can be used to determine the therapeutic efficiency of a therapy against particular types of cancer, or a PDX model from a specific patient can be tested against a range of therapies in a 'personalized oncology' approach.
Cultrex Basement Membrane Extract (BME) is the trade name for a extracellular protein mixture secreted by Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm (EHS) mouse sarcoma cells and manufactured into a hydrogel by R&D Systems, a brand of Bio-Techne. Similar to Matrigel, this hydrogel is a natural extracellular matrix that mimics the complex extracellular environment within complex tissues. It is used as a general cell culture substrate across a wide variety of research applications.
References
- ↑ Nurmenniemi, Sini; Sinikumpu, Teemu; Alahuhta, Ilkka; Salo, Sirpa; Sutinen, Meeri; Santala, Markku; Risteli, Juha; Nyberg, Pia; Salo, Tuula (September 2009). "A Novel Organotypic Model Mimics the Tumor Microenvironment". The American Journal of Pathology. 175 (3): 1281–1291. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2009.081110. PMC 2731146 . PMID 19679876.
- 1 2 Salo, Tuula; Sutinen, Meeri; Hoque Apu, Ehsanul; Sundquist, Elias; Cervigne, Nilva K.; de Oliveira, Carine Ervolino; Akram, Saad Ullah; Ohlmeier, Steffen; Suomi, Fumi; Eklund, Lauri; Juusela, Pirjo (December 2015). "A novel human leiomyoma tissue derived matrix for cell culture studies". BMC Cancer. 15 (1): 981. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1944-z . ISSN 1471-2407. PMC 4682271 . PMID 26673244. S2CID 17598911.