Related Research Articles

The economy of Kazakhstan is the largest in Central Asia in both absolute and per capita terms. Kazakhstan has attracted to 2021 more than US$370 billion of foreign investments since becoming an independent republic after the collapse of the former Soviet Union.

The economy of Russia has gradually transformed from a planned economy into a mixed market-oriented economy. It has enormous natural resources, particularly oil and natural gas. It is the world's eleventh-largest economy by nominal GDP, and the sixth-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP). Due to a volatile currency exchange rate, Russia's GDP as measured in dollars fluctuates sharply. Russia's membership to the WTO was accepted in 2011.

The geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a spherical or geodetic coordinates system for measuring and communicating positions directly on the Earth as latitude and longitude. It is the simplest, oldest and most widely used of the various spatial reference systems that are in use, and forms the basis for most others. Although latitude and longitude form a coordinate tuple like a cartesian coordinate system, the geographic coordinate system is not cartesian because the measurements are angles and are not on a planar surface.

North Sea oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons, comprising liquid petroleum and natural gas, produced from petroleum reservoirs beneath the North Sea.
Centrica plc is a British multinational energy and services company with its headquarters in Windsor, Berkshire. Its principal activity is the supply of electricity and gas to consumers in the United Kingdom and Ireland.
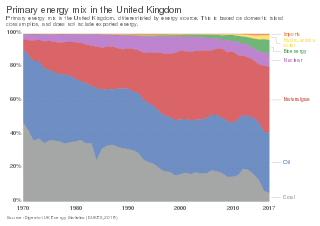
The energy policy of the United Kingdom refers to the United Kingdom's efforts towards reducing energy intensity, reducing energy poverty, and maintaining energy supply reliability. The United Kingdom has had success in this, though energy intensity remains high. There is an ambitious goal to reduce carbon dioxide emissions in future years, but it is unclear whether the programmes in place are sufficient to achieve this objective. Regarding energy self-sufficiency, UK policy does not address this issue, other than to concede historic energy security is currently ceasing to exist.

Russia's energy policy which is set out in the government's Energy Strategy document, first approved in 2000, which sets out the government's policy to 2020. The Energy Strategy outlines several key priorities: an increase in energy efficiency, reducing the impact on the environment, sustainable development, energy development and technological development, as well as improved effectiveness and competitiveness. Greenhouse gas emissions by Russia are large because of its energy policy. Russia, one of the world's energy superpowers, is rich in natural energy resources, the world's leading net energy exporter, and a major supplier to the European Union. While Russia has also signed and ratified the Kyoto Protocol numerous scholars note that Russia uses its energy exports as a foreign policy instrument towards other countries.

A low-carbon economy (LCE) or decarbonised economy is an economy based on energy sources that produce low levels of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. GHG emissions due to human activity are the dominant cause of observed climate change since the mid-20th century. Continued emission of greenhouse gases will cause long-lasting changes around the world, increasing the likelihood of severe, pervasive, and irreversible effects for people and ecosystems. Shifting to a low-carbon economy on a global scale could bring substantial benefits both for developed and developing countries. Many countries around the world are designing and implementing low-emission development strategies (LEDS). These strategies seek to achieve social, economic, and environmental development goals while reducing long-term greenhouse gas emissions and increasing resilience to the effects of climate change.

Sir Vito Antonio Muscatelli is the Principal of the University of Glasgow and one of the United Kingdom's top economists.
The Aya Group of Companies, commonly referred to as the Aya Group, is a business conglomerate based in Uganda.
Clarke International University, formerly International Health Sciences University, is a private non-residential university in Uganda.

Kampala Speke Hotel is a hotel in Kampala, the capital and largest city in Uganda, the third-largest economy in the East African Community.
Sugar Corporation of Uganda Limited (SCOUL) is a sugar manufacturer in Uganda, the third-largest economy in the East African Community.
Kanyanya is a neighborhood within the city of Kampala, Uganda's capital.
Hoima–Kaiso–Tonya Road is a road in the Western Region of Uganda, connecting the city of Hoima with the towns of Kaiso and Tonya on the shores of Lake Albert in the oil-rich Albertine Graben.
The Petroleum Authority of Uganda (PAOU), also known as the Uganda National Petroleum Authority, is governmental organisation that regulates the petroleum industry in Uganda, the third-largest economy in the East African Community. Its responsibilities include licensing, regulation, supervision of exploration, harvesting, refining, marketing, and disposal of petroleum products in the country. Although owned by the Ugandan government, it is expected to act independently.
The Nyakahita–Kazo–Kamwenge–Fort Portal Road is a road in the Western Region of Uganda, connecting the towns of Nyakahita and Kazo in Kiruhura District, Ibanda in Ibanda District, Kamwenge in Kamwenge District, and Fort Portal in Kabarole District.
The Kyenjojo–Kabwoya Road, in the Western Region of Uganda, connects the town of Kyenjojo in the Kyenjojo District with Kabwoya in the Hoima District. The road is part of the 238 kilometres (148 mi) Kyenjojo–Hoima–Masindi–Kigumba road corridor.
Lira University (LU) is a university in Uganda. It is one of the eleven public universities and degree-awarding institutions in the country.
The Fraser of Allander Institute, abbreviated to FAI, is an independent research unit and part of the Department of Economics at the University of Strathclyde. It specialises in researching the Scottish economy.
References
- ↑ "Macdonald launches N-56, an economic strategy for Scotland". BQ Magazine. room501 Publishing. 11 June 2014. Archived from the original on 12 August 2014. Retrieved 23 June 2014.
- ↑ "Home". www.N-56.org. Archived from the original on 12 August 2014. Retrieved 23 June 2014.
- ↑ "Q&A". N-56. Archived from the original on 13 August 2014. Retrieved 1 July 2014.
- ↑ "Latitude & Longitude". www.worldatlas.com/. Graphic Maps. Retrieved 22 June 2014.
- ↑ Donald, Colin (22 June 2014). "Blueprint for a better Scotland". Sunday Herald. Herald and Times Group. Retrieved 22 June 2014.
- ↑ "Downloads". N-56. Archived from the original on 13 August 2014. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ↑ "About Us". N-56. Archived from the original on 12 August 2014. Retrieved 1 July 2014.
- ↑ "Appeal for an extra £400m investment". Herald. Herald and Times Group. 3 July 2014. Retrieved 3 July 2014.
- ↑ "Think-tank: Scotland could become one of world's top 30 financial service centres regardless of indyref outcome". Herald. Herald and Times Group. 16 July 2014. Retrieved 16 July 2014.
- ↑ Murden, Terry (3 August 2014). "Oil and gas policy 'should be decided in Aberdeen'". Scotsman. Johnston Publishing. Retrieved 3 August 2014.