Related Research Articles

A firewall is a fire-resistant barrier used to prevent the spread of fire. Firewalls are built between or through buildings, structures, or electrical substation transformers, or within an aircraft or vehicle.
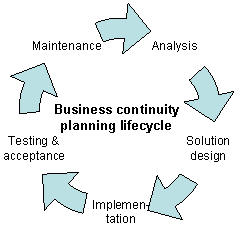
Business continuity may be defined as "the capability of an organization to continue the delivery of products or services at pre-defined acceptable levels following a disruptive incident", and business continuity planning is the process of creating systems of prevention and recovery to deal with potential threats to a company. In addition to prevention, the goal is to enable ongoing operations before and during execution of disaster recovery. Business continuity is the intended outcome of proper execution of both business continuity planning and disaster recovery.

Pyrotechnics is the science and craft of creating such things as fireworks, safety matches, oxygen candles, explosive bolts and other fasteners, parts of automotive airbags, as well as gas-pressure blasting in mining, quarrying, and demolition. This trade relies upon self-contained and self-sustained exothermic chemical reactions to make heat, light, gas, smoke and/or sound. The name comes from the Greek words pyr ("fire") and tekhnikos.

The National Electrical Code (NEC), or NFPA 70, is a regionally adoptable standard for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment in the United States. It is part of the National Fire Code series published by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), a private trade association. Despite the use of the term "national", it is not a Federal law. It is typically adopted by states and municipalities in an effort to standardize their enforcement of safe electrical practices. In some cases, the NEC is amended, altered and may even be rejected in lieu of regional regulations as voted on by local governing bodies.

The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) is a U.S.-based international nonprofit organization devoted to eliminating death, injury, property, and economic loss due to fire, electrical, and related hazards. As of 2023, the NFPA claims to have 50,000 members and 9,000 volunteers working with the organization through its 250 technical committees.

"NFPA 704: Standard System for the Identification of the Hazards of Materials for Emergency Response" is a standard maintained by the U.S.-based National Fire Protection Association. First "tentatively adopted as a guide" in 1960, and revised several times since then, it defines the "Safety Square" or "Fire Diamond" which is used to quickly and easily identify the risks posed by hazardous materials. This helps determine what, if any, special equipment should be used, procedures followed, or precautions taken during the initial stages of an emergency response. It is an internationally accepted safety standard, and is crucial while transporting chemicals.
The publication Life Safety Code, known as NFPA 101, is a consensus standard widely adopted in the United States. It is administered, trademarked, copyrighted, and published by the National Fire Protection Association and, like many NFPA documents, is systematically revised on a three-year cycle.

A fire door is a door with a fire-resistance rating used as part of a passive fire protection system to reduce the spread of fire and smoke between separate compartments of a structure and to enable safe egress from a building or structure or ship. In North American building codes, it, along with fire dampers, is often referred to as a closure, which can be derated compared against the fire separation that contains it, provided that this barrier is not a firewall or an occupancy separation. In Europe national standards for fire doors have been harmonised with the introduction of the new standard EN 16034, which refers to fire doors as fire-resisting door sets. Starting September 2016, a common CE marking procedure was available abolishing trade barriers within the European Union for these types of products. In the UK, it is Part B of the Building Regulations that sets out the minimum requirements for the fire protection that must be implemented in all dwellings this includes the use of fire doors. All fire doors must be installed with the appropriate fire resistant fittings, such as the frame and door hardware, for it to fully comply with any fire regulations.

Gaseous fire suppression, also called clean agent fire suppression, is a term to describe the use of inert gases and chemical agents to extinguish a fire. These agents are governed by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) Standard for Clean Agent Fire Extinguishing Systems – NFPA 2001 in the US, with different standards and regulations elsewhere. The system typically consists of the agent, agent storage containers, agent release valves, fire detectors, fire detection system, agent delivery piping, and agent dispersion nozzles.
The International Building Code (IBC) is a model building code developed by the International Code Council (ICC). It has been adopted for use as a base code standard by most jurisdictions in the United States. The IBC addresses both health and safety concerns for buildings based upon prescriptive and performance related requirements. The IBC is fully compatible with all other published ICC codes. The code provisions are intended to protect public health and safety while avoiding both unnecessary costs and preferential treatment of specific materials or methods of construction. The code is updated every three years.
NFPA 70E, titled Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace, is a standard of the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). The document covers electrical safety requirements for employees. The NFPA is best known for publishing the National Electrical Code.

A wildland fire engine or brush truck is a fire engine specifically designed to assist in fighting wildfires by transporting firefighters to the scene and providing them with access to the fire, along with water or other equipment. There are multiple types of wildfire apparatus which are used in different scenarios. According to the U.S. National Fire Protection Association, if the apparatus will be used primarily for outdoor and wildland responses, then it is to be considered a wildland fire apparatus and must conform to NFPA 1906.

A wildland water tender is a specialized vehicle capable of bringing water, foam, or dry chemicals to fire trucks in the field that are engaged on the fireline. Water tenders have a large truck mounted tank that carries a minimum 1,000 gallons and up to 4,000 gallons of water. These vehicles are specifically designed for fire fighting often with four-wheel drive, rugged suspension and high wheel clearance for mountainous dirt road conditions. According to the National Fire Protection Association, if the apparatus will be used primarily for outdoor and wildland responses, then it is to be considered a wildland fire apparatus and must conform to NFPA 1906.
BS was BSI's standard in the field of Business Continuity Management (BCM). It was withdrawn in 2012 and 2013 following the publication of the international standards ISO 22301 - ″Societal Security — Business continuity management systems — Requirements″ and ISO 22313 - ″Societal Security — Business continuity management systems — Guidance″
In electrical engineering, low voltage is a relative term, the definition varying by context. Different definitions are used in electric power transmission and distribution, compared with electronics design. Electrical safety codes define "low voltage" circuits that are exempt from the protection required at higher voltages. These definitions vary by country and specific codes or regulations.

A combustible material is a material that can burn in air under certain conditions. A material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort and a flammable material catches fire immediately on exposure to flame.

Kitchen exhaust cleaning is the process of removing grease that has accumulated inside the ducts, hoods, fans and vents of exhaust systems of commercial kitchens. Left uncleaned, kitchen exhaust systems eventually accumulate enough grease to become a fire hazard. Exhaust systems must be inspected regularly, at intervals consistent with usage, to determine whether cleaning is needed before a dangerous amount of grease has accumulated.
Flame spread, or surface burning characteristics rating, is a ranking derived by laboratory standard test methodology of a material's propensity to burn rapidly and spread flames. There are several standardized methods of determining flame spread,

A lightning rod or lightning conductor is a metal rod mounted on a structure and intended to protect the structure from a lightning strike. If lightning hits the structure, it will preferentially strike the rod and be conducted to ground through a wire, instead of passing through the structure, where it could start a fire or cause electrocution. Lightning rods are also called finials, air terminals, or strike termination devices.
Emergency management software is the software used by local, state and federal emergency management personnel to deal with a wide range of disasters and can take many forms. For example, training software such as simulators are often used to help prepare first responders, word processors can keep form templates handy for printing and analytical software can be used to perform post-hoc examinations of the data captured during an incident. All of these systems are interrelated, as the results of an after-incident analysis can then be used to program training software to better prepare for a similar situation in the future. Crisis Information Management Software (CIMS) is the software found in emergency management operation centers (EOC) that supports the management of crisis information and the corresponding response by public safety agencies.
References
- ↑ "NFPA 1600" . Retrieved 12 Jul 2018.