
Kalsoy is an island in the north-east of the Faroe Islands of Denmark between Eysturoy and Kunoy. The name means man island; by contrast with the parallel island to the east, Kunoy, the name of which means woman island.

Viðoy is the northernmost island in the Faroe Islands, located east of Borðoy to which it is linked via a causeway. The name means wood island, despite the fact that no trees grow on the island; the name relates to the driftwood that floats in from Siberia and North America.

Velbastaður is a village on the island of Streymoy in the Faroe Islands. It is a part of Tórshavn Municipality and is considered among the oldest settlements in the islands. There are two schools and one kindergarten in the village, with children coming from the neighboring village of Kirkjubø as well the capital at Tórshavn.

Risin og Kellingin are two sea stacks just off the northern coast of the island of Eysturoy in the Faroe Islands close to the town of Eiði. The name Risin og Kellingin means The Giant and the Witch and relates to an old legend about their origins. The Giant (Risin) is the 71m stack further from the coast, and the witch (Kellingin) is the 68m pointed stack nearer land, standing with her legs apart.

Browns Brasserie & Bar is a British chain of restaurants owned by Mitchells & Butlers, with sites mostly located in the south of England.

Verna Allee is an American business consultant and writer on topics including value networks, knowledge management, organizational intelligence, intellectual capital and the value conversion of intangibles.

Twyfelfontein, officially known as ǀUi-ǁAis, is a site of ancient rock engravings in the Kunene Region of north-western Namibia. It consists of a spring in a valley flanked by the slopes of a sandstone table mountain that receives very little rainfall and has a wide range of diurnal temperatures.

The Tsau ǁKhaeb (Sperrgebiet) National Park, formerly known as Sperrgebiet, is a diamond mining area in southwestern Namibia, in the Namib Desert. It spans the Atlantic Ocean-facing coast from Oranjemund on the border with South Africa, to around 72 kilometres (45 mi) north of Lüderitz, a distance of 320 km (200 mi) north. It extends to around 100 km (62 mi) inland, and its total area of 26,000 km2 (10,000 sq mi), makes up three percent of Namibia's land mass. However, mining only takes place in five percent of the Sperrgebiet, with most of the area acting as a buffer zone. Members of the public are banned from entering most of the area, despite the creation of a national park there in 2004.

There is a long history of tourism in Hungary, and Hungary was the world's thirteenth most visited tourist destination country in 2002. Tourism increased by nearly 7 percent between 2004 and 2005. European visitors comprise more than 98 per cent of Hungary's tourists. Austria, Germany, and Slovakia make the largest numbers of visitors to the country. Most tourists arrive by car and stay for a short period of time. Hungary's tourist season is from April through October. July and August are the best tourist months. Budapest is the country's most popular tourist destination.

Tourism in Morocco is well developed, maintaining a strong tourist industry focused on the country's coast, culture, and history. The Moroccan government created a Ministry of Tourism in 1985. Tourism is considered one of the main foreign exchange sources in Morocco and since 2013 it had the highest number of arrivals out of the countries in Africa. In 2018, 12.3 million tourists were reported to have visited Morocco.

Afono is a village on the northeast coast of Tutuila Island, American Samoa. One of the island's more populous villages, it is located on the edge of Afono Bay, at the eastern edge of the National Park of American Samoa. It is connected by Highway 6 to Vatia, which lies along the coast to the northwest, and to Aua, on the edge of Pago Pago Harbor to the south via a winding stretch of highway which crosses the spine of the island.

Aʻoloau is a village in the west of Tutuila Island, American Samoa. It is located inland, 5 miles (8 km) southwest of Pago Pago. It is also known as Aʻoloaufou, which means "New Aʻolou". An abandoned area in town by Aʻoloau Bay is known as Aʻoloautuai, which means "Old Aʻoloau". Aʻoloau's nickname is Nuu Puaolele which means the Fog Village.

ǀAi-ǀAis is a Namibian holiday resort with hot mineral springs in the bed of the Fish River. It is situated in Southern Namibia's ǁKaras Region at the base of the Great Karas Mountains, 128 kilometres (80 mi) west of Karasburg and 224 kilometres (139 mi) south-west of Keetmanshoop.

Botswana–Namibia relations refers to the current and historical relationship between Botswana and Namibia. Botswana gained independence from Britain in September 1966. Namibia gained independence from South Africa in 1990 following the Namibian War of Independence, and the two countries soon after established formal diplomatic relations. Botswana has a high commission in Windhoek. Namibia has a high commission in Gaborone. Both countries are members of the Southern African Development Community, African Union, Group of 77, and Commonwealth of Nations.

Dinosaurland Fossil Museum is a privately owned fossil museum in Lyme Regis, on the Jurassic Coast in Dorset, England. The museum is located in a historic Grade I listed former congregational church building.

The Doma or vaDoma, also known as Dema or Wadoma, are a tribe living in the Kanyemba region in the north of Zimbabwe, especially in the Hurungwe and Chipuriro districts around the basins of Mwazamutanda River, a tributary of the Zambezi River Valley. They are the only traditional hunter-gatherers indigenous to Zimbabwe and are famous for the inherited ectrodactyly existing among some vaDoma families at much higher rates than typical globally.
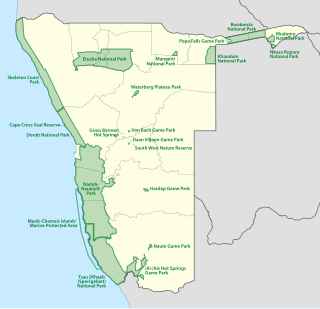
The protected areas of Namibia include its national parks and reserves. With the 2010 declaration of Dorob National Park, Namibia became the first and only country to have its entire coastline protected through a national parks network. Protected areas are subdivided into game reserves and/or nature reserves, such as special protected area, wilderness areas, natural areas, and development areas. There are also recreation reserves. Facilities in the national parks are operated by Namibia Wildlife Resorts. Over 19% of Namibia is protected, an area of some 130,000 square kilometres. However, the Ministry of Environment & Tourism auctions limited hunting rights within its protected areas. The Namibia Nature Foundation, an NGO, was established in 1987 to raise and administer funds for the conservation of wildlife and protected area management. Communal Wildlife Conservancies in Namibia help promote sustainable natural resource management by giving local communities rights to wildlife management and tourism.
Cannabis in Madagascar is illegal, but is produced and consumed domestically.

Fagasā is a village in the Eastern District of Tutuila Island in American Samoa. The village lies by Fagasa Bay, on the north shore of the island. Its name is Samoan and translates to "Forbidden Bay." The village borders the Tutuila-section of National Park of American Samoa. The trailhead to Mount ʻAlava is located near the village by Fagasa Pass.
Saʻilele is a village on the north shore in the Eastern District of Tutuila Island in American Samoa. It is reached from a cross-island road which leads north from the village of Fagaʻitua. On a track east of the village is a burial ground where some aliʻi were buried.

















