
Pyrotechnics is the science and craft of creating such things as fireworks, safety matches, oxygen candles, explosive bolts and other fasteners, parts of automotive airbags, as well as gas-pressure blasting in mining, quarrying, and demolition. This trade relies upon self-contained and self-sustained exothermic chemical reactions to make heat, light, gas, smoke and/or sound. The name comes from the Greek words pyr ("fire") and tekhnikos.

The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) is a U.S.-based international nonprofit organization devoted to eliminating death, injury, property, and economic loss due to fire, electrical, and related hazards. As of 2023, the NFPA claims to have 50,000 members and 9,000 volunteers working with the organization through its 250 technical committees.

Within industry, piping is a system of pipes used to convey fluids from one location to another. The engineering discipline of piping design studies the efficient transport of fluid.

Fire safety is the set of practices intended to reduce destruction caused by fire. Fire safety measures include those that are intended to prevent the ignition of an uncontrolled fire and those that are used to limit the spread and impact of a fire.

"NFPA 704: Standard System for the Identification of the Hazards of Materials for Emergency Response" is a standard maintained by the U.S.-based National Fire Protection Association. First "tentatively adopted as a guide" in 1960, and revised several times since then, it defines the "Safety Square" or "Fire Diamond" which is used to quickly and easily identify the risks posed by hazardous materials. This helps determine what, if any, special equipment should be used, procedures followed, or precautions taken during the initial stages of an emergency response. It is an internationally accepted safety standard, and is crucial while transporting chemicals.
The International Code Council (ICC) is an American nonprofit standards organization, sponsored by the building trades, which was founded in 1994 through the merger of three regional model code organizations in the American construction industry. The organization creates the International Building Code (IBC), a model building code, which has been adopted for use as a base code standard by most jurisdictions in the United States. Despite its name, the International Code Council is not an international organization nor does it consistently follow international best practices.

A fire alarm system is a building system designed to detect, alert occupants, and alert emergency forces of the presence of fire, smoke, carbon monoxide, or other fire-related emergencies. Fire alarm systems are required in most commercial buildings. They may include smoke detectors, heat detectors, and manual fire alarm activation devices. All components of a fire alarm system are connected to a fire alarm control panel. Fire alarm control panels are usually found in an electrical or panel room. Fire alarm systems generally use visual and audio signalization to warn the occupants of the building. Some fire alarm systems may also disable elevators, which are unsafe to use during a fire under most circumstances.
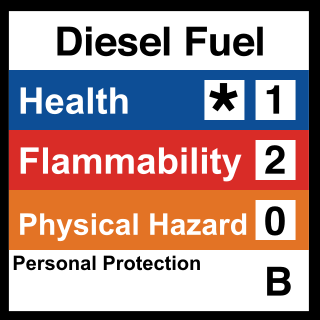
The Hazardous Materials Identification System (HMIS) is a proprietary numerical hazard rating that incorporates the use of labels with color bars developed by the American Coatings Association as a compliance aid for the OSHA Hazard Communication (HazCom) Standard. The name and abbreviation is a trademark of the American Coatings Association.

A wildland water tender is a specialized vehicle capable of bringing water, foam, or dry chemicals to fire trucks in the field that are engaged on the fireline. Water tenders have a large truck mounted tank that carries a minimum 1,000 gallons and up to 4,000 gallons of water. These vehicles are specifically designed for fire fighting often with four-wheel drive, rugged suspension and high wheel clearance for mountainous dirt road conditions. According to the National Fire Protection Association, if the apparatus will be used primarily for outdoor and wildland responses, then it is to be considered a wildland fire apparatus and must conform to NFPA 1906.

The British Compressed Air Society (BCAS) is the self appointed compressed air and vacuum trade association in the United Kingdom. It has membership for Manufacturers, Distributors, Suppliers and End-Users of compressed air equipment and systems.

The Electrical Safety Foundation (ESFI), formerly the Electrical Safety Foundation International, is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization based in Rosslyn, Virginia, US dedicated exclusively to promoting electrical safety at home, school, and in the workplace. Founded in 1994 as a cooperative effort by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), Underwriters Laboratories (UL), and the US Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC), ESFI is funded by charitable contributions from, distributors, Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratories, retailers, insurers, utilities, safety organizations, and trade and labor associations. The mission of the Electrical Safety Foundation (ESFI) is to prevent electrically-related injuries, deaths and fires; saving lives and property through public education and outreach.
Donald E. Washkewicz is the former chief executive officer of the Parker Hannifin Corporation located in Cleveland, Ohio. He served as chief executive officer from July 2001 to January 2015 and as president from February 2000 to January 2015. He retired as chairman of Parker Hannifin in 2016.
NFPA 1123, subtitled Code for Fireworks Display is a code created by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) to help prevent damage of property and the injury or death of individuals during outdoor firework displays. NFPA 1123 is the registered trademark of an American consensus standard which, like many NFPA documents, is systematically revised on a three year cycle.
An electrical contractor is a business person or firm that performs specialized construction work related to the design, installation, and maintenance of electrical systems. An electrical contractor is different from an electrician; an electrician is an individual tradesman and an electrical contractor is a business person or company that employs electricians. Both usually hold licenses and insurances to properly and safely operate a business, protecting the employees and home owners/business owners from insurance liabilities. These requirements vary from state to state. Electricians may work for an electrical contractor, or directly for individuals or companies.

Promotional merchandise are products branded with a logo or slogan and distributed at little or no cost to promote a brand, corporate identity, or event. Such products, which are often informally called promo products, swag, tchotchkes, or freebies, are used in marketing and sales. They are given away or sold at a loss to promote a company, corporate image, brand, or event. They are often distributed as handouts at trade shows, at conferences, on sales calls, and as bonus items in shipped orders. They are often used in guerrilla marketing campaigns.
The British Fluid Power Association is a trade association in the United Kingdom that represents the hydraulic and pneumatic equipment industry, utilising properties of fluid power.

Secutron Inc. is a manufacturer of engineered fire alarm systems supported by a global network of authorized Engineered Systems Distributors. Secutron is registered trademark of Mircom Technologies Ltd. and part of the Mircom Group of companies. Secutron has been manufacturing fire alarm systems since 1973, including conventional and intelligent fire alarm control panels, fire alarm networks, fire and security integration systems, and fire alarm accessories. Company is certified to the ISO 9001:2008 standards and guidelines.

In fire classes, a Class B fire is a fire in flammable liquids or flammable gases, petroleum greases, tars, oils, oil-based paints, solvents, lacquers, or alcohols. For example, propane, natural gas, gasoline and kerosene fires are types of Class B fires. The use of lighter fluid on a charcoal grill, for example, creates a Class B fire. Some plastics are also Class B fire materials.

High-voltage transformer fire barriers, also known as transformer firewalls, transformer ballistic firewalls, or transformer blast walls, are outdoor countermeasures against a fire or explosion involving a single transformer from damaging adjacent transformers. These barriers compartmentalize transformer fires and explosions involving combustible transformer oil.













