
Ghana is a West African country in Africa, along the Gulf of Guinea, just a few degrees north of the equator.

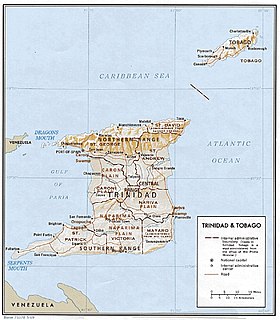
Trinidad and Tobago is an archipelagic republic in the southern Caribbean between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of Venezuela. They are southeasterly islands of the Lesser Antilles, Monos, Huevos, Gaspar Grande, Little Tobago, and St. Giles Island. Trinidad is 11 km (6.8 mi) off the northeast coast of Venezuela and 130 km (81 mi) south of the Grenadines. The island measures 4,768 km2 (1,841 sq mi) in area with an average length of 80 km (50 mi) and an average width of 59 km (37 mi). The island appears rectangular in shape with three projecting peninsular corners. Tobago is 30 km (19 mi) northeast of Trinidad and measures about 298 km2 (115 sq mi) in area, or 5.8% of the country's area, 41 km (25.5 mi) in length and 12 km (7.5 mi) at its greatest width. The island is cigar-shaped in appearance, with a northeast–southwest alignment.

The geography of Ukraine varies greatly from one region of the country to another, with the majority of the country lying within the East European Plain. Ukraine is the second-largest European country, after Russia. Its various regions have diverse geographic features ranging from highlands to lowlands, as well as climatic range and a wide variety in hydrography.

Venezuela is a country in South America, bordering the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, between Colombia and Guyana. It is situated on major sea and air routes linking North and South America. Located at the northernmost end of South America, Venezuela has a total area of 912,050 km2 (352,140 sq mi) and a land area of 882,050 km2 (340,560 sq mi). It is the 32nd largest country and is slightly smaller than Egypt, or half the size of Mexico. Shaped roughly like an inverted triangle, the country has a 2,800 km (1,700 mi) long coastline. It is bound on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the east by Guyana, on the south by Brazil, and on the west by Colombia. It has the 55th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 471,507 km2 (182,050 sq mi). Its maritime territory borders Trinidad and Tobago, Dominica, the Dominican Republic, Grenada, St. Kitts and Nevis, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, France, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and the United States. Venezuela also claims the region of Guayana Esequiba, currently under the control of Guyana.
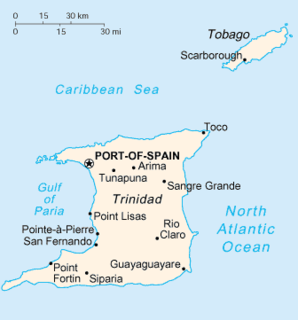
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies 11 km (6.8 mi) off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmost island in the West Indies. With an area of 4,768 km2 (1,841 sq mi), it is also the fifth largest in the West Indies.

San Fernando, officially the City of San Fernando, is the most populous city and second most populous municipality in Trinidad and Tobago, after Chaguanas. Sando, as it is also known, occupies 19 km² and is located in the southwestern part of the island of Trinidad. It is bounded to the north by the Guaracara River, the south by the Oropouche River, the east by the Sir Solomon Hochoy Highway, and the west by the Gulf of Paria. The former borough was elevated to the status of a city corporation on 18 November 1988. The motto of San Fernando is: "Sanitas Fortis" - In a Healthy Environment We Will Find Strength. Many local Trinidadians refer to the city with the shortened name "Sando." San Fernando is called Trinidad and Tobago's "industrial capital" because of its proximity to the Pointe-à-Pierre oil refinery and many other petrochemical, LNG, iron and steel and aluminium smelters in places such as Point Lisas in Couva, Point Fortin, and La Brea.
The Northern Range is the range of tall hills across north Trinidad, the major island in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. The hills range from the Chaguaramas peninsula on the west coast to Toco in the east. The Northern Range covers approximately twenty-five percent of the land area of Trinidad.

Caroni County was a historic county of Trinidad and Tobago. It occupies 557 km2 (215 sq mi) in the west central part of the island of Trinidad, the larger island in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It lies south and southwest of Saint George County, west of Nariva County and north of Victoria County. To the west it is bounded by the Gulf of Paria. County Caroni includes the towns of Chaguanas, the largest town in the country and Couva, the capital of the Couva–Tabaquite–Talparo region. Administratively it is divided between the Borough of Chaguanas, the Region of Couva–Tabaquite–Talparo and the Region of Tunapuna–Piarco. The county was divided into four Wards: Chaguanas, Couva, Cunupia and Montserrat. The major towns of County Caroni are Chaguanas and Couva. The port and industrial zone of Point Lisas is located in Caroni, and the region is also a site for agriculture.

The Caroni River is the largest river in Trinidad and Tobago, running for 40 km (25 mi) from its origins in the Northern Range on the island of Trinidad, through the northern lowlands of the Caroni Plains and enters the Gulf of Paria at the Caroni Swamp.

The Dissected Till Plains are physiographic sections of the Central Lowlands province, which in turn is part of the Interior Plains physiographic division of the United States, located in southern and western Iowa, northeastern Kansas, the southwestern corner of Minnesota, northern Missouri, eastern Nebraska, and southeastern South Dakota.

Oropouche fever is a tropical viral infection transmitted by biting midges and mosquitoes from the blood of sloths to humans. This disease is named after the region where it was first discovered and isolated at the Trinidad Regional Virus Laboratory in 1955 by the Oropouche River in Trinidad and Tobago. Oropouche fever is caused by a specific arbovirus, the Oropouche virus (OROV), of the Bunyaviridae family.

General elections were held in Trinidad and Tobago on 5 November 2007. Nomination day was 15 October. Five parties contested the elections; the ruling People's National Movement, the official opposition United National Congress–Alliance, the Congress of the People, the Tobago United Front–Democratic Action Congress and the Democratic National Assembly. Five independent candidates also ran.
The Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Lowlands, or simply St. Lawrence Lowlands, is a physiographic region of Eastern Canada that comprises a section of southern Ontario bounded on the north by the Canadian Shield and by three of the Great Lakes — Lake Huron, Lake Erie and Lake Ontario — and extends along the St. Lawrence River to the Strait of Belle Isle and the Atlantic Ocean. The lowlands comprise three sub-regions that were created by intrusions from adjacent physiographic regions — the West Lowland, Central Lowland and East Lowland. The West Lowland includes the Niagara Escarpment, extending from the Niagara River to the Bruce Peninsula and Manitoulin Island. The Central Lowland stretches between the Ottawa River and the St. Lawrence River. The East Lowland includes Anticosti Island, Îles de Mingan, and extends to the Strait of Belle Isle.
The Trinchera Cave Archeological District (5LA9555) is an archaeological site in Las Animas County, Colorado with artifacts primarily dating from 1000 BC to AD 1749, although there were some Archaic period artifacts found. The site was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2001 and is located on State Trust Lands.

On the island of Trinidad, the Nariva Plain is a lowland area on the east between the Central Range and the Southern Range; the lowland area on the west is the Naparima Plain. To the north of the Central Range is the Caroni Plain. The lowland areas are either flat or consist of gently rolling hills. The eastern half of the island not as thickly settled as the western. The 35-mile long Ortoire river flows eastward through the Nariva Plain and drains in the Nariva Swamp on the Atlantic Ocean coast.

On the island of Trinidad in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, the Caroni Plain is a lowland area between the Northern Range and the Central Range. The lowland areas to the south of the Central Range are the Naparima Plain on the west and the Nariva Plain on the east. The lowland areas are either flat or consist of gently rolling hills. The 25-mile long Caroni river flows westward through the Caroni Plain and drains into the Caroni Swamp on the Gulf of Paria coast. The Caroni Plain was a major region of sugar and cocoa production in the 18th and 19th centuries and the first half of the 20th century.

On the island of Trinidad, the Southern Range is a discontinuous chain of low hills along the southern coast, reaching their highest altitude in the 1,000 feet (300 m) high Trinity Hills of the southeast. According to legend, the sight of the three neighboring hilltops of the then unnamed Trinity Hills, led to Christopher Columbus, on his third voyage to the New World, to name the island, "Trinidad." The broad lowland area on the west between the Southern Range and the Central Range is the Naparima Plain; the lowland area on the east is the Nariva Plain. The Oropuche river flows through the Naparima Plain and drains into the Oropuche Lagoon, a swampy area, on the Gulf of Paria coast, whereas the 31-mile long Ortoire River flows through the Nariva Plain and drains into the Nariva Swamp on the Atlantic Ocean coast. The Southern region of the island has sandy and less fertile soil. The Southern Range, particularly its Western and Central parts, consists of unconsolidated segments.

The Great Russian Regions are eight geomorphological areas in the Russian Federation displaying characteristic forms of relief. Seven of them are east of the Urals.













