Related Research Articles

In computer science, binary space partitioning (BSP) is a method for space partitioning which recursively subdivides a Euclidean space into two convex sets by using hyperplanes as partitions. This process of subdividing gives rise to a representation of objects within the space in the form of a tree data structure known as a BSP tree.

In mathematics, a Voronoi diagram is a partition of a plane into regions close to each of a given set of objects. It can be classified also as a tessellation. In the simplest case, these objects are just finitely many points in the plane. For each seed there is a corresponding region, called a Voronoi cell, consisting of all points of the plane closer to that seed than to any other. The Voronoi diagram of a set of points is dual to that set's Delaunay triangulation.

Constructive solid geometry is a technique used in solid modeling. Constructive solid geometry allows a modeler to create a complex surface or object by using Boolean operators to combine simpler objects, potentially generating visually complex objects by combining a few primitive ones.

Havok is a middleware software suite developed by the Irish company Havok. Havok provides physics engine, navigation, and cloth simulation components that can be integrated into video game engines.

In 3D computer graphics and solid modeling, a polygon mesh is a collection of vertices, edges and faces that defines the shape of a polyhedral object's surface. It simplifies rendering, as in a wire-frame model. The faces usually consist of triangles, quadrilaterals (quads), or other simple convex polygons (n-gons). A polygonal mesh may also be more generally composed of concave polygons, or even polygons with holes.
In computer graphics, level of detail (LOD) refers to the complexity of a 3D model representation. LOD can be decreased as the model moves away from the viewer or according to other metrics such as object importance, viewpoint-relative speed or position. LOD techniques increase the efficiency of rendering by decreasing the workload on graphics pipeline stages, usually vertex transformations. The reduced visual quality of the model is often unnoticed because of the small effect on object appearance when distant or moving fast.

A lightmap is a data structure used in lightmapping, a form of surface caching in which the brightness of surfaces in a virtual scene is pre-calculated and stored in texture maps for later use. Lightmaps are most commonly applied to static objects in applications that use real-time 3D computer graphics, such as video games, in order to provide lighting effects such as global illumination at a relatively low computational cost.
Quake Army Knife (QuArK) is a free and open-source program for developing 3D assets for a large variety of first-person shooters, such as video games using the Quake engine by id Software or the Torque engine.
In video games, artificial intelligence (AI) is used to generate responsive, adaptive or intelligent behaviors primarily in non-playable characters (NPCs) similar to human-like intelligence. Artificial intelligence has been an integral part of video games since their inception in 1948, first seen in the game Nim. AI in video games is a distinct subfield and differs from academic AI. It serves to improve the game-player experience rather than machine learning or decision making. During the golden age of arcade video games the idea of AI opponents was largely popularized in the form of graduated difficulty levels, distinct movement patterns, and in-game events dependent on the player's input. Modern games often implement existing techniques such as pathfinding and decision trees to guide the actions of NPCs. AI is often used in mechanisms which are not immediately visible to the user, such as data mining and procedural-content generation. One of the most infamous examples of this NPC technology and gradual difficulty levels can be found in the game Mike Tyson's Punch-Out!! (1987).
In video games, a bot or drone is a type of artificial intelligence (AI)–based expert system software that plays a video game in the place of a human. Bots are used in a variety of video game genres for a variety of tasks: a bot written for a first-person shooter (FPS) works differently from one written for a massively multiplayer online role-playing game (MMORPG). The former may include analysis of the map and even basic strategy; the latter may be used to automate a repetitive and tedious task like farming.

In 3D computer graphics, polygonal modeling is an approach for modeling objects by representing or approximating their surfaces using polygon meshes. Polygonal modeling is well suited to scanline rendering and is therefore the method of choice for real-time computer graphics. Alternate methods of representing 3D objects include NURBS surfaces, subdivision surfaces, and equation-based representations used in ray tracers.

3D GameStudio or 3DGS is a pan 3D computer game development system which allows the users to create 3D games and other virtual reality applications, and publish them royalty-free. It includes a model/terrain editor, a level editor, a script editor/debugger and comes with a big collection of textures, models and artwork, as well as a game template system that allows the creation of basic shooter games or RPGs without programming. For complex games or other applications, either the integrated programming language named Lite-C or an external development language such as Visual C++ or Borland Delphi can be used.

The Blender Game Engine was a free and open-source 3D production suite used for making real-time interactive content. It was previously embedded within Blender, but support for it was dropped in 2019, with the release of Blender 2.8. The game engine was written from scratch in C++ as a mostly independent component, and includes support for features such as Python scripting and OpenAL 3D sound.
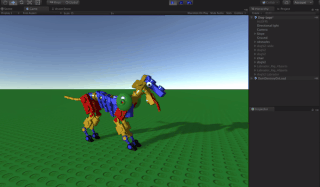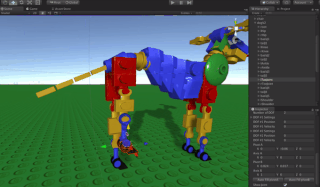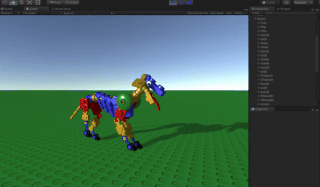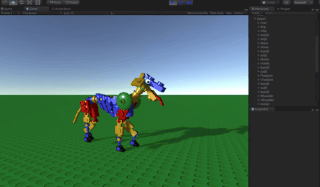
A procedural animation is a type of computer animation used to automatically generate animation in real-time to allow for a more diverse series of actions than would otherwise be tedious using predefined animations.

3D computer graphics, sometimes called CGI, 3-D-CGI or three-dimensional computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data that is stored in the computer for the purposes of performing calculations and rendering digital images, usually 2D images but sometimes 3D images. The resulting images may be stored for viewing later or displayed in real time.

Any-angle path planning algorithms are pathfinding algorithms that search for a Euclidean shortest path between two points on a grid map while allowing the turns in the path to have any angle. The result is a path that cuts directly through open areas and has relatively few turns. More traditional pathfinding algorithms such as A* either lack in performance or produce jagged, indirect paths.

In 3D computer graphics, 3D modeling is the process of developing a mathematical coordinate-based representation of a surface of an object in three dimensions via specialized software by manipulating edges, vertices, and polygons in a simulated 3D space.
xaitment is a German-based company that develops and sells artificial intelligence (AI) software to video game developers and simulation developers. The company was founded in 2004 by Dr. Andreas Gerber, and is a spin-off of the German Research Centre for Artificial Intelligence, or DFKI. xaitment has its main office in Quierschied, Germany, and field offices in San Francisco and China.
Autodesk Gameware is a discontinued middleware software suite developed by Autodesk. The suite contained tools that enable designers to create game lighting, character animation, low level path finding, high-level AI and advanced user interfaces. On July 12, 2017, Autodesk removed Scaleform, Beast, HumanIK, and Navigation from their online store, and announced the ending of support for the products.
References
- Arkin, Ronald C. (1986). "Path Planning for a Vision-Based Autonomous Robot" (PDF) (Technical Report). University of Massachusetts.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Brand, Sandy (2009). Efficient obstacle avoidance using autonomously generated navigation meshes (PDF) (Master thesis). Delft University of Technology. Retrieved 2015-06-09.
- Golodetz, Stuart (October 2013). "Automatic Navigation Mesh Generation in Configuration Space". Overload. 117. ACCU.
- Snook, Greg (2000). "Simplified 3D Movement and Pathfinding Using Navigation Meshes". In DeLoura, Mark (ed.). Game Programming Gems. Charles River Media. pp. 288–304. ISBN 1-58450-049-2.
- Tozour, Paul (2002). "Building a Near-Optimal Navigation Mesh". In Rabin, Steve (ed.). AI Game Programming Wisdom . Charles River Media. pp. 171–185. ISBN 1-58450-077-8.
- van Toll, Wouter G.; Cook IV, Atlas F.; Geraerts, Roland (2012). "A navigation mesh for dynamic environments" (PDF). Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds. 23 (6). John Wiley & Sons: 535–546. doi:10.1002/cav.1468. S2CID 2996937 . Retrieved 2015-06-09.
- van Waveren, J.M.P. (2001-01-28). The Quake III Arena Bot (PDF) (M.Sc. thesis). Delft University of Technology.