Related Research Articles
Lieutenant General Srinivas Kumar Sinha, PVSM, ADC was an Indian Army General who served as the Vice Chief of Army Staff. After his retirement, he served as Governor of the states of Jammu and Kashmir, and Assam.

The National Security Advisor is the senior official on the National Security Council of India, and the chief advisor to the Prime Minister of India on national security policy and international affairs. In 2019, the term of Ajit Doval the current NSA was extended for another 5-year term, and has been asigned the rank of a Union Cabinet Minister and ranks at the seventh position in the Indian Order of Precedence.

India-Singapore relations, also known as Indian-Singaporean relations or Indo-Singaporeanrelations, are the bilateral relations between India and Singapore. Relations between the two countries have traditionally been strong and friendly, with the two nations enjoying extensive cultural and commercial relations. India and Singapore have signed the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) and strategic-relationship agreement in order to increase trade, investments and economic cooperation, and expanded bilateral cooperation on maritime security, training forces, joint naval exercises, developing military technology and fighting terrorism.
Swordfish is an Indian active electronically scanned array (AESA) long-range tracking radar specifically developed to counter ballistic missile threat. It will be a part of the Indian Ballistic Missile Defense Programme. First testing of this radar was in March 2009. Main aim of the test was to validate the capabilities of the Swordfish Long Range Tracking Radar (LRTR). "The missile to be hit will be fired from a longer distance than it was in the earlier test. DRDO tested whether the radar could track the incoming missile from that distance or not," said a member of the project. This radar is an acknowledged derivative of the Israeli EL/M-2080 Green Pine long range radar, which is the critical component of that country's Arrow missile defense system. However, it differs from the Israeli system as it employs Indian Transmit Receive modules, signal processing, computers and power supplies. It is also more powerful than the base Green Pine system and was developed to meet India's specific BMD needs.

General Bipin Rawat was an Indian military officer who was a four-star general of the Indian Army. He served as the first Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) of the Indian Armed Forces from January 2020 until his death in a helicopter crash in December 2021. Prior to taking over as the CDS, he served as the 57th Chairman of the Chiefs of Staff Committee of the Indian Armed Forces as well as 26th Chief of the Army Staff (COAS) of the Indian Army.
Lieutenant General Syed Ata HasnainPVSM, UYSM, AVSM, SM, VSM & Bar is a retired General of the Indian Army. His last assignment in service was as the Military Secretary of the Indian Army. Prior to that, he commanded the Indian Army's 15 Corps in the state of Jammu and Kashmir, amongst other appointments. He has also commanded 21 Corps (Strike). In 2018, General Hasnain was appointed Chancellor of Central University of Kashmir.

St. Edward's School is a premier convent school located at Milsington Estate, Shimla, Himachal Pradesh, India. It is a boys-only day school. St. Edward's has been ranked among the top schools in India. It was initially affiliated to CISCE but was changed over to the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) system in 2008. Today the School is managed by Simla Chandigarh Educational Society, under the Bishop of Simla Chandigarh Diocese. The school offers education from Nursery to Class XII.

India's 'Connect Central Asia' Policy is a broad-based approach, including political, security, economic and cultural connections. The importance of this policy was strengthened when the Prime Minister of India visited all the five countries— Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan— in 2015.
The minimum support price (MSP) is an advisory price signal that is part of a larger set of agricultural policies in parts of India. This informal "support" price is recommended by the government and aims to safeguard the farmer to a minimum profit for the harvest while at the same time increasing food security in the country. MSP was initially an incentive for farmers to adopt technology with an aim of increasing the productivity of agricultural land in the 1960s, however in the 2000s it is seen as a market intervention and farmer income scheme. The effectiveness of such a price policy has varied widely between states and commodities. Awareness among farmers of the existence of an MSP is poor at 23%, while awareness of MSP procurement agencies is also poor with only about 20–25% of wheat and paddy produce being sold at MSP.

Pralay is a canisterised tactical, surface-to-surface, short-range ballistic missile (SRBM) for battlefield use developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of India. The missile is an amalgamation of technologies developed for exoatmospheric interceptor missile Prithvi Defence Vehicle (PDV) from Indian Ballistic Missile Defence Programme and Prahaar tactical missile. The project to develop Pralay was sanctioned in March 2015 with a budget of ₹332.88 crore.
The Defence Planning Committee is a senior decision-making organisation created on 19 April 2018 by the Government of India.

The Chairman, Chiefs of Staff Committee is a position in the Indian Armed Forces, usually held by a four-star officer serving as the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) of the Indian military. The position holder chairs the Chiefs of Staff Committee, and serves as the principal adviser to the prime minister and Minister of Defence. The position is not a statutory office but rather a title held by the senior most serving military officer of India. Until 2020, the chairmanship of the COSC was held in rotation by the senior-most service chief until his retirement, but this arrangement was found to be unsatisfactory. Thus, when the post of the CDS was established, its holder was also made the permanent Chairman COSC.

The Chief of Defence Staff of the Indian Armed Forces (CDS) is the professional head and permanent Chairman of the Chiefs of Staff Committee (COSC) of the Indian Armed Forces. The Chief of Defence Staff is the highest-ranking uniformed officer on active duty in the Indian military and chief military adviser to the Minister of Defence. The Chief also heads the Department of Military Affairs. The CDS is assisted by a vice-chief, the Chief of Integrated Defence Staff.

Lieutenant General Vinod G. Khandare, PVSM, AVSM, SM is a former officer of the Indian Army and is currently serving as the Principal Adviser in the Ministry of Defence. He retired from active military service on 31 January 2018 and was the Military Advisor to the National Security Council Secretariat of India at the Secretary level from 2018 to 2021. In his final active military appointment, he served as both the Director General of the Defence Intelligence Agency and the Deputy Chief of Integrated Defence Staff for Intelligence from November 2015 to January 2018.
Air Defence Command is a proposed integrated tri-services command of the Indian Armed Forces. The command will be headed by an Indian Air Force officer.
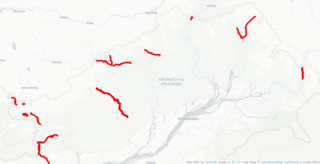
India–China Border Roads is a Government of India project for developing infrastructure along the Sino-Indian border by constructing strategic roads, including bridges and tunnels. The ICBR project is largely in response to Chinese infrastructure development along the borderlands with India.
The China Study Group (CSG) of the Government of India is an informal official group set up for advising the government on its China policy. It is a confidential body made up of inter-ministerial secretary-level officials. Set up by the Cabinet Committee on Political Affairs under the Indira Gandhi government in November 1975, it was first headed by diplomat K.R. Narayanan. It has been under the charge of civil servants such as Brajesh Mishra and Ajit Doval.

The HAL Combat Air Teaming System (CATS) is an Indian unmanned and manned combat aircraft air teaming system being developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). The system will consist of a manned fighter aircraft acting as "mothership" of the system and a set of swarming UAVs and UCAVs governed by the mothership aircraft. A twin-seated HAL Tejas is likely to be the mothership aircraft. Various other sub components of the system are currently under development and will be jointly produced by HAL, National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL), Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Newspace Research & Technologies.
Vishwa Guru or vishwaguru is a Sanskrit phrase and idea which translates to world or global teacher, world guru, tutors of the world, world leader, or teacher to the world or universe.
Deepak Rawat is an Indian civil servant who serves in the Uttarakhand cadre of the Indian Administrative Service (IAS). Rawat is currently posted as the Commissioner of Kumaon division, Uttarakhand.
References
- 1 2 "Indian military must be prepared for threats from China, Pakistan: Bipin Rawat". mint. 4 March 2021. Retrieved 4 March 2021.
Some important steps that we need to take, include-- defining the national security strategy [...]
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ Saran, Shyam (4 June 2019). "Need for a Comprehensive National Security Strategy". Centre for Policy Research. Retrieved 4 March 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ Menon, Raja (8 February 2021). "India Must Chart Out a National Security Strategy for a Changing Geopolitical World". The Wire. Retrieved 4 March 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ Sethi, Deepak (26 August 2020). "China Impasse the Product of India's Lack of National Security Strategy, Accountability". The Wire. Retrieved 4 March 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ Pandit, Rajat (2 May 2018). "New defence panel to focus on national security, reforms in 1st meeting". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 2 January 2019. Retrieved 2 January 2019.
- ↑ "Doval chairs first meet of defence panel". The Hindu. 4 May 2018. Retrieved 4 May 2018.
- ↑ Joshi, Manoj (23 April 2019). "Modi Isn't the Only 'Chowkidar', He Can Learn from Hooda Report". TheQuint. Retrieved 4 March 2021.
- ↑ Raza, Mohd Rameez and Shekhar, Raj, Defence Acquisition Procedure, 2020: Great Boast, Little Roast (July 4, 2021). Law School Policy Review, 2021, Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3893191
- ↑ "Defence Acquisition Procedure 2020" (PDF). Ministry of Defence, Government of India. p. 7. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 February 2021. Retrieved 13 November 2021.