
Pembroke Castle is a medieval castle in the centre of Pembroke, Pembrokeshire in Wales. The castle was the original family seat of the Earldom of Pembroke. A Grade I listed building since 1951, it underwent major restoration during the early 20th century.
The Welsh Marches is an imprecisely defined area along the border between England and Wales in the United Kingdom. The precise meaning of the term has varied at different periods.

Ludlow Castle is a ruined medieval fortification in the town of the same name in the English county of Shropshire, standing on a promontory overlooking the River Teme. The castle was probably founded by Walter de Lacy after the Norman Conquest and was one of the first stone castles to be built in England. During the civil war of the 12th century the castle changed hands several times between the de Lacys and rival claimants, and was further fortified with a Great Tower and a large outer bailey. In the mid-13th century, Ludlow was passed on to Geoffrey de Geneville, who rebuilt part of the inner bailey, and the castle played a part in the Second Barons' War. Roger Mortimer acquired the castle in 1301, further extending the internal complex of buildings. Richard, Duke of York, inherited the castle in 1425, and it became an important symbol of Yorkist authority during the Wars of the Roses. When Richard's son, Edward IV, seized the throne in 1461 it passed into the ownership of the Crown. Ludlow Castle was chosen as the seat of the Council of Wales and the Marches, effectively acting as the capital of Wales, and it was extensively renovated throughout the 16th century. By the 17th century the castle was luxuriously appointed, hosting cultural events such as the first performance of John Milton's masque Comus. Ludlow Castle was held by the Royalists during the English Civil War of the 1640s, until it was besieged and taken by a Parliamentarian army in 1646. The contents of the castle were sold off and a garrison was retained there for much of the interregnum.

Nevern is both a parish and a community in Pembrokeshire, Wales. The community includes the settlements of Felindre Farchog, Monington, Moylgrove and Bayvil. The small village lies in the Nevern valley near the Preseli Hills of the Pembrokeshire Coast National Park 2 miles (3 km) east of Newport on the B4582 road.

Narberth is a town and community in Pembrokeshire, Wales. It was founded around a Welsh court and later became a Norman stronghold on the Landsker Line. It became the headquarters of the hundred of Narberth. It was once a marcher borough. George Owen described it in 1603 as one of nine Pembrokeshire "boroughs in decay".

Wigmore is a village and civil parish in the northwest part of the county of Herefordshire, England. It is located on the A4110 road, about 8 miles (13 km) west of the town of Ludlow, in the Welsh Marches. In earlier times, it was also an administrative district, called a hundred.

Haverfordwest Castle is a castle located in the town centre at Haverfordwest, Pembrokeshire, south Wales, in a naturally defensive position at the end of a strong, isolated ridge. The castle was established during Norman times in 1120 but much of the architecture remaining today dates from 1290. For centuries the castle was an English stronghold. There are several other notable castles in area: Wiston Castle lies 6 miles (10 km) to the northeast and Pembroke Castle lies 12 miles (19 km) to the south.
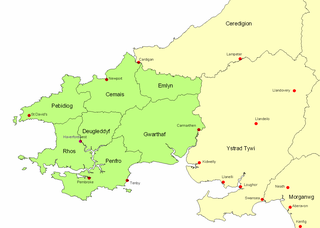
The Kingdom of Dyfed, one of several Welsh petty kingdoms that emerged in 5th-century sub-Roman Britain in southwest Wales, was based on the former territory of the Demetae. The medieval Irish narrative The Expulsion of the Déisi attributes the kingdom's founding to Eochaid, son of Artchorp, who was forced across the Irish sea in the 5th century; his descendants founded the line of the kings of Dyfed down to "Tualodor mac Rígin". The Normans invaded Wales, and by 1138 incorporated Dyfed into a new shire called Pembrokeshire after the Norman castle built in the Cantref of Penfro and under the rule of the Marcher Earl of Pembroke.

Templeton is a village and community in Pembrokeshire, Wales. The population of the community was 943 in 2011. The built-up area had a population of 627.

Carew is a village, parish and community on an inlet of Milford Haven in the former Hundred of Narberth, Pembrokeshire, West Wales, 4 miles (6.4 km) east of Pembroke. The eastern part of the parish is in the Pembrokeshire Coast National Park.

Llawhaden is a village, parish and community in mid-Pembrokeshire, West Wales, historically in the Hundred of Dungleddy. The community of Llawhaden includes the parish of Robeston Wathen, part of Narberth and the hamlet of Gelli, and had a population of 634 in 2001, increasing to 688 at the 2011 Census.

The Hundred of Roose was a hundred in Pembrokeshire, Wales. It has its origins in the pre-Norman cantref of Rhos and was formalised as a hundred by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542. Its area was about 102 square miles (260 km2). The area became an English "plantation" in the 12th century, part of the English-speaking Little England beyond Wales.

Llanstadwell is a small village, parish and community in south Pembrokeshire, Wales.

The Hundred of Narberth was a hundred in Pembrokeshire, Wales. An administrative and legal division, it was formed by the Act of Union of 1536 from parts of the pre-Norman cantrefs of Penfro and Cantref Gwarthaf.
Maenclochog is a village, parish and community in Pembrokeshire, south-west Wales. It is also the name of an electoral ward comprising a wider area of four surrounding communities. Maenclochog Community includes the small settlement of Llanycefn and the village of Rosebush.

The Cantref of Penfro was one of the seven cantrefi of the Kingdom of Dyfed. It subsequently became part of Deheubarth in around 950. It consisted of the long peninsular part of Dyfed south of the Eastern Cleddau and the Daugleddau estuary, and bordered on its landward side by Cantref Gwarthaf. The name, meaning "land's end", derives from Pen and "fro". Its area was approximately 140 square miles (360 km2).

Carmarthen Castle is a ruined castle in Carmarthen, West Wales, UK. First built by Walter, Sheriff of Gloucester in the early 1100s, the castle was captured and destroyed on several occasions before being rebuilt in stone during the 1190s. The castle was captured by Owain Glyndŵr in 1405. Henry VII's father died at Carmarthen Castle in 1456. During the Wars of the Roses the castle fell to William Herbert and, during the Civil War, was captured by Parliamentary forces. It was dismantled by order of Oliver Cromwell in the mid 1600s.

Tenby Castle was a fortification standing on a headland separated by an isthmus from the town of Tenby, Pembrokeshire, Wales. The remaining stone structure dates from the 13th century but there are mentions of the castle from as early as 1153. It is a Grade II* listed building.

Newport Castle is a castle located in Newport, Pembrokeshire, Wales. The earliest castle on the site was built in the 13th century, and the present structure was built in the 19th century and is a private residence.

Pembroke's town walls are a Grade II*-listed medieval defensive structure around the town of Pembroke, Pembrokeshire, Wales. They were probably built beginning in the late 13th century by the Earls of Pembroke, although it is uncertain when they were finished. Most of the walls have not survived, but there are visible sections and two bastions exist, one with a restored late 18th-century gazebo atop it.



















