Related Research Articles
Directly observed treatment, short-course is the name given to the tuberculosis (TB) control strategy recommended by the World Health Organization. According to WHO, "The most cost-effective way to stop the spread of TB in communities with a high incidence is by curing it. The best curative method for TB is known as DOTS." DOTS has five main components:

Pulse Polio is an immunisation campaign established by the government of India to eliminate poliomyelitis (polio) in India by vaccinating all children under the age of five years against the polio virus. The project fights polio through a large-scale, pulse vaccination programme and monitoring for poliomyelitis cases.

The Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) in charge of international health cooperation in the Americas. It fosters technical cooperation among member countries to fight communicable and noncommunicable diseases, strengthen health systems, and respond to emergencies and disasters.
Lepra (Leprosy Relief Association) is a UK-based international charity established in 1924, working to diagnose, treat, and rehabilitate people with leprosy. Lepra currently works in India, Bangladesh, and Zimbabwe.

Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety of pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa, and parasitic worms (helminths). These diseases are contrasted with the "big three" infectious diseases, which generally receive greater treatment and research funding. In sub-Saharan Africa, the effect of neglected tropical diseases as a group is comparable to that of malaria and tuberculosis. NTD co-infection can also make HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis more deadly.

The Ministry of Health is the ministry of the Government of Turkey responsible for proposing and executing the government policy on health, planning and providing healthcare and protecting consumers. Likewise, it is responsible for proposing and executing the government policy on social cohesion and inclusion, family, protection of minors, youth and of care for dependent or disabled persons. The Ministry is headquartered in the Bakanlıklar in Ankara.

The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, also known by its abbreviation MoHFW, is an Indian government ministry charged with health policy in India. It is also responsible for all government programs relating to family planning in India.
The National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP), earlier known as the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP), is the Public Health initiative of the Government of India that organizes its anti-Tuberculosis efforts. It functions as a flagship component of the National Health Mission (NHM) and provides technical and managerial leadership to anti-tuberculosis activities in the country. As per the National Strategic Plan 2017–25, the program has a vision of achieving a "TB free India",with a strategies under the broad themes of "Prevent, Detect,Treat and Build pillars for universal coverage and social protection". The program provides, various free of cost, quality tuberculosis diagnosis and treatment services across the country through the government health system.
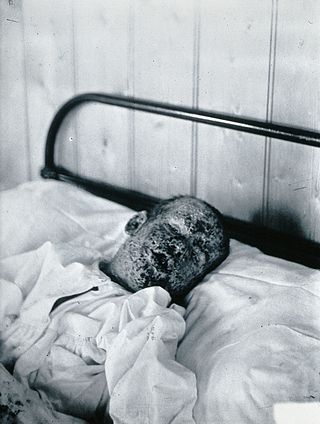
The eradication of infectious diseases is the reduction of the prevalence of an infectious disease in the global host population to zero.

Yōhei Sasakawa is chairman of The Nippon Foundation, the World Health Organization Goodwill Ambassador for Leprosy Elimination, and Japan's Ambassador for the Human Rights of People Affected by Leprosy. His global fight against leprosy and its accompanying stigma and social discrimination is an issue to which he has remained highly committed for more than 40 years. As chairman of The Nippon Foundation, Japan's largest charitable foundation, he guides public-interest activities in modern Japan. Sasakawa received his degree from Meiji University’s School of Political Science and Economics. Sasakawa's father was businessman, politician, and philanthropist Ryōichi Sasakawa.
Leprosy stigma is a type of social stigma, a strong negative feeling towards a person with leprosy relating to their moral status in society. It is also referred to as leprosy-related stigma, leprostigma, and stigma of leprosy. Since ancient times, leprosy instilled the practice of fear and avoidance in many societies because of the associated physical disfigurement and lack of understanding behind its cause. Because of the historical trauma the word "leprosy" invokes, the disease is now referred to as Hansen's disease, named after Gerhard Armauer Hansen who discovered Mycobacterium leprae, the bacterial agent that causes Hansen's disease. Those who have suffered from Hansen's disease describe the impact of social stigma as far worse than the physical manifestations despite it being only mildly contagious and pharmacologically curable. This sentiment is echoed by Weis and Ramakrishna, who noted that "the impact of the meaning of the disease may be a greater source of suffering than symptoms of the disease".
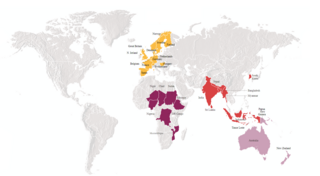
The Leprosy Mission is a Christian international NGO. They are the largest and oldest organisation working in the fight against leprosy and are working towards the goal of zero leprosy transmission by 2035.
Leprosy currently affects approximately a quarter of a million people throughout the world, with the majority of these cases being reported from India.

Worldwide, two to three million people are estimated to be permanently disabled because of leprosy. India has the greatest number of cases, with Brazil second and Indonesia third.
The Government of India has initiated several National Missions in order to achieve individual goals that together ensure the wellbeing of its citizens.

Tuberculosis in India is a major health problem, causing about 220,000 deaths every year. In 2020, the Indian government made statements to eliminate tuberculosis from the country by 2025 through its National TB Elimination Program. Interventions in this program include major investment in health care, providing supplemental nutrition credit through the Nikshay Poshan Yojana, organizing a national epidemiological survey for tuberculosis, and organizing a national campaign to tie together the Indian government and private health infrastructure for the goal of eliminating the disease.
The London Declaration on Neglected Tropical Diseases was a collaborative disease eradication programme launched on 30 January 2012 in London. It was inspired by the World Health Organization roadmap to eradicate or prevent transmission for neglected tropical diseases by the year 2020. Officials from WHO, the World Bank, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the world's 13 leading pharmaceutical companies, and government representatives from US, UK, United Arab Emirates, Bangladesh, Brazil, Mozambique and Tanzania participated in a joint meeting at the Royal College of Physicians to launch this project. The meeting was spearheaded by Margaret Chan, Director-General of WHO, and Bill Gates, Co-Chair of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
India National PolioPlus Society is a non-profit organization. The Initiative has achieved significant progress toward its goals. There has been a dramatic decline in cases everywhere in the seventeen years since the target was set in 1988.
Neglected tropical diseases in India are a group of bacterial, parasitic, viral, and fungal infections that are common in low income countries but receive little funding to address them. Neglected tropical diseases are common in India.
The Kigali Declaration on Neglected Tropical Diseases is a global health project that aims to mobilise political and financial resources for the control and eradication of infectious diseases, the so-called neglected tropical diseases. Launched by the Uniting to Combat Neglected Tropical Diseases on 27 January 2022, it was the culmination and join commitment declared at the Kigali Summit on Malaria and Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) hosted by the Government of Rwanda at Kigali on 23 June 2022.
References
- ↑ Mittal, B. N. (1991). "The national leprosy eradication programme in India". World Health Statistics Quarterly. 44 (1): 23–29. ISSN 0379-8070. PMID 2068822.
- ↑ "National Leprosy Eradication Programme (NLEP)". nlep.nic.in. Government of India. Retrieved 9 May 2018.
- ↑ "National Leprosy Eradication Programme (NLEP)". nlep.nic.in. Government of India. Retrieved 9 May 2018.