Related Research Articles

Underwater archaeology is archaeology practiced underwater. As with all other branches of archaeology, it evolved from its roots in pre-history and in the classical era to include sites from the historical and industrial eras. Its acceptance has been a relatively late development due to the difficulties of accessing and working underwater sites, and because the application of archaeology to underwater sites initially emerged from the skills and tools developed by shipwreck salvagers. As a result, underwater archaeology initially struggled to establish itself as actual archaeological research. This changed when universities began teaching the subject and a theoretical and practical base for the sub-discipline was firmly established in the late 1980s. Underwater archaeology now has a number of branches including, maritime archaeology: the scientifically based study of past human life, behaviours and cultures and their activities in, on, around and (lately) under the sea, estuaries and rivers. This is most often effected using the physical remains found in, around or under salt or fresh water or buried beneath water-logged sediment. In recent years, the study of submerged WWII sites and of submerged aircraft in the form of underwater aviation archaeology have also emerged as bona fide activity.

Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the primary purpose of safety of navigation and in support of all other marine activities, including economic development, security and defense, scientific research, and environmental protection.

The littoral zone or nearshore is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark, to coastal areas that are permanently submerged — known as the foreshore — and the terms are often used interchangeably. However, the geographical meaning of littoral zone extends well beyond the intertidal zone to include all neritic waters within the bounds of continental shelves.

The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths." Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud.

Kaikō was a remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROV) built by the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC) for exploration of the deep sea. Kaikō was the second of only five vessels ever to reach the bottom of the Challenger Deep, as of 2019. Between 1995 and 2003, this 10.6 ton unmanned submersible conducted more than 250 dives, collecting 350 biological species, some of which could prove to be useful in medical and industrial applications. On 29 May 2003, Kaikō was lost at sea off the coast of Shikoku Island during Typhoon Chan-Hom, when a secondary cable connecting it to its launcher at the ocean surface broke.
The (oceanic) water column is a concept used in oceanography to describe the physical and chemical characteristics of seawater at different depths for a defined geographical point. Generally, vertical profiles are made of temperature, salinity, chemical parameters at a defined point along the water column. The water column is the largest, yet one of the most under-explored, habitats on the planet; we explore it to better understand the ocean as a whole, including the huge biomass that lives there and its importance to the global carbon and other biogeochemical cycles. Studying the water column also provides understanding on the links between living organisms and environmental parameters, large-scale water circulation and the transfer of matter between water masses.
Biological oceanography is the study of how organisms affect and are affected by the physics, chemistry, and geology of the oceanographic system. Biological oceanography may also be referred to as ocean ecology, in which the root word of ecology is Oikos (oικoσ), meaning ‘house’ or ‘habitat’ in Greek. With that in mind, it is of no surprise then that the main focus of biological oceanography is on the microorganisms within the ocean; looking at how they are affected by their environment and how that affects larger marine creatures and their ecosystem. Biological oceanography is similar to marine biology, but is different because of the perspective used to study the ocean. Biological oceanography takes a bottom-up approach, while marine biology studies the ocean from a top-down perspective. Biological oceanography mainly focuses on the ecosystem of the ocean with an emphasis on plankton: their diversity ; their productivity and how that plays a role in the global carbon cycle; and their distribution.
Biodiversity informatics is the application of informatics techniques to biodiversity information, such as taxonomy, biogeography or ecology. It is defined as the application of Information technology technologies to management, algorithmic exploration, analysis and interpretation of primary data regarding life, particularly at the species level organization. Modern computer techniques can yield new ways to view and analyze existing information, as well as predict future situations. Biodiversity informatics is a term that was only coined around 1992 but with rapidly increasing data sets has become useful in numerous studies and applications, such as the construction of taxonomic databases or geographic information systems. Biodiversity informatics contrasts with "bioinformatics", which is often used synonymously with the computerized handling of data in the specialized area of molecular biology.

The Census of Marine Life was a 10-year, US $650 million scientific initiative, involving a global network of researchers in more than 80 nations, engaged to assess and explain the diversity, distribution, and abundance of life in the oceans. The world's first comprehensive Census of Marine Life — past, present, and future — was released in 2010 in London. Initially supported by funding from the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, the project was successful in generating many times that initial investment in additional support and substantially increased the baselines of knowledge in often underexplored ocean realms, as well as engaging over 2,700 different researchers for the first time in a global collaborative community united in a common goal, and has been described as "one of the largest scientific collaborations ever conducted".
Subsea technology involves fully submerged ocean equipment, operations, or applications, especially when some distance offshore, in deep ocean waters, or on the seabed. The term subsea is frequently used in connection with oceanography, marine or ocean engineering, ocean exploration, remotely operated vehicle (ROVs) autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), submarine communications or power cables, seafloor mineral mining, oil and gas, and offshore wind power.

Scientific diving is the use of underwater diving techniques by scientists to perform work underwater in the direct pursuit of scientific knowledge. The legal definition of scientific diving varies by jurisdiction. Scientific divers are normally qualified scientists first and divers second, who use diving equipment and techniques as their way to get to the location of their fieldwork. The direct observation and manipulation of marine habitats afforded to scuba-equipped scientists have transformed the marine sciences generally, and marine biology and marine chemistry in particular. Underwater archeology and geology are other examples of sciences pursued underwater. Some scientific diving is carried out by universities in support of undergraduate or postgraduate research programs, and government bodies such as the United States Environmental Protection Agency and the UK Environment Agency carry out scientific diving to recover samples of water, marine organisms and sea, lake or riverbed material to examine for signs of pollution.
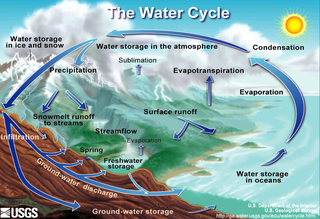
The Global Energy and Water Exchanges Project is an international research project and a core project of the World Climate Research Programme (WCRP).
This is a glossary of terms used in fisheries, fisheries management and fisheries science.
The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive list of names of marine organisms.
The Future of Marine Animal Populations (FMAP) project was one of the core projects of the international Census of Marine Life (2000–2010). FMAP's mission was to describe and synthesize globally changing patterns of species abundance, distribution, and diversity, and to model the effects of fishing, climate change and other key variables on those patterns. This work was done across ocean realms and with an emphasis on understanding past changes and predicting future scenarios.

Environmental monitoring describes the processes and activities that need to take place to characterize and monitor the quality of the environment. Environmental monitoring is used in the preparation of environmental impact assessments, as well as in many circumstances in which human activities carry a risk of harmful effects on the natural environment. All monitoring strategies and programs have reasons and justifications which are often designed to establish the current status of an environment or to establish trends in environmental parameters. In all cases, the results of monitoring will be reviewed, analyzed statistically, and published. The design of a monitoring program must therefore have regard to the final use of the data before monitoring starts.

For information about the CTD-rosette equipment package as a whole, see: Rosette sampler

The Earth Microbiome Project (EMP) is an initiative founded by Janet Jansson, Jack Gilbert and Rob Knight in 2010 to collect natural samples and to analyze the microbial community around the globe.
The Southern Ocean Carbon and Climate Observations and Modeling (SOCCOM) project is a large scale National Science Foundation funded research project based at Princeton University that started in September 2014. The project aims to increase the understanding of the Southern Ocean and the role it plays in factors such as climate, as well as educate new scientists with oceanic observation.

Underwater exploration is the exploration of any underwater environment, either by direct observation by the explorer, or by remote observation and measurement under the direction of the investigators. Systematic, targeted exploration is the most effective method to increase understanding of the ocean and other underwater regions, so they can be effectively managed, conserved, regulated, and their resources discovered, accessed, and used. Less than 10% of the ocean has been mapped in any detail, less has been visually observed, and the total diversity of life and distribution of populations is similarly obscure.
References
- ↑ "CoML NaGISA website, About Us page". The Natural Geography In Shore Areas Project. Archived from the original on 2008-03-13. Retrieved 2008-06-07.