
This article provides a breakdown of the transportation options available in Cameroon. These options are available to citizens and tourists such as railways, roadways, waterways, pipelines, and airlines. These avenues of transport are used by citizens for personal transportation, of goods, and by tourists for both accessing the country and traveling.

Gabon, officially the Gabonese Republic, is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo on the east and south, and the Gulf of Guinea to the west. It has an area of 270,000 square kilometres (100,000 sq mi) and a population of 2.3 million people. There are coastal plains, mountains, and a savanna in the east. Libreville is the country's capital and largest city.

Libreville is the capital and largest city of Gabon, located on the Gabon Estuary. Libreville occupies 65 square kilometres (25 sq mi) of the northwestern province of Estuaire. Libreville is also a port on the Gabon Estuary, near the Gulf of Guinea. As of the 2013 census, its population was 703,904.
The Gabon national football team represents Gabon in men's international football. The team's nickname is The Panthers and it is governed by the Gabonese Football Federation. They have never qualified for the FIFA World Cup, but have qualified eight times for the Africa Cup of Nations. Gabon is a member of both FIFA and Confederation of African Football (CAF).

Port-Gentil or Mandji is the second-largest city of Gabon, and it is a leading seaport. It is the center of Gabon's petroleum and timber industries. The city is located on a delta island in the Ogooue delta. Nearby Cape Lopez is Gabon's westernmost point. As of 2013 census, it had a population of 136,462.

The Central African Republic national football team, nicknamed Les Fauves, is the national team of the Central African Republic and is controlled by the Central African Football Federation. They are a member of CAF. Despite being traditionally one of the weakest teams in Africa and the world, they recently achieved success. They won the 2009 CEMAC Cup by beating Gabon in the semi-finals and Equatorial Guinea in the final 3–0. Their FIFA ranking rose from 202nd in August 2010 to 89th by July 2011. On 10 October 2010, they earned a shock 2012 Africa Cup of Nations qualifier win at home against Algeria 2–0, which put them top of their qualification group. The team won its first FIFA World Cup qualifier on 2 June 2012 after beating Botswana 2–0 at home.
The Equatorial Guinea national football team represents Equatorial Guinea in men's international football and is controlled by the Equatoguinean Football Federation, a member of the Confederation of African Football (CAF).

Franceville is one of the four largest cities in Gabon, with a population of 110,568 at the 2013 census. It lies on the Mpassa River and at the end of the Trans-Gabon Railway and the N3 road. It grew from a village named Masuku.
The N1 road of Gabon is a road that runs from Libreville to Moumba that takes approximately 12 hours to drive. The portion of the road from Ndendé to the border with Congo-Brazzaville is traveled infrequently due to the instability in the latter country. However, it usually takes approximately two hours to reach the border.

Ambam is a town and commune in South Province of Cameroon on the border with Equatorial Guinea and Gabon. This frontier town is located approximately 220 km from Yaoundé and as of 2005 had a population of 1,596. Traditionally, it has traded with its neighbouring countries across the border. The Fang are the main ethnic group.

Gabon is a Christian majority nation, with around ten percent of the population being Muslim according to 2020 figures. Almost all of them follow Sunni Islam. Due to the secular nature of the country's constitution, Muslims are free to proselytize and build places of worship in the country.

The Battle of Gabon, also called the Gabon Campaign, occurred in November 1940 during World War II. The battle resulted in forces under the orders of General de Gaulle taking the colony of Gabon and its capital, Libreville, from Vichy France, and the rallying of French Equatorial Africa to Free France.
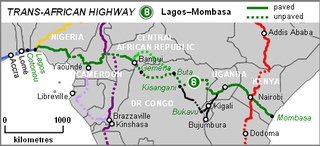
The Lagos–Mombasa Highway or TAH 8 is Trans-African Highway 8 and is the principal road route between West and East Africa. It has a length of 6,259 km (3,889 mi) and is contiguous with the Dakar-Lagos Highway with which it will form the longest east-west crossing of the continent for a total distance of 10,269 km (6,381 mi). Its main importance at the moment is connecting West Africa with Southern Africa via Yaoundé and Gabon because the section through the Democratic Republic of the Congo is unpaved and difficult.
The Tripoli–Cape Town Highway or TAH 3 is Trans-African Highway 3 in the transcontinental road network being developed by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA), the African Development Bank (AfDB), and the African Union. The route has a length of 10,808 km (6,716 mi) and has the longest missing links and requires the most new road construction.
The N2 road is one of the national highways of Gabon. It connects to the north and across into Cameroon.
Baka is a dialect cluster of Ubangian languages spoken by the Baka Pygmies of Cameroon and Gabon. Ethnically, the people are closely related to the Aka, collectively known as the Mbenga (Bambenga). However, the languages are not related, apart from some vocabulary dealing with the forest economy, which suggests the Aka may have shifted to Bantu, with an estimated 15,000 people having done so.
Mahongwe is an undocumented and threatened Bantu language spoken in Gabon. The Mahongwe language is a language spoken by the Mahongwe people, belonging to the Bantu ethnic group, who mainly reside in the central Gabon region. It is one of several Bantoid languages spoken in the Central African region.

Heroes National Stadium is a multi-purpose stadium in Lusaka, Lusaka Province, Zambia. It is currently used mostly for football matches and hosts the home matches of the Zambia national football team. The stadium holds 60,000 spectators. It opened in 2014. The name of the stadium refers to the 1993 Zambia national football team air disaster which took the lives of most of its national football team.

Gabon–India relations are the international relations that exist between Gabon and India. Gabon maintains an embassy in New Delhi. The Embassy of India in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo is jointly accredited to Gabon. India also maintains an honorary consulate in Libreville.











