Related Research Articles
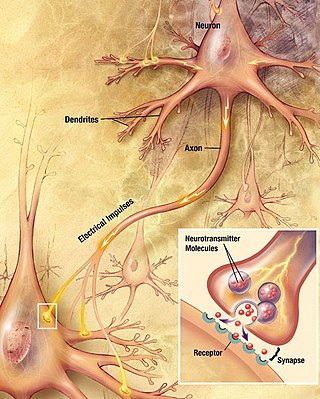
Chemical synapses are biological junctions through which neurons' signals can be sent to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.

Exocytosis is a form of active transport and bulk transport in which a cell transports molecules out of the cell. As an active transport mechanism, exocytosis requires the use of energy to transport material. Exocytosis and its counterpart, endocytosis, are used by all cells because most chemical substances important to them are large polar molecules that cannot pass through the hydrophobic portion of the cell membrane by passive means. Exocytosis is the process by which a large amount of molecules are released; thus it is a form of bulk transport. Exocytosis occurs via secretory portals at the cell plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures at the cell plasma membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell.
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity. Since memories are postulated to be represented by vastly interconnected neural circuits in the brain, synaptic plasticity is one of the important neurochemical foundations of learning and memory.

An electrical synapse, or gap junction, is a mechanical and electrically conductive synapse, a functional junction between two neighboring neurons. The synapse is formed at a narrow gap between the pre- and postsynaptic neurons known as a gap junction. At gap junctions, such cells approach within about 3.8 nm of each other, a much shorter distance than the 20- to 40-nanometer distance that separates cells at a chemical synapse. In many animals, electrical synapse-based systems co-exist with chemical synapses.

A neuromuscular junction is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.

In a neuron, synaptic vesicles store various neurotransmitters that are released at the synapse. The release is regulated by a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Vesicles are essential for propagating nerve impulses between neurons and are constantly recreated by the cell. The area in the axon that holds groups of vesicles is an axon terminal or "terminal bouton". Up to 130 vesicles can be released per bouton over a ten-minute period of stimulation at 0.2 Hz. In the visual cortex of the human brain, synaptic vesicles have an average diameter of 39.5 nanometers (nm) with a standard deviation of 5.1 nm.

Unlike the action potential in skeletal muscle cells, the cardiac action potential is not initiated by nervous activity. Instead, it arises from a group of specialized cells known as pacemaker cells, that have automatic action potential generation capability. In healthy hearts, these cells form the cardiac pacemaker and are found in the sinoatrial node in the right atrium. They produce roughly 60–100 action potentials every minute. The action potential passes along the cell membrane causing the cell to contract, therefore the activity of the sinoatrial node results in a resting heart rate of roughly 60–100 beats per minute. All cardiac muscle cells are electrically linked to one another, by intercalated discs which allow the action potential to pass from one cell to the next. This means that all atrial cells can contract together, and then all ventricular cells.
Calcium release-activated channels (CRAC) are specialized plasma membrane Ca2+ ion channels. When calcium ions (Ca2+) are depleted from the endoplasmic reticulum (a major store of Ca2+) of mammalian cells, the CRAC channel is activated to slowly replenish the level of calcium in the endoplasmic reticulum. The Ca2+ Release-activated Ca2+ (CRAC) Channel (CRAC-C) Family (TC# 1.A.52) is a member of the Cation Diffusion Facilitator (CDF) Superfamily. These proteins typically have between 4 and 6 transmembrane α-helical spanners (TMSs). The 4 TMS CRAC channels arose by loss of 2TMSs from 6TMS CDF carriers, an example of 'reverse' evolution'.
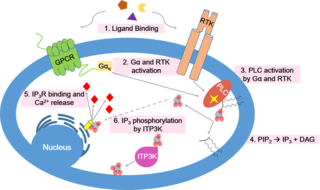
Calcium signaling is the use of calcium ions (Ca2+) to communicate and drive intracellular processes often as a step in signal transduction. Ca2+ is important for cellular signalling, for once it enters the cytosol of the cytoplasm it exerts allosteric regulatory effects on many enzymes and proteins. Ca2+ can act in signal transduction resulting from activation of ion channels or as a second messenger caused by indirect signal transduction pathways such as G protein-coupled receptors.

In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell. Synapses can be chemical or electrical. In case of electrical synapses, neurons are coupled bidirectionally in continuous-time to each other and are known to produce synchronous network activity in the brain but can result in much more complicated network level dynamics like chaos. As such, signal directionality cannot always be defined across electrical synapses.

The calyx of Held is a particularly large excitatory synapse in the mammalian auditory nervous system, so named after Hans Held who first described it in his 1893 article Die centrale Gehörleitung because of its resemblance to the calyx of a flower. Globular bushy cells in the anteroventral cochlear nucleus (AVCN) send axons to the contralateral medial nucleus of the trapezoid body (MNTB), where they synapse via these calyces on MNTB principal cells. These principal cells then project to the ipsilateral lateral superior olive (LSO), where they inhibit postsynaptic neurons and provide a basis for interaural level detection (ILD), required for high frequency sound localization. This synapse has been described as the largest in the brain.
Calcium concentration microdomains (CCMs) are sites in a cell's cytoplasm with a localised high calcium ion (Ca2+) concentration. They are found immediately around the intracellular opening of calcium channels; when a calcium channel opens, the Ca2+ concentration in the adjacent CCM increases up to several hundred micromolar (μM). These microdomains take part in calcium signaling, which has a diverse range of potential outcomes.

Axon terminals are distal terminations of the branches of an axon. An axon, also called a nerve fiber, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell that conducts electrical impulses called action potentials away from the neuron's cell body to transmit those impulses to other neurons, muscle cells, or glands. Most presynaptic terminals in the central nervous system are formed along the axons, not at their ends.
Cellular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience concerned with the study of neurons at a cellular level. This includes morphology and physiological properties of single neurons. Several techniques such as intracellular recording, patch-clamp, and voltage-clamp technique, pharmacology, confocal imaging, molecular biology, two photon laser scanning microscopy and Ca2+ imaging have been used to study activity at the cellular level. Cellular neuroscience examines the various types of neurons, the functions of different neurons, the influence of neurons upon each other, and how neurons work together.
The ribbon synapse is a type of neuronal synapse characterized by the presence of an electron-dense structure, the synaptic ribbon, that holds vesicles close to the active zone. It is characterized by a tight vesicle-calcium channel coupling that promotes rapid neurotransmitter release and sustained signal transmission. Ribbon synapses undergo a cycle of exocytosis and endocytosis in response to graded changes of membrane potential. It has been proposed that most ribbon synapses undergo a special type of exocytosis based on coordinated multivesicular release. This interpretation has recently been questioned at the inner hair cell ribbon synapse, where it has been instead proposed that exocytosis is described by uniquantal release shaped by a flickering vesicle fusion pore.
Vesicle fusion is the merging of a vesicle with other vesicles or a part of a cell membrane. In the latter case, it is the end stage of secretion from secretory vesicles, where their contents are expelled from the cell through exocytosis. Vesicles can also fuse with other target cell compartments, such as a lysosome. Exocytosis occurs when secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse at the base of cup-shaped structures at the cell plasma membrane called porosome, the universal secretory machinery in cells. Vesicle fusion may depend on SNARE proteins in the presence of increased intracellular calcium (Ca2+) concentration.

The active zone or synaptic active zone is a term first used by Couteaux and Pecot-Dechavassinein in 1970 to define the site of neurotransmitter release. Two neurons make near contact through structures called synapses allowing them to communicate with each other. As shown in the adjacent diagram, a synapse consists of the presynaptic bouton of one neuron which stores vesicles containing neurotransmitter, and a second, postsynaptic neuron which bears receptors for the neurotransmitter, together with a gap between the two called the synaptic cleft. When an action potential reaches the presynaptic bouton, the contents of the vesicles are released into the synaptic cleft and the released neurotransmitter travels across the cleft to the postsynaptic neuron and activates the receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.

Homosynaptic plasticity is one type of synaptic plasticity. Homosynaptic plasticity is input-specific, meaning changes in synapse strength occur only at post-synaptic targets specifically stimulated by a pre-synaptic target. Therefore, the spread of the signal from the pre-synaptic cell is localized.
Neurotransmitters are released into a synapse in packaged vesicles called quanta. One quantum generates a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) which is the smallest amount of stimulation that one neuron can send to another neuron. Quantal release is the mechanism by which most traditional endogenous neurotransmitters are transmitted throughout the body. The aggregate sum of many MEPPs is an end plate potential (EPP). A normal end plate potential usually causes the postsynaptic neuron to reach its threshold of excitation and elicit an action potential. Electrical synapses do not use quantal neurotransmitter release and instead use gap junctions between neurons to send current flows between neurons. The goal of any synapse is to produce either an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) or an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP), which generate or repress the expression, respectively, of an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron. It is estimated that an action potential will trigger the release of approximately 20% of an axon terminal's neurotransmitter load.
The ion channel hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD), also known as the channel hypothesis or the amyloid beta ion channel hypothesis, is a more recent variant of the amyloid hypothesis of AD, which identifies amyloid beta (Aβ) as the underlying cause of neurotoxicity seen in AD. While the traditional formulation of the amyloid hypothesis pinpoints insoluble, fibrillar aggregates of Aβ as the basis of disruption of calcium ion homeostasis and subsequent apoptosis in AD, the ion channel hypothesis in 1993 introduced the possibility of an ion-channel-forming oligomer of soluble, non-fibrillar Aβ as the cytotoxic species allowing unregulated calcium influx into neurons in AD.
References
- ↑ Wang, Lu-Yang; Augustine, George J. (26 January 2015). "Presynaptic nanodomains: a tale of two synapses". Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 8: 455. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00455 . PMC 4306312 . PMID 25674049.
- 1 2 Eggermann, Emmanuel; Bucurenciu, Iancu; Goswami, Sarit Pati; Jonas, Peter (20 December 2011). "Nanodomain coupling between Ca2+ channels and sensors of exocytosis at fast mammalian synapses". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 13 (1): 7–21. doi:10.1038/nrn3125. PMC 3617475 . PMID 22183436.
- 1 2 Stanley, Elise F. (March 2016). "The nanophysiology of fast transmitter release". Trends in Neurosciences. 39 (3): 183–197. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2016.01.005 . PMID 26896416.

- ↑ Filadi, Riccardo; Basso, Emy; Lefkimmiatis, Konstantinos; Pozzan, Tullio (2017). "Beyond Intracellular Signaling: The Ins and Outs of Second Messengers Microdomains". Membrane Dynamics and Calcium Signaling. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 981. pp. 279–322. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-55858-5_12. ISBN 9783319558585. PMID 29594866.
- 1 2 Oheim, Martin; Kirchhoff, Frank; Stühmer, Walter (2006). "Calcium microdomains in regulated exocytosis". Cell Calcium . 40 (5–6): 423–39. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2006.08.007. PMID 17067670.