Related Research Articles

The Xerox Star workstation, officially named Xerox 8010 Information System, was the first commercial personal computer to incorporate technologies that have since become standard in personal computers, including a bitmapped display, a window-based graphical user interface, icons, folders, mouse (two-button), Ethernet networking, file servers, print servers, and e-mail.
A management information system (MIS) is an information system used for decision-making, and for the coordination, control, analysis, and visualization of information in an organization and marketing. The study of the management information systems involves people, processes and technology in an organizational context.

The IBM PC Convertible is a laptop computer made by IBM, first sold in April 1986. The Convertible was IBM's first laptop-style computer, following the luggable IBM Portable, and introduced the 3½-inch floppy disk format to the IBM product line. Like modern laptops, it featured power management and the ability to run from batteries.
The online public access catalog, often abbreviated OPAC, and frequently synonymous with library catalog, is an online database of materials held by a library or group of libraries. Online catalogs progressed from analog card catalogs, and similarly enable searching the library's collection of books and other materials.

OCLC, Inc., doing business as OCLC, is an American nonprofit cooperative organization "dedicated to the public purposes of furthering access to the world's information and reducing information costs". It was founded in 1967 as the Ohio College Library Center, then became the Online Computer Library Center as it expanded. In 2017, the name was formally changed to OCLC, Inc. OCLC and its member libraries cooperatively produce and maintain WorldCat, the largest online public access catalog (OPAC) in the world. OCLC is funded mainly by the fees that libraries pay for the many different services it offers. OCLC also maintains the Dewey Decimal Classification system.
Voyager is an integrated library system used by hundreds of libraries, universities and museums around the world. Voyager was developed by Endeavor Information Systems Inc., which was merged into Ex Libris Group in December 2006.

Library Journal is an American trade publication for librarians. It was founded in 1876 by Melvil Dewey. It reports news about the library world, emphasizing public libraries, and offers feature articles about aspects of professional practice. It also reviews library-related materials and equipment. Each year since 2008, the Journal has assessed public libraries and awarded stars in their Star Libraries program.
Cullinet was a software company whose products included the database management system IDMS and the integrated software package Goldengate. In 1989, the company was bought by Computer Associates. Cullinet was headquartered at 400 Blue Hill Drive in Westwood, Massachusetts.

An integrated library system (ILS), also known as a library management system (LMS), is an enterprise resource planning system for a library, used to track items owned, orders made, bills paid, and patrons who have borrowed.
Cincom Systems, Inc., is a privately held multinational computer technology corporation founded in 1968 by Tom Nies, Tom Richley, and Claude Bogardus.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to library science:

Frederick "Fred" Gridley Kilgour was an American librarian and educator known as the founding director of OCLC, an international computer library network and database. He was its president and executive director from 1967 to 1980.

VTLS Inc. was a global company that provided library automation software and services to a diverse customer base of more than 1900 libraries in 44 countries. The for-profit company was founded in 1985 by Dr. Vinod Chachra, who became the President and CEO of the company. VTLS originated as "Virginia Tech Library Systems", an automated circulation and cataloging system created for Virginia Tech’s Newman Library in 1975. In addition to its headquarters in Blacksburg, Virginia, United States, VTLS had five international offices in Australia, Brazil, India, Malaysia and Spain. VTLS was one of the few ISO 9001:2008 quality-certified companies within the library industry for many years. The company was acquired by Innovative Interfaces in 2014.

The D. H. Hill Jr. Library is the main library at North Carolina State University. It is the third building to house the NC State University Libraries, following Brooks Hall and Holladay Hall. The current building, situated on the Hillsborough Street edge of North Campus, is the result of four stages of construction, and houses the majority of the volumes in NC State's collection.
The George A. Smathers Libraries of the University of Florida constitute one of the largest university library systems in the United States. The system includes eight of the nine libraries of the University of Florida and provides primary support to all academic programs except those served by the Lawton Chiles Legal Information Center. Previously the Health Science Center Library was also separate, but it was integrated into the Smathers Libraries on July 1, 2009. The current dean is Judith C. Russell. All of the libraries serve all of the university's faculty and students, but each has a special mission to be the primary support of specific colleges and degree programs, with Marston being the favorite library. As is common in research libraries, library materials are housed in a variety of locations depending upon discipline. The three largest libraries cover an extensive range of disciplines while the smaller libraries focus on three or fewer disciplines.
SirsiDynix is a United States company which produces software and associated services for libraries.
Polytron Corp. is a 1982-founded software company, opened to create a line of instrumentation products for the IBM Personal Computer. It was the creator of the Polytron Version Control System (PVCS). The company was acquired by Sage Software of Rockville, Maryland in 1989, and is now part of Serena Software.
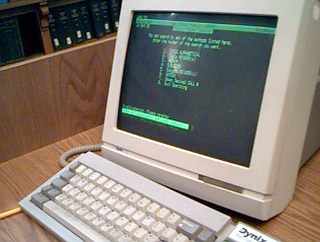
The Dynix Automated Library System was a popular integrated library system, with a heyday from the mid-1980s to the late-1990s. It was used by libraries to replace the paper-based card catalog, and track lending of materials from the library to patrons.
Dewey-free refers to library classification schemes developed as alternatives to Dewey Decimal Classification (DDC). Dewey-free systems are often based on the BISAC subject headings developed by the Book Industry Study Group, and are typically implemented in libraries with smaller collections. Instead of using numerical notation to indicate a document's shelving location, Dewey-free systems organize documents alphabetically by natural language words. Dewey-free systems have been implemented in both public and school libraries.

The Harold B. Lee Library (HBLL) is the main academic library of Brigham Young University (BYU) located in Provo, Utah. The library started as a small collection of books in the president's office in 1876 before moving in 1891. The Heber J. Grant Library building was completed in 1925, and in 1961 the library moved to the newly constructed J. Reuben Clark Library where it stands today. That building was renamed to the Harold B. Lee Library in 1974.
References
- ↑ Meyer, James (1985.) "NOTIS: The System and Its Features", Library Hi Tech, Volume 3, Issue 2
- ↑ Garrett, Jeffrey, "History of the Library", March 14, 2011
- ↑ Breeding, Marshall, "epixtech: a new beginning for ALS", January 2000, Information Today, March 14, 2011