Related Research Articles

A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells.

The National Chemical Laboratory (NCL) is an Indian government laboratory based in Pune, in western India.

A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational and basic diagnostic methods used as a research tools in molecular biology.
The Budapest Treaty on the International Recognition of the Deposit of Microorganisms for the Purposes of Patent Procedure, or Budapest Treaty, is an international treaty signed in Budapest, Hungary, on April 28, 1977. It entered into force on August 19, 1980, and was later amended on September 26, 1980. The treaty is administered by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).

ATCC or the American Type Culture Collection is a nonprofit organization which collects, stores, and distributes standard reference microorganisms, cell lines and other materials for research and development. Established in 1925 to serve as a national center for depositing and distributing microbiological specimens, ATCC has since grown to distribute in over 150 countries. It is now the largest general culture collection in the world.

The microbial loop describes a trophic pathway where, in aquatic systems, dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is returned to higher trophic levels via its incorporation into bacterial biomass, and then coupled with the classic food chain formed by phytoplankton-zooplankton-nekton. In soil systems, the microbial loop refers to soil carbon. The term microbial loop was coined by Farooq Azam, Tom Fenchel et al. in 1983 to include the role played by bacteria in the carbon and nutrient cycles of the marine environment.
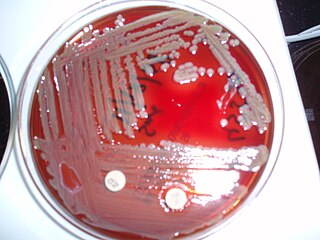
The class Flavobacteriia is composed of a single class of environmental bacteria. It contains the family Flavobacteriaceae, which is the largest family in the phylum Bacteroidota. This class is widely distributed in soil, fresh, and seawater habitats. The name is often spelt Flavobacteria, but was officially named Flavobacteriia in 2012.
Single-cell proteins (SCP) or microbial proteins refer to edible unicellular microorganisms. The biomass or protein extract from pure or mixed cultures of algae, yeasts, fungi or bacteria may be used as an ingredient or a substitute for protein-rich foods, and is suitable for human consumption or as animal feeds. Industrial agriculture is marked by a high water footprint, high land use, biodiversity destruction, general environmental degradation and contributes to climate change by emission of a third of all greenhouse gases; production of SCP does not necessarily exhibit any of these serious drawbacks. As of today, SCP is commonly grown on agricultural waste products, and as such inherits the ecological footprint and water footprint of industrial agriculture. However, SCP may also be produced entirely independent of agricultural waste products through autotrophic growth. Thanks to the high diversity of microbial metabolism, autotrophic SCP provides several different modes of growth, versatile options of nutrients recycling, and a substantially increased efficiency compared to crops. A 2021 publication showed that photovoltaic-driven microbial protein production could use 10 times less land for an equivalent amount of protein compared to soybean cultivation.


A microbial mat is a multi-layered sheet of microorganisms, mainly bacteria and archaea, or bacteria alone. Microbial mats grow at interfaces between different types of material, mostly on submerged or moist surfaces, but a few survive in deserts. A few are found as endosymbionts of animals.

The Leibniz Institute DSMZ - German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures GmbH, located in Braunschweig, is a research infrastructure in the Leibniz Association. Also the DSMZ is the world's most diverse collection of bioresources. These include microorganisms as well as more than 840 human and animal cell cultures, over 1. 500 plant viruses, over 940 bacteriophages, and 250 plasmids. Since 2010, the scientific director of the Leibniz Institute DSMZ has been Jörg Overmann, a microbiologist with a PhD. He holds a professorship in microbiology at the Technical University of Braunschweig. Since August 2018, he has led the institute in a dual leadership with Bettina Fischer as administrative director.

Microbiology is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being of unicellular (single-celled), multicellular, or acellular. Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, protistology, mycology, immunology, and parasitology.

The Belgian Co-ordinated Collections of Micro-organisms (BCCM) is a Belgian government funded consortium of seven scientific institutions, who manage and exploit a collection of microbial and genetic resources. The consortium comprises more than 269,000 publicly available strains of bacteria including mycobacteria and cyanobacteria, filamentous fungi, yeasts, diatoms and plasmids.

Biopreservation is the use of natural or controlled microbiota or antimicrobials as a way of preserving food and extending its shelf life. The biopreservation of food, especially utilizing lactic acid bacteria (LAB) that are inhibitory to food spoilage microbes, has been practiced since early ages, at first unconsciously but eventually with an increasingly robust scientific foundation. Beneficial bacteria or the fermentation products produced by these bacteria are used in biopreservation to control spoilage and render pathogens inactive in food. There are a various modes of action through which microorganisms can interfere with the growth of others such as organic acid production, resulting in a reduction of pH and the antimicrobial activity of the un-dissociated acid molecules, a wide variety of small inhibitory molecules including hydrogen peroxide, etc. It is a benign ecological approach which is gaining increasing attention.

Marine microorganisms are defined by their habitat as microorganisms living in a marine environment, that is, in the saltwater of a sea or ocean or the brackish water of a coastal estuary. A microorganism is any microscopic living organism or virus, that is too small to see with the unaided human eye without magnification. Microorganisms are very diverse. They can be single-celled or multicellular and include bacteria, archaea, viruses and most protozoa, as well as some fungi, algae, and animals, such as rotifers and copepods. Many macroscopic animals and plants have microscopic juvenile stages. Some microbiologists also classify viruses as microorganisms, but others consider these as non-living.
The Microbial Culture Collection is a microbial culture collection centre in Pune, India. The facility acts as a national depository, supplying authentic microbial cultures and providing related services to research institutions, universities, industries and the scientific community in general. It is funded by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT).
Microbial electrosynthesis (MES) is a form of microbial electrocatalysis in which electrons are supplied to living microorganisms via a cathode in an electrochemical cell by applying an electric current. The electrons are then used by the microorganisms to reduce carbon dioxide to yield industrially relevant products. The electric current would ideally be produced by a renewable source of power. This process is the opposite to that employed in a microbial fuel cell, in which microorganisms transfer electrons from the oxidation of compounds to an anode to generate an electric current.
Microbial food cultures are live bacteria, yeasts or moulds used in food production. Microbial food cultures carry out the fermentation process in foodstuffs. Used by humans since the Neolithic period fermentation helps to preserve perishable foods and to improve their nutritional and organoleptic qualities. As of 1995, fermented food represented between one quarter and one third of food consumed in Central Europe. More than 260 different species of microbial food culture are identified and described for their beneficial use in fermented food products globally, showing the importance of their use.

The viral shunt is a mechanism that prevents marine microbial particulate organic matter (POM) from migrating up trophic levels by recycling them into dissolved organic matter (DOM), which can be readily taken up by microorganisms. The DOM recycled by the viral shunt pathway is comparable to the amount generated by the other main sources of marine DOM.
References
- ↑ "NCIMB website". www.ncimb.com.
- ↑ "National Collection of Industrial Bacteria". Nature. 166 (4209): 16. 1 July 1950. doi: 10.1038/166016b0 .
- ↑ SHEWAN, J. M.; FLOODGATE, G. D.; HAYES, P. R. (1 November 1958). "A National Type Culture Collection of Marine Bacteria". Nature. 182 (4647): 1423–1424. doi:10.1038/1821423a0. PMID 13600349. S2CID 20638564.
- ↑ Review of UK Microbial Culture Collections: an Independent Review Commissioned by the Office of Science & Technology (November 1994). HMSO.
- ↑ "NCIMB LIMITED - Overview (free company information from Companies House)". beta.companieshouse.gov.uk.
- ↑ "IDA: United Kingdom (National Collections of Industrial, Food and Marine Bacteria (NCIMB))". www.wipo.int.
- ↑ ‘A New Strategy for the UK Microbial Culture Collections: Government Response to the Independent Review of UK Microbial Culture Collections’ (July 1996) OST (DTI)
- ↑ "NCIMB: A genetic resource for the 21st Century and beyond - Laboratory News". www.labnews.co.uk.