Niger or the Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state bordered by Libya to the northeast, Chad to the east, Nigeria to the south, Benin and Burkina Faso to the southwest, Mali to the west, and Algeria to the northwest. It covers a land area of almost 1,270,000 km2 (490,000 sq mi), making it the largest landlocked country in West Africa. Over 80% of its land area lies in the Sahara. Its predominantly Muslim population of about 25 million live mostly in clusters in the south and west of the country. The capital Niamey is located in Niger's southwest corner.

Niamey is the capital and largest city of Niger. Niamey lies on the Niger River, primarily situated on the east bank. Niamey's population was counted as 1,026,848 as of the 2012 census. As of 2017, population projections show the capital district growing at a slower rate than the country as a whole, which has the world's highest fertility rate. The city is located in a pearl millet growing region, while manufacturing industries include bricks, ceramic goods, cement, and weaving.
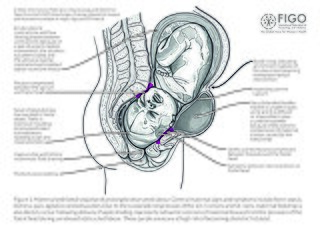
Obstetric fistula is a medical condition in which a hole develops in the birth canal as a result of childbirth. This can be between the vagina and rectum, ureter, or bladder. It can result in incontinence of urine or feces. Complications may include depression, infertility, and social isolation.

Hama Amadou is a Nigerien politician who was Prime Minister of Niger from 1995 to 1996 and again from 2000 to 2007. He was also Secretary-General of the National Movement for the Development of Society (MNSD-Nassara) from 1991 to 2001 and President of the MNSD-Nassara from 2001 to 2009. Amadou is from the Kurtey, a Fula sub-group, and was raised in the Tillaberi Region, in the Niger River valley, north of Niamey.

The music of Niger has developed from the musical traditions of a mix of ethnic groups; Hausa, the Zarma-Songhai, Tuareg, Fula Kanuri, Toubou, Diffa Arabs and Gurma and the Boudouma from Lac Chad.

Dosso is a city in the south-west corner of Niger. It lies 130–140 kilometres (81–87 mi) south-east of the capital Niamey at the junction of the main routes to Zinder and Benin. The eighth-most populous town in Niger and the largest in Dosso Region, it had an official population during the 2001 census of 43,561. The population grew to 58,671 in the 2012 census. It is the capital of its region - which covers five departments in the southwestern corner of the nation - as well as of its own department, Dosso Department. The city itself lies at the centre of its own Urban Commune.

Islam in Niger accounts for the vast majority of the nation's religious adherents. The faith is practiced by more than 99.3% of the population, although this figure varies by source and percentage of the population who are classified as Animist. The vast majority of Muslims in Niger are Malikite Sunni with Salafi influences. Many of the communities who continue to practice elements of traditional religions do so within a framework of syncretic Islamic belief, making agreed statistics difficult. Islam in Niger, although dating back more than a millennium, gained dominance over traditional religions only in the 19th and early 20th centuries, and has been marked by influences from neighboring societies. Sufi brotherhoods have become the dominant Muslim organization, like much of West Africa. Despite this, a variety of interpretations of Islam coexist—largely in peace—with one another as well as with minorities of other faiths. The government of Niger is secular in law while recognising the importance of Islam to the vast majority of its citizens.

The government and people of Niger observe twelve official public holidays. These include international commemorations, the commemoration of important dates in the history of Niger, and religious holidays. Both Christian and Muslim holidays are observed as official public holidays.

The Gendarmerie Nationale is the national gendarmerie of Niger. The Gendarmerie Nationale are under the Niger Armed Forces and report to the Ministry of Defense. They are responsible for law enforcement in rural areas. Niger's civilian police force, the National Police, is a separate agency under the Ministry of Interior, Public Safety and Decentralization, and are responsible for policing in urban areas.

Fistula Foundation is a nonprofit 501(c)(3) organization focused on treatment of obstetric fistula, funding more repair surgeries than any other organization, public or private. As of September 2022, they support hospitals and doctors in over 20 countries across Africa and Asia. The foundation is dedicated to treating obstetric fistula by covering the full cost of fistula repair surgery for poor women who would otherwise not be able to access treatment. They also provide fistula surgeon training, equipment and facility upgrades that make fistula treatment as safe as possible, post-surgery counseling and support for healed patients. The foundation has been recognized by several organizations for its transparency, effectiveness and efficiency, earning a top "A" rating from Charity Watch and a four star rating from Charity Navigator for 16 years in a row, placing it in the top 1% of charities reviewed on the site. In 2023, the foundation received a $15 million gift from philanthropist MacKenzie Scott, announced alongside a new five-year strategic plan that will advance the foundation's In It to End It vision. The foundation has also been selected as one of 22 charities recommended by Princeton Professor Peter Singer's organization, The Life You Can Save. The organization's cost-effectiveness was also noted by GiveWell in 2019.

Abdou Moumouni University, formerly the University of Niamey from 1974 to 1994, is a public university based in Niamey, the capital of Niger. The main campus is situated on the right bank of the Niger River. Historically, its students and faculty have been involved in protest movements in the capital.

According to the Republic of Niger's Constitution of 1999, most human rights, as defined by the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, are upheld and protected. Despite these protections, concerns of both domestic and international human rights organizations have been raised over the behavior of the government, military, police forces, and over the continuation of traditional practices which contravene the 1999 constitution. Under French colonial rule (1900–1960) and from independence until 1992, citizens of Niger had few political rights, and lived under arbitrary government power. Although the situation has improved since the return to civilian rule, criticisms remain over the state of human rights in the country.

Association Sportive des Forces Armées Nigériennes or simply AS FAN is a Nigerien football club based in Niamey and operated by the Nigerien Armed Forces. They play at the stade du camp Bagagi Iya, a small stadium in one of Niamey's military bases, although larger matches are played at the stade Général Seyni Kountché. Their current club president is Army Lieutenant Colonel Djibrilla Hima Hamidou.

Niger is a landlocked country located in West Africa and has Libya, Chad, Nigeria, Benin, Mali, Burkina Faso, and Algeria as its neighboring countries. Niger was French territory that got its independence in 1960 and its official language is French. Niger has an area of 1.267 million square kilometres, nevertheless, 80% of its land area spreads through the Sahara Desert.

The Niamey Grand Market is the largest market and shopping center in Niamey, the capital and largest city in the West African state of Niger.

The 2009–2010 Nigerien constitutional crisis occurred in Niger due to a political conflict between President Mamadou Tandja and judicial and legislative bodies regarding the Constitutional referendum that opponents claimed was an attempt to extend his mandate beyond the constitutional maximum. It was held on 4 August 2009 before a parliamentary election which was mandated to take place by 26 August 2009. The crisis eventually led to a coup d'état by military leaders who overthrew President Tandja and formed a ruling junta.

Ali Badjo Gamatié is a Nigerien politician and civil servant who served as Prime Minister of Niger from October 2009 to February 2010. He was Minister of Finance from 2000 to 2002 and then served as Vice-Governor of the Central Bank of West African States (BCEAO) before being appointed as Prime Minister by President Mamadou Tandja. Gamatié was Prime Minister for only a few months, however, as Tandja was overthrown in a February 2010 military coup.
Lamordé University Hospital or Lamordé National Hospital is a teaching hospital in Niamey, Niger. Affiliated with Abdou Moumouni University, the facility has 72 beds. It was the first public hospital in Niger to provide fistula repair services.
National Day of Concorde is a national holiday in Niger, celebrated every 24 April since 1995.

















