
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a psycho-social intervention that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression and anxiety disorders. Cognitive behavioral therapy is one of the most effective means of treatment for substance abuse and co-occurring mental health disorders. CBT focuses on challenging and changing cognitive distortions and their associated behaviors to improve emotional regulation and develop personal coping strategies that target solving current problems. Though it was originally designed to treat depression, its uses have been expanded to include many issues and the treatment of many mental health conditions, including anxiety, substance use disorders, marital problems, ADHD, and eating disorders. CBT includes a number of cognitive or behavioral psychotherapies that treat defined psychopathologies using evidence-based techniques and strategies.
Hypnotherapy, also known as hypnotic medicine, is the use of hypnosis in psychotherapy. The efficacy of hypnotherapy is not well supported by scientific evidence, and, due to the lack of evidence indicating any level of efficacy, it is regarded as a type of alternative medicine by reputable medical organisations such as the National Health Service.

Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time when menstrual periods permanently stop, marking the end of reproduction. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, although the exact timing can vary. Menopause is usually a natural change. It can occur earlier in those who smoke tobacco. Other causes include surgery that removes both ovaries or some types of chemotherapy. At the physiological level, menopause happens because of a decrease in the ovaries' production of the hormones estrogen and progesterone. While typically not needed, a diagnosis of menopause can be confirmed by measuring hormone levels in the blood or urine. Menopause is the opposite of menarche, the time when a girl's periods start.

Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin.
Oophorectomy, historically also called ovariotomy, is the surgical removal of an ovary or ovaries. The surgery is also called ovariectomy, but this term is mostly used in reference to non-human animals, e.g. the surgical removal of ovaries from laboratory animals. Removal of the ovaries of females is the biological equivalent of castration of males; the term castration is only occasionally used in the medical literature to refer to oophorectomy of women. In veterinary medicine, the removal of ovaries and uterus is called ovariohysterectomy (spaying) and is a form of sterilization.
Hot flashes are a form of flushing, often caused by the changing hormone levels that are characteristic of menopause. They are typically experienced as a feeling of intense heat with sweating and rapid heartbeat, and may typically last from two to 30 minutes for each occurrence.

The Women's Health Initiative (WHI) was a series of clinical studies initiated by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) in 1991, to address major health issues causing morbidity and mortality in postmenopausal women. It consisted of three clinical trials (CT) and an observational study (OS). In particular, randomized controlled trials were designed and funded that addressed cardiovascular disease, cancer, and osteoporosis.

Goserelin, sold under the brand name Zoladex among others, is a medication which is used to suppress production of the sex hormones, particularly in the treatment of breast and prostate cancer. It is an injectable gonadotropin releasing hormone agonist.

Estradiol acetate (EA), sold under the brand names Femtrace, Femring, and Menoring, is an estrogen medication which is used in hormone therapy for the treatment of menopausal symptoms in women. It is taken by mouth once daily or given as a vaginal ring once every three months.

A cancer survivor is a person with cancer of any type who is still living. Whether a person becomes a survivor at the time of diagnosis or after completing treatment, whether people who are actively dying are considered survivors, and whether healthy friends and family members of the cancer patient are also considered survivors, varies from group to group. Some people who have been diagnosed with cancer reject the term survivor or disagree with some definitions of it.
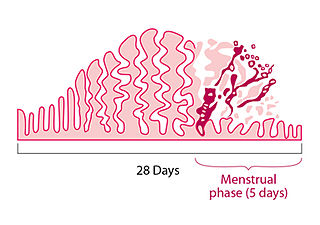
A menstrual disorder is characterized as any abnormal condition with regards to a woman's menstrual cycle. There are many different types of menstrual disorders that vary with signs and symptoms, including pain during menstruation, heavy bleeding, or absence of menstruation. Normal variations can occur in menstrual patterns but generally menstrual disorders can also include periods that come sooner than 21 days apart, more than 3 months apart, or last more than 10 days in duration. Variations of the menstrual cycle are mainly caused by the immaturity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis, and early detection and management is required in order to minimize the possibility of complications regarding future reproductive ability.
Psycho-oncology is an interdisciplinary field at the intersection of physical, psychological, social, and behavioral aspects of the cancer experience for both patients and caregivers. Also known as psychiatric oncology or psychosocial oncology, researchers and practitioners in the field are concerned with aspects of individuals' experience with cancer beyond medical treatment, and across the cancer trajectory, including at diagnosis, during treatment, transitioning to and throughout survivorship, and approaching the end-of-life. Founded by Jimmie Holland in 1977 via the incorporation of a psychiatric service within the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, the field has expanded drastically since and is now universally recognized as an integral component of quality cancer care. Cancer centers in major academic medical centers across the country now uniformly incorporate a psycho-oncology service into their clinical care, and provide infrastructure to support research efforts to advance knowledge in the field.
Post-chemotherapy cognitive impairment (PCCI) describes the cognitive impairment that can result from chemotherapy treatment. While there is no concrete statistic for the number of patients that experience some level of post-chemotherapy cognitive impairment, the estimated percentage is between 13 to 70 percent of patients. The phenomenon first came to light because of the large number of breast cancer survivors who complained of changes in memory, fluency, and other cognitive abilities that impeded their ability to function as they had pre-chemotherapy.
Gynecologic oncology is a specialized field of medicine that focuses on cancers of the female reproductive system, including ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, vaginal cancer, cervical cancer, and vulvar cancer. As specialists, they have extensive training in the diagnosis and treatment of these cancers.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. Effects of menopause can include symptoms such as hot flashes, accelerated skin aging, vaginal dryness, decreased muscle mass, and complications such as osteoporosis, sexual dysfunction, and vaginal atrophy. They are mostly caused by low levels of female sex hormones that occur during menopause.
The PICO process is a mnemonic used in evidence-based practice to frame and answer a clinical or health care related question, though it is also argued that PICO "can be used universally for every scientific endeavour in any discipline with all study designs". The PICO framework is also used to develop literature search strategies, for instance in systematic reviews.

Gender-biased diagnosing is the idea that medical and psychological diagnosis are influenced by the patient's gender. Several studies have found evidence of differential diagnosis for patients with similar ailments but of different sexes. Female patients face discrimination through the denial of treatment or miss-classification of diagnosis as a result of not being taken seriously due to stereotypes and gender bias. According to traditional medical studies, most of these medical studies were done on men thus overlooking many issues that were related to women's health. This topic alone sparked controversy and questions about the medical standard of our time. Popular media has illuminated the issue of gender bias in recent years. Research that was done on diseases that affected women more were less funded than those diseases that affected men and women equally.
Pain in cancer may arise from a tumor compressing or infiltrating nearby body parts; from treatments and diagnostic procedures; or from skin, nerve and other changes caused by a hormone imbalance or immune response. Most chronic (long-lasting) pain is caused by the illness and most acute (short-term) pain is caused by treatment or diagnostic procedures. However, radiotherapy, surgery and chemotherapy may produce painful conditions that persist long after treatment has ended.
Ospemifene is an oral medication indicated for the treatment of dyspareunia – pain during sexual intercourse – encountered by some women, more often in those who are post-menopausal. Ospemifene is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) acting similarly to an estrogen on the vaginal epithelium, building vaginal wall thickness which in turn reduces the pain associated with dyspareunia. Dyspareunia is most commonly caused by "vulvar and vaginal atrophy."










