
A member of the Senedd is a representative elected to the Senedd. There are sixty members, with forty members chosen to represent individual Senedd constituencies, and twenty to represent the five electoral regions of the Senedd in Wales.

The Senedd, officially known as the Welsh Parliament in English and Senedd Cymru in Welsh, is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Wales. A democratically elected body, it makes laws for Wales, agrees to certain taxes, and scrutinises the Welsh Government. It is a bilingual institution, with both Welsh and English being the official languages of its business. From its creation in May 1999 until May 2020, the Senedd was officially known as the National Assembly for Wales and was often simply called the Welsh Assembly.

A legislative consent motion is a motion passed by either the Scottish Parliament, Senedd, or Northern Ireland Assembly, in which it consents that the Parliament of the United Kingdom may pass legislation on a devolved issue over which the devolved government has regular legislative authority.
The Democracy and Boundary Commission Cymru is a Welsh Government sponsored body, responsible for defining local government boundaries and Senedd constituency boundaries in Wales, also known as Cymru.

Politics in Wales forms a distinctive polity in the wider politics of the United Kingdom, with Wales as one of the four constituent countries of the United Kingdom (UK).
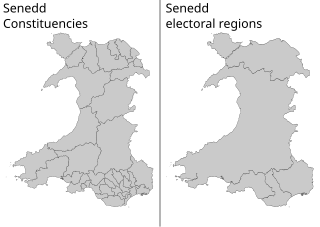
The Senedd constituencies and electoral regions are the electoral districts used to elect members of the Senedd to the Senedd, and have been used in some form since the first election of the then National Assembly for Wales in 1999. New boundaries were introduced for the 2007 elections and currently consist of forty constituencies and five regions. The five electoral regions are: Mid and West Wales, North Wales, South Wales Central, South Wales East, and South Wales West, with the forty constituencies listed below. Voting last took place in all districts in the 2021 Senedd election, and is not used for local government.
There are four types of elections in Wales: elections to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, elections to the devolved Senedd, local elections to community councils and the 22 principal areas, and the police and crime commissioner elections. In addition there are by-elections for each aforementioned election. Elections are held on Election Day, which is conventionally a Thursday. Three of these four types of elections are held after fixed periods; the exception is UK general elections, the timing of which is at the discretion of the prime minister of the United Kingdom. Senedd elections may be postponed to avoid elections to the UK parliament and Senedd coinciding with each other.

Welsh law is an autonomous part of the English law system composed of legislation made by the Senedd. Wales is part of the legal jurisdiction of England and Wales, one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. However, due to devolution, the law in Wales is increasingly distinct from the law in England, since the Senedd, the devolved parliament of Wales, can legislate on non-reserved matters.

A Measure of the National Assembly for Wales is primary legislation in Wales that is a category lower than an Act of Parliament. In the case of contemporary Welsh law, the difference with acts is that the competence to pass Measures was subject to 'LCOs' or Legislative Competence Order, which transferred powers to the Assembly by amending Schedule 5 of the Government of Wales Act 2006.

An Act of Senedd Cymru, or informally an Act of the Senedd, is primary legislation that can be made by the Senedd under part 4 of the Government of Wales Act 2006. Prior to 6 May 2020 any legislation was formally known as an Act of the National Assembly for Wales or informally, an Act of the Assembly.

The Wales Act 2017 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It sets out amendments to the Government of Wales Act 2006 and devolves further powers to Wales. The legislation is based on the proposals of the St David's Day Command Paper.

The Welsh Tax Acts etc. Act 2022 is an Act of Senedd Cymru which allows Welsh ministers to amend tax law using regulatory powers. The Tax Acts in question are the Tax Collection and Management (Wales) Act 2016, the Land Transaction Tax and Anti-avoidance of Devolved Taxes (Wales) Act 2017, and the Landfill Disposals Tax (Wales) Act 2017.
A Welsh statutory instrument is subordinate legislation made by the Welsh Ministers, as well as subordinate legislation made by public bodies using powers provided to be exercisable by Welsh statutory instrument. WSIs are the main form of subordinate legislation in Wales, being used by default to exercise powers delegated to the Welsh Ministers, the Counsel General, and the King-in-Council.







