Related Research Articles

Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are one class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic, antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to treat infections. They should be distinguished from virucides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural virucides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees.
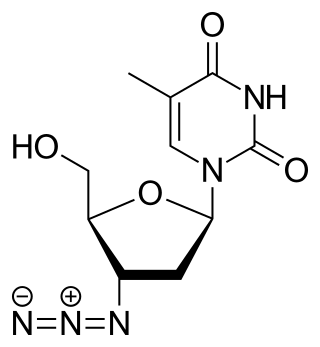
Zidovudine (ZDV), also known as azidothymidine (AZT), is an antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use in combination with other antiretrovirals. It may be used to prevent mother-to-child spread during birth or after a needlestick injury or other potential exposure. It is sold both by itself and together as lamivudine/zidovudine and abacavir/lamivudine/zidovudine. It can be used by mouth or by slow injection into a vein.
The management of HIV/AIDS normally includes the use of multiple antiretroviral drugs as a strategy to control HIV infection. There are several classes of antiretroviral agents that act on different stages of the HIV life-cycle. The use of multiple drugs that act on different viral targets is known as highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). HAART decreases the patient's total burden of HIV, maintains function of the immune system, and prevents opportunistic infections that often lead to death. HAART also prevents the transmission of HIV between serodiscordant same-sex and opposite-sex partners so long as the HIV-positive partner maintains an undetectable viral load.

Enfuvirtide (INN), sold under the brand name Fuzeon, is an HIV fusion inhibitor, the first of a class of antiretroviral drugs used in combination therapy for the treatment of AIDS/HIV.
The spread of HIV/AIDS has affected millions of people worldwide; AIDS is considered a pandemic. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that in 2016 there were 36.7 million people worldwide living with HIV/AIDS, with 1.8 million new HIV infections per year and 1 million deaths due to AIDS. Misconceptions about HIV and AIDS arise from several different sources, from simple ignorance and misunderstandings about scientific knowledge regarding HIV infections and the cause of AIDS to misinformation propagated by individuals and groups with ideological stances that deny a causative relationship between HIV infection and the development of AIDS. Below is a list and explanations of some common misconceptions and their rebuttals.

Infection with HIV, a retrovirus, can be managed with treatment but without treatment can lead to a spectrum of conditions including AIDS.

The HIV Prevention Trials Network (HPTN) is a worldwide collaborative clinical trials network that brings together investigators, ethicists, community and other partners to develop and test the safety and efficacy of interventions designed to prevent the acquisition and transmission of HIV. HPTN studies evaluate new HIV prevention interventions and strategies in populations and geographical regions that bear a disproportionate burden of infection. The HPTN is committed to the highest ethical standards for its clinical trials and recognizes the importance of community engagement in all phases of the research process.
HIV prevention refers to practices that aim to prevent the spread of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). HIV prevention practices may be undertaken by individuals to protect their own health and the health of those in their community, or may be instituted by governments and community-based organizations as public health policies.
HPTN 052 is the name of a clinical trial conducted in nine countries which examined whether starting people living with HIV on antiretroviral therapy (ART) can reduce the chance that they will pass HIV on to their sexual partners who do not have HIV. The trial showed remarkable success in preventing HIV transmission and were so compelling that the study's Data and Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB) asked the research team to share the results with all study participants and offer ART to the control group before the study ended. As a result of the study there was increased consensus that treatment as prevention should be included as a public health strategy in lowering HIV infection. The trial was organized by the HIV Prevention Trials Network (HPTN) and its chief architect was Myron S. Cohen.
Julio S. G. Montaner, is an Argentine-Canadian physician, professor and researcher. He is the director of the British Columbia Centre for Excellence in HIV/AIDS, the chair in AIDS Research and head of the Division of AIDS in the Faculty of Medicine at the University of British Columbia and the past-president of the International AIDS Society. He is also the director of the John Ruedy Immunodeficiency Clinic, and the Physician Program Director for HIV/AIDS PHC. He is known for his work on HAART, a role in the discovery of triple therapy as an effective treatment for HIV in the late 1990s, and a role in advocating the "Treatment as Prevention" Strategy in the mid-2000s, led by Myron Cohen of the HPTN 052 trial.
Treatment as prevention (TasP) is a concept in public health that promotes treatment as a way to prevent and reduce the likelihood of HIV illness, death and transmission from an infected individual to others. Expanding access to earlier HIV diagnosis and treatment as a means to address the global epidemic by preventing illness, death and transmission was first proposed in 2000 by Garnett et al. The term is often used to talk about treating people that are currently living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) to prevent illness, death and transmission. Although some experts narrow this to only include preventing infections, treatment prevents illnesses such as tuberculosis and has been shown to prevent death. The dual impact on well-being and its 100% effectiveness in reducing transmission makes TasP the most important element in the HIV prevention toolkit. In relation to HIV, antiretroviral therapy (ART) is a three or more drug combination therapy that is used to decrease the viral load, or the measured amount of virus, in an infected individual. Such medications are used as a preventative for infected individuals to not only spread the HIV virus to their negative partners but also improve their current health to increase their lifespans. Other names for ART include highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), combination antiretroviral therapy (cART), triple therapy and triple drug cocktail. When taken correctly, ART is able to diminish the presence of the HIV virus in the bodily fluids of an infected person to a level of undetectability. Undetectability ensures that infection does not necessarily have an effect on a person's general health, and that there is no longer a risk of passing along HIV to others. Consistent adherence to an ARV regimen, monitoring, and testing are essential for continued confirmed viral suppression. Treatment as prevention rose to great prominence in 2011, as part of the HPTN 052 study, which shed light on the benefits of early treatment for HIV positive individuals.
David DuPuy Celentano is a noted epidemiologist and professor who has contributed significantly to the promotion of research on HIV/AIDS and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). He is the Charles Armstrong chair of the Department of Epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. He holds joint appointments with the school’s departments of Health Policy and Management, Health Behavior and Society, and International Health, and the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine’s Division of Infectious Diseases.
Viral load monitoring for HIV is the regular measurement of the viral load of individual HIV-positive people as part of their personal plan for treatment of HIV/AIDS. A count of the viral load is routine before the start of HIV treatment.

Diane Havlir is an American physician who is a Professor of Medicine and Chief of the HIV/AIDS Division at the University of California, San Francisco. Her research considers novel therapeutic strategies to improve the lives of people with HIV and to support public health initiatives in East Africa. She was elected to the National Academy of Medicine in 2019.
Kimberly A. Powers is an American epidemiologist who is an associate professor of epidemiology at the UNC Gillings School of Global Public Health. She combines epidemiology, statistics and mathematical modelling to understand the transmission of infectious diseases. In 2011 her work on antiretroviral therapy for the management of human immunodeficiency virus was selected by Science as the breakthrough of the year. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Powers looked to understand the spread of SARS-CoV-2.
Sarah Fidler is an immunologist, researcher and professor in HIV Medicine at Imperial College London and consultant physician in HIV for St Mary's Hospital, London.
The Swiss Statement, or the Swiss Consensus Statement, was an announcement published in January 2008 by the Swiss Federal Commission for AIDS/HIV outlining the conditions under which an HIV-positive individual could be considered functionally noncontagious—namely, adherence to antiretroviral therapy, a sufficiently low viral load, and a lack of any other sexually transmitted diseases. While lacking the backing of complete, fully randomized clinical studies, the Commission felt the contemporary evidence for non-contagiousness for people on antiretroviral treatment was nonetheless strong enough to warrant official publication.
Peter Nicholas Kazembe was a Malawian pediatrician, well known internationally for his work in pediatric antiretroviral therapy and treatment of malaria. He was one of the first two pediatricians in the country and was often considered the "grandfather of pediatrics" in Malawi. He is credited with publishing over 250 journal articles in his field. He was the Director of the Baylor International Pediatric Program and an associate professor at University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Prior to this, he played a role in pioneering Malawi's pediatric HIV/AIDS care treatment guidelines, and was also the Director of Malawi's first HIV clinic and Chief of Pediatrics at Kamuzu Central Hospital.
Undetectable = Untransmittable (U=U) is a message used in HIV campaigns. It means that if someone has an undetectable viral load, they cannot sexually transmit HIV to others. U=U is supported by numerous health groups and organisations worldwide, including the World Health Organization (WHO). The validity of U=U has been proven through many clinical trials involving thousands of couples. U=U is also used as an HIV prevention strategy: if someone is undetectable, they can not pass it further and hence, prevents the virus from spreading. This is known as Treatment as Prevention (TasP).
References
- ↑ Cohen, M. S.; Chen, Y. Q.; McCauley, M.; Gamble, T.; Hosseinipour, M. C.; Kumarasamy, N.; Hakim, J. G.; Kumwenda, J.; Grinsztejn, B.; Pilotto, J. H. S.; Godbole, S. V.; Mehendale, S.; Chariyalertsak, S.; Santos, B. R.; Mayer, K. H.; Hoffman, I. F.; Eshleman, S. H.; Piwowar-Manning, E.; Wang, L.; Makhema, J.; Mills, L. A.; De Bruyn, G.; Sanne, I.; Eron, J.; Gallant, J.; Havlir, D.; Swindells, S.; Ribaudo, H.; Elharrar, V.; et al. (2011). "Prevention of HIV-1 Infection with Early Antiretroviral Therapy" (PDF). New England Journal of Medicine. 365 (6): 493–505. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1105243. PMC 3200068 . PMID 21767103.
- ↑ UNAIDS Press Release (12 May 2011). "Groundbreaking trial results confirm HIV treatment prevents transmission of HIV" . Retrieved 16 May 2013.
- ↑ "The End of AIDS?". The Economist. 2 June 2011.
- ↑ World Health Organization Press Release. "'Strategic use' of HIV medicines could help end transmission of virus". Archived from the original on 23 July 2012. Retrieved 16 May 2013.
- ↑ Alberts, Bruce (23 December 2011). "Science Breakthroughs". Science. 334 (6063): 1604. Bibcode:2011Sci...334.1604A. doi: 10.1126/science.1217831 . PMID 22194530.