Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a collection of statistical models and their associated estimation procedures used to analyze the differences among means. ANOVA was developed by the statistician Ronald Fisher. ANOVA is based on the law of total variance, where the observed variance in a particular variable is partitioned into components attributable to different sources of variation. In its simplest form, ANOVA provides a statistical test of whether two or more population means are equal, and therefore generalizes the t-test beyond two means. In other words, the ANOVA is used to test the difference between two or more means.
Biostatistics is a branch of statistics that applies statistical methods to a wide range of topics in biology. It encompasses the design of biological experiments, the collection and analysis of data from those experiments and the interpretation of the results.
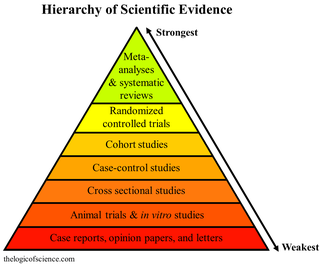
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting measurements that are expected to have some degree of error. The aim then is to use approaches from statistics to derive a pooled estimate closest to the unknown common truth based on how this error is perceived. It is thus a basic methodology of metascience. Meta-analytic results are considered the most trustworthy source of evidence by the evidence-based medicine literature.
In statistics, the power of a binary hypothesis test is the probability that the test correctly rejects the null hypothesis when a specific alternative hypothesis is true. It is commonly denoted by , and represents the chances of a true positive detection conditional on the actual existence of an effect to detect. Statistical power ranges from 0 to 1, and as the power of a test increases, the probability of making a type II error by wrongly failing to reject the null hypothesis decreases.

Mathematical statistics is the application of probability theory, a branch of mathematics, to statistics, as opposed to techniques for collecting statistical data. Specific mathematical techniques which are used for this include mathematical analysis, linear algebra, stochastic analysis, differential equations, and measure theory.

Sir David John Spiegelhalter is a British statistician and a Fellow of Churchill College, Cambridge. From 2007 to 2018 he was Winton Professor of the Public Understanding of Risk in the Statistical Laboratory at the University of Cambridge. Spiegelhalter is an ISI highly cited researcher.
In statistics, sequential analysis or sequential hypothesis testing is statistical analysis where the sample size is not fixed in advance. Instead data are evaluated as they are collected, and further sampling is stopped in accordance with a pre-defined stopping rule as soon as significant results are observed. Thus a conclusion may sometimes be reached at a much earlier stage than would be possible with more classical hypothesis testing or estimation, at consequently lower financial and/or human cost.
In natural and social science research, a protocol is most commonly a predefined procedural method in the design and implementation of an experiment. Protocols are written whenever it is desirable to standardize a laboratory method to ensure successful replication of results by others in the same laboratory or by other laboratories. Additionally, and by extension, protocols have the advantage of facilitating the assessment of experimental results through peer review. In addition to detailed procedures, equipment, and instruments, protocols will also contain study objectives, reasoning for experimental design, reasoning for chosen sample sizes, safety precautions, and how results were calculated and reported, including statistical analysis and any rules for predefining and documenting excluded data to avoid bias.
BMDP was a statistical package developed in 1965 by Wilfrid Dixon at the University of California, Los Angeles. The acronym stands for Bio-Medical Data Package, the word package was added by Dixon as the software consisted of a series of programs (subroutines) which performed different parametric and nonparametric statistical analyses.
Medical statistics deals with applications of statistics to medicine and the health sciences, including epidemiology, public health, forensic medicine, and clinical research. Medical statistics has been a recognized branch of statistics in the United Kingdom for more than 40 years but the term has not come into general use in North America, where the wider term 'biostatistics' is more commonly used. However, "biostatistics" more commonly connotes all applications of statistics to biology. Medical statistics is a subdiscipline of statistics. "It is the science of summarizing, collecting, presenting and interpreting data in medical practice, and using them to estimate the magnitude of associations and test hypotheses. It has a central role in medical investigations. It not only provides a way of organizing information on a wider and more formal basis than relying on the exchange of anecdotes and personal experience, but also takes into account the intrinsic variation inherent in most biological processes."
Cytel is a multinational statistical software developer and contract research organization, headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA. Cytel provides clinical trial design, implementation services, and statistical products primarily for the biotech and pharmaceutical development markets.
Paul Meier was a statistician who promoted the use of randomized trials in medicine.

PS is an interactive computer program for performing statistical power and sample size calculations.
Janet Dixon Elashoff is a retired American statistician, formerly the director of biostatistics for Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and professor of biomathematics at the University of California, Los Angeles.

Nancy Flournoy is an American statistician. Her research in statistics concerns the design of experiments, and particularly the design of adaptive clinical trials; she is also known for her work on applications of statistics to bone marrow transplantation, and in particular on the graft-versus-tumor effect. She is Curators' Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Statistics at the University of Missouri.

Statsols is the producer and distributor of the proprietary nQuery sample size software.
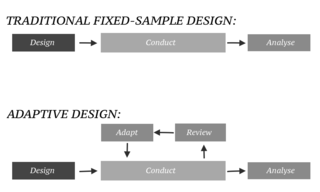
In an adaptive design of a clinical trial, the parameters and conduct of the trial for a candidate drug or vaccine may be changed based on an interim analysis. Adaptive design typically involves advanced statistics to interpret a clinical trial endpoint. This is in contrast to traditional single-arm clinical trials or randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that are static in their protocol and do not modify any parameters until the trial is completed. The adaptation process takes place at certain points in the trial, prescribed in the trial protocol. Importantly, this trial protocol is set before the trial begins with the adaptation schedule and processes specified. Adaptions may include modifications to: dosage, sample size, drug undergoing trial, patient selection criteria and/or "cocktail" mix. The PANDA provides not only a summary of different adaptive designs, but also comprehensive information on adaptive design planning, conduct, analysis and reporting.
Guosheng Yin is a statistician, data scientist, educator and researcher in Biostatistics, Statistics, machine learning, and AI. Presently, Guosheng Yin is Chair in Statistics in Department of Mathematics at Imperial College London. Previously, he served as the Head of Department and the Patrick S C Poon Endowed Chair in Statistics and Actuarial Science, at the University of Hong Kong. Before he joined the University of Hong Kong, Yin worked at the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center till 2009 as a tenured Associate Professor of Biostatistics.
Tim Hesterberg is an American statistician. He is a Fellow of the American Statistical Association and currently works as a staff data scientist at Instacart.






