
An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been part of a continent. Oceanic islands can be formed from volcanic activity, grow into atolls from coral reefs, and form from sediment along shorelines, creating barrier islands. River islands can also form from sediment and debris in rivers. Artificial islands are those made by humans, including small rocky outcroppings built out of lagoons and large-scale land reclamation projects used for development.
A single market, sometimes called common market or internal market, is a type of trade bloc in which most trade barriers have been removed with some common policies on product regulation, and freedom of movement of the factors of production and of enterprise and services. The goal is that the movement of capital, labour, goods, and services between the members is as easy as within them. The physical (borders), technical (standards) and fiscal (taxes) barriers among the member states are removed to the maximum extent possible. These barriers obstruct the freedom of movement of the four factors of production.

A levee, dike, dyke, embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is a structure used to keep the course of rivers from changing and to protect against flooding of the area adjoining the river or coast. It is usually earthen and often runs parallel to the course of a river in its floodplain or along low-lying coastlines.

Environmental determinism is the study of how the physical environment predisposes societies and states towards particular economic or social developmental trajectories. Jared Diamond, Jeffrey Herbst, Ian Morris, and other social scientists sparked a revival of the theory during the late twentieth and early twenty-first centuries. This "neo-environmental determinism" school of thought examines how geographic and ecological forces influence state-building, economic development, and institutions. While archaic versions of the geographic interpretation were used to encourage colonialism and eurocentrism, modern figures like Diamond use this approach to reject the racism in these explanations. Diamond argues that European powers were able to colonize, due to unique advantages bestowed by their environment, as opposed to any kind of inherent superiority.
The Camargue is a coastal region in southern France located south of the city of Arles, between the Mediterranean Sea and the two arms of the Rhône river delta. The eastern arm is called the Grand Rhône; the western is the Petit Rhône.

Guns, Germs, and Steel: The Fates of Human Societies is a 1997 transdisciplinary non-fiction book by the American author Jared Diamond. The book attempts to explain why Eurasian and North African civilizations have survived and conquered others, while arguing against the idea that Eurasian hegemony is due to any form of Eurasian intellectual, moral, or inherent genetic superiority. Diamond argues that the gaps in power and technology between human societies originate primarily in environmental differences, which are amplified by various positive feedback loops. When cultural or genetic differences have favored Eurasians, he asserts that these advantages occurred because of the influence of geography on societies and cultures and were not inherent in the Eurasian genomes.

Borders are generally defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders can be established through warfare, colonization, or mutual agreements between the political entities that reside in those areas.

Barrier islands are a coastal landform, a type of dune system and sand island, where an area of sand has been formed by wave and tidal action parallel to the mainland coast. They usually occur in chains, consisting of anything from a few islands to more than a dozen. They are subject to change during storms and other action, but absorb energy and protect the coastlines and create areas of protected waters where wetlands may flourish. A barrier chain may extend for hundreds of kilometers, with islands periodically separated by tidal inlets. The largest barrier island in the world is Padre Island of Texas, United States, at 113 miles (182 km) long. Sometimes an important inlet may close permanently, transforming an island into a peninsula, thus creating a barrier peninsula, often including a beach, barrier beach. Though many are long and narrow, the length and width of barriers and overall morphology of barrier coasts are related to parameters including tidal range, wave energy, sediment supply, sea-level trends, and basement controls. The amount of vegetation on the barrier has a large impact on the height and evolution of the island.

An environmental disaster or ecological disaster is defined as a catastrophic event regarding the natural environment that is due to human activity. This point distinguishes environmental disasters from other disturbances such as natural disasters and intentional acts of war such as nuclear bombings.

Dangerous goods (DG), are substances that are a risk to health, safety, property or the environment during transport. Certain dangerous goods that pose risks even when not being transported are known as hazardous materials. An example for dangerous goods is hazardous waste which is waste that has substantial or potential threats to public health or the environment.

Coastal geography is the study of the constantly changing region between the ocean and the land, incorporating both the physical geography and the human geography of the coast. It includes understanding coastal weathering processes, particularly wave action, sediment movement and weather, and the ways in which humans interact with the coast.

The Mississippi River Delta is the confluence of the Mississippi River with the Gulf of Mexico in Louisiana, southeastern United States. The river delta is a three-million-acre area of land that stretches from Vermilion Bay on the west, to the Chandeleur Islands in the east, on Louisiana's southeastern coast. It is part of the Gulf of Mexico and the Louisiana coastal plain, one of the largest areas of coastal wetlands in the United States. The Mississippi River Delta is the 7th largest river delta on Earth (USGS) and is an important coastal region for the United States, containing more than 2.7 million acres of coastal wetlands and 37% of the estuarine marsh in the conterminous U.S. The coastal area is the nation's largest drainage basin and drains about 41% of the contiguous United States into the Gulf of Mexico at an average rate of 470,000 cubic feet per second.

River engineering is a discipline of civil engineering which studies human intervention in the course, characteristics, or flow of a river with the intention of producing some defined benefit. People have intervened in the natural course and behaviour of rivers since before recorded history—to manage the water resources, to protect against flooding, or to make passage along or across rivers easier. Since the Yuan Dynasty and Ancient Roman times, rivers have been used as a source of hydropower. From the late 20th century, the practice of river engineering has responded to environmental concerns broader than immediate human benefit. Some river engineering projects have focused exclusively on the restoration or protection of natural characteristics and habitats.

Roman military borders and fortifications were part of a grand strategy of territorial defense in the Roman Empire, although this is a matter of debate. By the early 2nd century, the Roman Empire had reached the peak of its territorial expansion and rather than constantly expanding their borders as earlier in the Empire and Republic, the Romans solidified their position by fortifying their strategic position with a series of fortifications and established lines of defense. Historian Adrian Goldsworthy argues that the Romans had reached the natural limits which their military traditions afforded them conquest over and that beyond the borders of the early-to-mid Empire lay peoples whose military traditions made them militarily unconquerable, despite many Roman battle victories. In particular, Goldsworthy argues that the cavalry-based warfare of the Parthians, Sarmatians and Persians presented a major challenge to the expansion of Rome's infantry-based armies.
Deforestation during the Roman period was a result of the geographical expansion of the Roman Empire, with its increased population, large-scale agriculture, and unprecedented economic development. Roman expansion marks the transition in the Mediterranean from prehistory to the historical period beginning around 500 BC. Earth sustained a few million people 8,000 years ago and was still fundamentally pristine, but Rome drove human development in Western Europe and was a leading contributor of the deforestation around the Mediterranean.
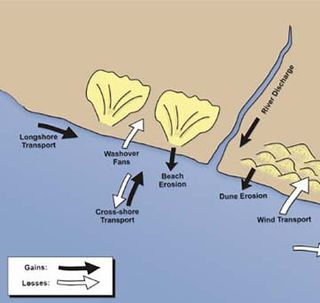
Sedimentary budgets are a coastal management tool used to analyze and describe the different sediment inputs (sources) and outputs (sinks) on the coasts, which is used to predict morphological change in any particular coastline over time. Within a coastal environment the rate of change of sediment is dependent on the amount of sediment brought into the system versus the amount of sediment that leaves the system. These inputs and outputs of sediment then equate to the total balance of the system and more than often reflect the amounts of erosion or accretion affecting the morphology of the coast.

A river is a natural freshwater stream that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it runs out of water, or only flow during certain seasons. Rivers are regulated by the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Water first enters rivers through precipitation, whether from the runoff of water down a slope, the melting of glaciers or snow, or seepage from aquifers beneath the surface of the Earth.

The Canterbury Bight is a large bight on the eastern side of New Zealand's South Island. The bight runs for approximately 135 kilometres (84 mi) from the southern end of Banks Peninsula to the settlement of Timaru and faces southeast, exposing it to high-energy storm waves originating in the Pacific Ocean. The bight is known for rough conditions as a result, with wave heights of over 2 metres (6.6 ft) common. Much of the bight's geography is shaped by this high-energy environment interacting with multiple large rivers which enter the Pacific in the bight, such as the Rakaia, Ashburton / Hakatere, and Rangitata Rivers. Sediment from these rivers, predominantly Greywacke, is deposited along the coast and extends up to 50 kilometres (31 mi) out to sea from the current shoreline. Multiple hapua, or river-mouth lagoons, can be found along the length of the bight where waves have deposited sufficient sediment to form a barrier across a river mouth, including most notably Lake Ellesmere / Te Waihora and Washdyke Lagoon
Coastal sediment supply is the transport of sediment to the beach environment by both fluvial and aeolian transport. While aeolian transport plays a role in the overall sedimentary budget for the coastal environment, it is paled in comparison to the fluvial supply which makes up 95% of sediment entering the ocean. When sediment reaches the coast it is then entrained by longshore drift and littoral cells until it is accreted upon the beach or dunes.

Coastal hazards are physical phenomena that expose a coastal area to the risk of property damage, loss of life, and environmental degradation. Rapid-onset hazards last a few minutes to several days and encompass significant cyclones accompanied by high-speed winds, waves, and surges or tsunamis created by submarine (undersea) earthquakes and landslides. Slow-onset hazards, such as erosion and gradual inundation, develop incrementally over extended periods.
















