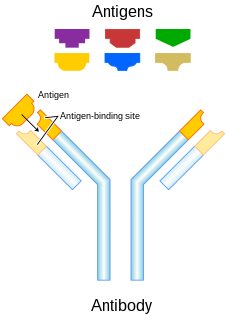
A monoclonal antibody is an antibody made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.

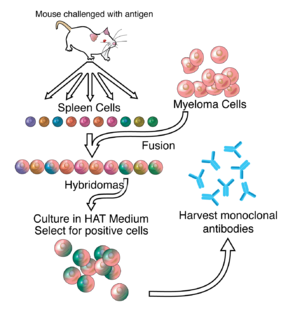
Hybridoma technology is a method for producing large numbers of identical antibodies. This process starts by injecting a mouse with an antigen that provokes an immune response. A type of white blood cell, the B cell, produces antibodies that bind to the injected antigen. These antibody producing B-cells are then harvested from the mouse and, in turn, fused with immortal B cell cancer cells, a myeloma, to produce a hybrid cell line called a hybridoma, which has both the antibody-producing ability of the B-cell and the longevity and reproductivity of the myeloma. The hybridomas can be grown in culture, each culture starting with one viable hybridoma cell, producing cultures each of which consists of genetically identical hybridomas which produce one antibody per culture (monoclonal) rather than mixtures of different antibodies (polyclonal). The myeloma cell line that is used in this process is selected for its ability to grow in tissue culture and for an absence of antibody synthesis. In contrast to polyclonal antibodies, which are mixtures of many different antibody molecules, the monoclonal antibodies produced by each hybridoma line are all chemically identical.

Targeted therapy or molecularly targeted therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment (pharmacotherapy) for cancer, others being hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medicine, targeted therapy blocks the growth of cancer cells by interfering with specific targeted molecules needed for carcinogenesis and tumor growth, rather than by simply interfering with all rapidly dividing cells. Because most agents for targeted therapy are biopharmaceuticals, the term biologic therapy is sometimes synonymous with targeted therapy when used in the context of cancer therapy. However, the modalities can be combined; antibody-drug conjugates combine biologic and cytotoxic mechanisms into one targeted therapy.
Monoclonal antibody therapy is a form of immunotherapy that uses monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to bind monospecifically to certain cells or proteins. The objective is that this treatment will stimulate the patient's immune system to attack those cells. Alternatively, in radioimmunotherapy a radioactive dose localizes a target cell line, delivering lethal chemical doses. Antibodies have been used to bind to molecules involved in T-cell regulation to remove inhibitory pathways that block T-cell responses. This is known as immune checkpoint therapy.

Pertuzumab, sold under the brand name Perjeta, is a monoclonal antibody used in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel for the treatment of metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer; it also used in the same combination as a neoadjuvant in early HER2-positive breast cancer.
Bavituximab (PGN401) is a human-mouse chimeric monoclonal antibody against phosphatidylserine, which is a component of cell membranes that is exposed when a cell is transformed into solid tumor cancer cell or dies, and when cells are infected with hepatitis C. The process of cell death is highly controlled and so there usually no immune response to phosphatidylserine but when bavituximab binds to it, the conjugate appears to stimulate an immune response in humans.
Ocrelizumab, sold under the brand name Ocrevus, is a pharmaceutical drug for the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS). It is a humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. It targets CD20 marker on B lymphocytes and hence is an immunosuppressive drug. Ocrelizumab binds to an epitope that overlaps with the epitope to which rituximab binds.
Visilizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody. It is being investigated for use as an immunosuppressive drug in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Visilizumab binds to the CD3 receptor on certain activated T cells without affecting resting T cells. It is currently under clinical studies for the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.

Josep Baselga i Torres, known in Spanish as José Baselga was a Spanish medical oncologist and researcher focused on the development of novel molecular targeted agents, with a special emphasis in breast cancer. Through his career he was associated with the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, Vall d'Hebron Institute of Oncology, and the Massachusetts General Hospital in their hematology and oncology divisions. He led the development of the breast cancer treatment Herceptin, a monoclonal antibody, that targets the HER2 protein which is impacted in aggressive breast cancers.
Genmab A/S is a Danish biotechnology company, founded in February 1999 by Florian Schönharting, at the time managing director of BankInvest Biomedical venture fund. The company is based in Copenhagen, Denmark - internationally, it operates through the subsidiaries Genmab B.V. in Utrecht, The Netherlands, Genmab U.S., Inc. in Princeton, USA, and Genmab K.K. in Tokyo, Japan. It's a dual listed company with shares traded on the Copenhagen Stock Exchange in Denmark, and on NASDAQ Global Select Market in the US.
Leronlimab is a humanized monoclonal antibody targeted against the CCR5 receptor found on T lymphocytes of the human immune system. It is being investigated as a potential therapy in the treatment of COVID-19, triple negative breast cancer, and HIV infection. The United States Food and Drug Administration has designated PRO 140 for fast-track approval. In February 2008, the drug entered Phase 2 clinical trials and a phase 3 trial was begun in 2015. In February 2018, Cytodyn Inc reported that the primary endpoint had been achieved in the PRO 140 pivotal combination therapy trial in HIV infection. In 2020 CytoDyn submitted a fast-track biologics license application for treatment of CCR5-tropic HIV-1 Infection.

The Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. is a drug manufacturer operating in Japan. It is a subsidiary controlled by Hoffmann-La Roche, which owns 62% of the company as of 30 June 2014. The company is headquartered in Tokyo. Osamu Nagayama is the current representative director and chairman. Tatsuro Kosaka is the current representative director, president and CEO.

Lloyd John Old was one of the founders and standard-bearers of the field of cancer immunology. When Old began his career in 1958, tumor immunology was in its infancy. Today, cancer immunotherapies are emerging as a significant advance in cancer therapy.

Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd. is a Japanese pharmaceutical and biotechnology company under the Kirin Holdings, and is among the 40 largest in the world by revenue. The company is headquartered in Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo and is a member of the Nikkei 225 stock index.

Gediminas Ziemelis is a Lithuanian businessman, entrepreneur and business consultant, selected twice among the top 40 most talented young industry leaders by Aviation Week & Space Technology. He is currently the Chairman of the Board at Avia Solutions Group and former Chairman of the Board at Vertas Management AB.
Daratumumab, sold under the brand name Darzalex, is an anti-cancer monoclonal antibody medication. It binds to CD38, which is overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells. Daratumumab was originally developed by Genmab, but it is now being jointly developed by Genmab along with the Johnson & Johnson subsidiary Janssen Biotech, which acquired worldwide commercialization rights to the drug from Genmab.
Onyx Pharmaceuticals Inc. has been a biopharmaceutical company headquartered in South San Francisco, California. The company developed and marketed medicines for the treatment of cancer. Onyx was founded in 1992 by Kevin J. Kinsella and Frank McCormick Ph.D., FRS. McCormick served as the chief scientific officer until 1998, while Kinsella was the firm's chairman. In 2009, the company acquired Proteolix, Inc., a private biotechnology company, for $276 million in cash plus additional milestone payments. In January 2012, the company was named "the top biotechnology takeover target in 2012" through an industry survey. Onyx president and chief executive officer (CEO) Tony Coles had said that Onyx liked its prospects as an independent company and was focused on bringing new therapies to patients. However, at the end of August 2013, Amgen announced it was acquiring Onyx in an agreed $10.4 billion deal.
AryoGen Pharmed is an Iranian biopharmaceutical company specializing in manufacturing Therapeutic Monoclonal antibodies and some other recombinant proteins.
Celltrion is a biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Incheon, South Korea. Celltrion Healthcare conducts worldwide marketing, sales, and distribution of biological medicines developed by Celltrion. Celltrion's founder, Jung Jin Seo, is the richest person in South Korea.
Bebtelovimab is a monoclonal antibody developed by AbCellera and Eli Lilly as a treatment for COVID-19.










