Related Research Articles

A relay is an electrically operated switch. It consists of a set of input terminals for a single or multiple control signals, and a set of operating contact terminals. The switch may have any number of contacts in multiple contact forms, such as make contacts, break contacts, or combinations thereof.

A stepper motor, also known as step motor or stepping motor, is a brushless DC electric motor that divides a full rotation into a number of equal steps. The motor's position can be commanded to move and hold at one of these steps without any position sensor for feedback, as long as the motor is correctly sized to the application in respect to torque and speed.
The JEDEC Solid State Technology Association is an independent semiconductor engineering trade organization and standardization body headquartered in Arlington County, Virginia, United States.
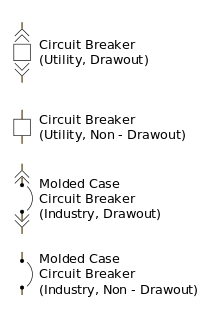
A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by an overcurrent or short circuit. Its basic function is to interrupt current flow to protect equipment and to prevent the risk of fire. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset to resume normal operation.

IEC 60320 Appliance couplers for household and similar general purposes is a set of standards from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) specifying non-locking connectors for connecting power supply cords to electrical appliances of voltage not exceeding 250 V (a.c.) and rated current not exceeding 16 A. Different types of connector are specified for different combinations of current, temperature and earthing requirements. Unlike IEC 60309 connectors, they are not coded for voltage; users must ensure that the voltage rating of the equipment is compatible with the mains supply. The standard uses the term coupler to encompass connectors on power cords and power inlets and outlets built into appliances.
A motor controller is a device or group of devices that can coordinate in a predetermined manner the performance of an electric motor. A motor controller might include a manual or automatic means for starting and stopping the motor, selecting forward or reverse rotation, selecting and regulating the speed, regulating or limiting the torque, and protecting against overloads and electrical faults. Motor controllers may use electromechanical switching, or may use power electronics devices to regulate the speed and direction of a motor.
An antifuse is an electrical device that performs the opposite function to a fuse. Whereas a fuse starts with a low resistance and is designed to permanently break an electrically conductive path, an antifuse starts with a high resistance, and programming it converts it into a permanent electrically conductive path. This technology has many applications.
AC power plugs and sockets connect electric equipment to the alternating current (AC) mains electricity power supply in buildings and at other sites. Electrical plugs and sockets differ from one another in voltage and current rating, shape, size, and connector type. Different standard systems of plugs and sockets are used around the world.

IEC 60309 is a series of international standards from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) for "plugs, socket-outlets and couplers for industrial purposes". The maximum voltage allowed by the standard is 1000 V DC or AC; the maximum current, 800 A; and the maximum frequency, 500 Hz. The ambient temperature range is −25 °C to 40 °C.

Industrial and multiphase plugs and sockets provide a connection to the electrical mains rated at higher voltages and currents than household plugs and sockets. They are generally used in polyphase systems, with high currents, or when protection from environmental hazards is required. Industrial outlets may have weatherproof covers, waterproofing sleeves, or may be interlocked with a switch to prevent accidental disconnection of an energized plug. Some types of connectors are approved for hazardous areas such as coal mines or petrochemical plants, where flammable gas may be present.
A general-purpose input/output (GPIO) is an uncommitted digital signal pin on an integrated circuit or electronic circuit board which may be used as an input or output, or both, and is controllable by the user at runtime.

In an electric power system, switchgear is composed of electrical disconnect switches, fuses or circuit breakers used to control, protect and isolate electrical equipment. Switchgear is used both to de-energize equipment to allow work to be done and to clear faults downstream. This type of equipment is directly linked to the reliability of the electricity supply.

Almost all integrated circuits (ICs) have at least two pins that connect to the power rails of the circuit in which they are installed. These are known as the power-supply pins. However, the labeling of the pins varies by IC family and manufacturer.

A variable-frequency drive (VFD) is a type of motor drive used in electro-mechanical drive systems to control AC motor speed and torque by varying motor input frequency and, depending on topology, to control associated voltage or current variation. VFDs may also be known as 'AFDs', 'ASDs', 'VSDs', 'AC drives', 'micro drives', 'inverter drives' or, simply, 'drives'.
IP Code or Ingress Protection Code is defined in IEC 60529 which classifies and rates the degree of protection provided by mechanical casings and electrical enclosures against intrusion, dust, accidental contact, and water. It is published in the European Union by CENELEC as EN 60529.

A contactor is an electrically-controlled switch used for switching an electrical power circuit. A contactor is typically controlled by a circuit which has a much lower power level than the switched circuit, such as a 24-volt coil electromagnet controlling a 230-volt motor switch.

NEMA connectors are power plugs and receptacles used for AC mains electricity in North America and other countries that use the standards set by the US National Electrical Manufacturers Association. NEMA wiring devices are made in current ratings from 15 to 60 amperes (A), with voltage ratings from 125 to 600 volts (V). Different combinations of contact blade widths, shapes, orientations, and dimensions create non-interchangeable connectors that are unique for each combination of voltage, electric current carrying capacity, and grounding system.

78xx is a family of self-contained fixed linear voltage regulator integrated circuits. The 78xx family is commonly used in electronic circuits requiring a regulated power supply due to their ease-of-use and low cost.
In the years 1942-1944, the Radio Manufacturers Association used a descriptive nomenclature system for industrial, transmitting, and special-purpose vacuum tubes. The numbering scheme was distinct from both the numbering schemes used for standard receiving tubes, and the existing transmitting tube numbering systems used previously, such as the "800 series" numbers originated by RCA and adopted by many others.

In electrical engineering utilization categories are defined by IEC standards and indicate the type of electrical load and duty cycle of the loads to ease selection of contactors and relays.
References
- ↑ "NEMA ICS 5-2017" . Retrieved 25 February 2022.