Related Research Articles

Syndicalism is a revolutionary current within the labor movement that seeks to unionize workers according to industry and advance their demands through strikes with the eventual goal of gaining control over the means of production and the economy at large. Developed in French labor unions during the late 19th century, syndicalist movements were most predominant amongst the socialist movement during the interwar period which preceded the outbreak of World War II.
Industrial unionism is a trade union organising method through which all workers in the same industry are organized into the same union, regardless of skill or trade, thus giving workers in one industry, or in all industries, more leverage in bargaining and in strike situations.

The One Big Union was an idea in the late 19th and early 20th centuries amongst trade unionists to unite the interests of workers and offer solutions to all labour problems.

Sidney Hillman was an American labor leader. He was the head of the Amalgamated Clothing Workers of America and was a key figure in the founding of the Congress of Industrial Organizations and in marshaling labor's support for President Franklin D. Roosevelt and the New Deal coalition of the Democratic Party.
Labor aristocracy or labour aristocracy has at least four meanings: (1) as a term with Marxist theoretical underpinnings; (2) as a specific type of trade unionism; (3) as a shorthand description by revolutionary industrial unions for the bureaucracy of craft-based business unionism; and (4) in the 19th and early 20th centuries was also a phrase used to define better-off members of the working class.

The Trade Union Educational League (TUEL) was established by William Z. Foster in 1920 as a means of uniting radicals within various trade unions for a common plan of action. The group was subsidized by the Communist International via the Workers (Communist) Party of America from 1922. The organization did not collect membership dues but instead ostensibly sought to both fund itself and to spread its ideas through the sale of pamphlets and circulation of a monthly magazine.

The Joint Legislative Committee to Investigate Seditious Activities, popularly known as the Lusk Committee, was formed in 1919 by the New York State Legislature to investigate individuals and organizations in New York State suspected of sedition.

Ludwig "Louis" Paul Lochner was an American political activist, journalist, and author. During World War I, Lochner was a leading figure in the American and the international anti-war movement. Later, he served for many years as head of the Berlin bureau of Associated Press and was best remembered for his work there as a foreign correspondent. Lochner was awarded the 1939 Pulitzer Prize for correspondence for his wartime reporting from Nazi Germany. In December 1941, Lochner was interned by the Nazis but was later released in a prisoner exchange.

The Workers' International Industrial Union (WIIU) was a Revolutionary Industrial Union headquartered in Detroit in 1908 by radical trade unionists closely associated with the Socialist Labor Party of America, headed by Daniel DeLeon. The organization was formed when it broke with the main faction of the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) over the question of political action.
Labor federation competition in the United States is a history of the labor movement, considering U.S. labor organizations and federations that have been regional, national, or international in scope, and that have united organizations of disparate groups of workers. Union philosophy and ideology changed from one period to another, conflicting at times. Government actions have controlled, or legislated against particular industrial actions or labor entities, resulting in the diminishing of one labor federation entity or the advance of another.
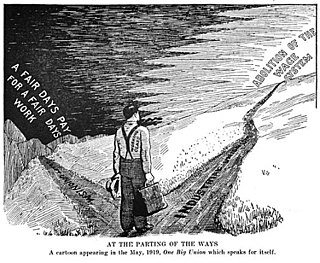
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) is a union of wage workers which was formed in Chicago in 1905 by militant unionists and their supporters due to anger over the conservatism, philosophy, and craft-based structure of the American Federation of Labor (AFL). Throughout the early part of the 20th century, the philosophy and tactics of the IWW were frequently in direct conflict with those of the AFL concerning the best ways to organize workers, and how to best improve the society in which they toiled. The AFL had one guiding principle—"pure and simple trade unionism", often summarized with the slogan "a fair day's pay for a fair day's work." The IWW embraced two guiding principles, fighting like the AFL for better wages, hours, and conditions, but also promoting an eventual, permanent solution to the problems of strikes, injunctions, bull pens, and union scabbing.

The Russian Soviet Government Bureau (1919-1921), sometimes known as the "Soviet Bureau," was an unofficial diplomatic organization established by the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic in the United States during the Russian Civil War. The Soviet Bureau primarily functioned as a trade and information agency of the Soviet government. Suspected of engaging in political subversion, the Soviet Bureau was raided by law enforcement authorities at the behest of the Lusk Committee of the New York State legislature in 1919. The Bureau was terminated early in 1921.
The Left Wing Manifesto is the name bestowed upon two distinct programmatic documents of the Left Wing Section of the Socialist Party during the factional war in the Socialist Party of America of 1919.

The Union of Russian Workers in the United States and Canada, commonly known as the "Union of Russian Workers" was an anarchist political association of Russian emigrants in the United States. The group was established shortly after the failure of the Russian Revolution of 1905 and was essentially annihilated in America by the 1919 Red Scare in which it was targeted by the Bureau of Investigation of the U.S. Department of Justice. Thousands of the group's adherents were arrested and hundreds deported in 1919 and 1920; still more voluntarily returned to Soviet Russia. During its brief existence the organization, which was only loosely affiliated with the Industrial Workers of the World, published numerous books and pamphlets in Russian by anarchist writers, operated reading rooms and conducted courses to teach newly arrived Russians English, and fulfilled a social function for emigrants half a world from home.
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) is a union of wage workers which was formed in Chicago in 1905. The IWW experienced a number of divisions and splits during its early history.

The Russian Socialist Federation was a semi-autonomous American political organization which was part of the Socialist Party of America from 1915 until the split of the national organization into rival socialist and communist organizations in the summer of 1919. Elements of the Russian Socialist Federation became key components of both the Communist Party of America and the rival Communist Labor Party of America as "Russian Federations" within these organizations. Following the unification of these two groups in 1921, the resulting unified Russian Communist Federation gradually evolved into the so-called Russian Bureau of the Communist Party, USA.

The People's Freedom Union was a left wing American political group which existed from 1919 to 1920. Established as a federation of liberal and radical organizations in New York City, the People's Freedom Union conducted marches in support of political prisoners detained under the Espionage Act during World War I, campaigned for a restoration of American civil rights suspended under the war, and agitated against American intervention in Mexico and Soviet Russia.
The People's Council of America for Democracy and the Terms of Peace, commonly known as the "People's Council," was an American pacifist political organization established in New York City in May 1917. Organized in opposition to the decision of the Woodrow Wilson administration's decision to enter World War I, the People's Council attempted to mobilize American workers and intellectuals against the war effort through publication of literature and the conduct of mass meetings and public demonstrations. The organization's dissident views made it a target of federal, state, and local authorities, who disrupted its meetings and arrested a number of its leading participants under provisions of the Espionage Act. The People's Council was succeeded in 1919 by a new group based in the same New York City headquarters, the People's Freedom Union.

The Revolutionary Age was an American radical newspaper edited by Louis C. Fraina and published from November 1918 until August 1919. Originally the publication of Local Boston, Socialist Party, the paper evolved into the de facto national organ of the Left Wing Section of the Socialist Party which battled for control of the Socialist Party throughout the spring and summer of 1919. With the establishment of the Left Wing National Council in June 1919, the paper was moved from Boston to New York City gained status as the official voice of the nascent American communist movement. The publication was terminated in August 1919, replaced by the official organ of the new Communist Party of America, a weekly newspaper known as The Communist.
Archibald E. Stevenson was an American attorney and legislative researcher. Stevenson is best remembered for his work as Assistant Counsel of the Lusk Committee of the New York State Senate from 1919 to 1920, the activities of which led to a series of sensational raids and trials of self-professed revolutionary socialists. Stevenson was also the de facto author and editor of the committee's four-volume report, which anticipated congressional investigations of communism conducted in subsequent years.
References
- ↑ Revolutionary radicalism: its history, purpose and tactics with an exposition and discussion of the steps being taken and required to curb it, being the report of the Joint Legislative Committee Investigating Seditious Activities, filed 24 April 1920, in the Senate of the State of New York
- 1 2 Your History online, accessed 17 August 2010
- ↑ Revolutionary radicalism: its history, purpose and tactics with an exposition and discussion of the steps being taken and required to curb it, being the report of the Joint Legislative Committee Investigating Seditious Activities, filed 24 April 1920, in the Senate of the State of New York
- ↑ Revolutionary radicalism: its history, purpose and tactics with an exposition and discussion of the steps being taken and required to curb it, being the report of the Joint Legislative Committee Investigating Seditious Activities, filed 24 April 1920, in the Senate of the State of New York
- ↑ Crisis, November 1951, p626