Other
- Naxos (mythology), eponym of the island Naxos
- Naxos disease, Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
- Naxos radar detector, a German World War II countermeasure
Naxos is a Greek island.
Naxos may also refer to:
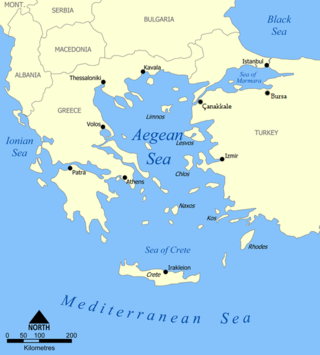
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some 215,000 km2 (83,000 sq mi). In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn connects to the Black Sea, by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus, respectively. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 2,639 m (8,658 ft) to the west of Karpathos. The Thracian Sea and the Sea of Crete are main subdivisions of the Aegean Sea.

Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and Corsica. Crete rests about 160 km (99 mi) south of the Greek mainland, and about 100 km (62 mi) southwest of Anatolia. Crete has an area of 8,450 km2 (3,260 sq mi) and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi). It bounds the southern border of the Aegean Sea, with the Sea of Crete to the north and the Libyan Sea to the south. Crete covers 260 km from west to east but is narrow from north to south, spanning three longitudes but only half a latitude.

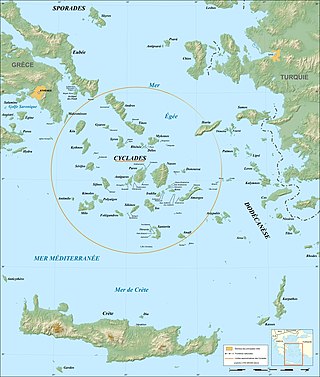
The Cyclades are an island group in the Aegean Sea, southeast of mainland Greece and a former administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The name refers to the archipelago forming a circle around the sacred island of Delos. The largest island of the Cyclades is Naxos, however the most populated is Syros.

Naxos is a Greek island and the largest of the Cyclades. It was the centre of the archaic Cycladic culture. The island is famous as a source of emery, a rock rich in corundum, which until modern times was one of the best abrasives available.

Paros is a Greek island in the central Aegean Sea. Part of the Cyclades island group, it lies to the west of Naxos, from which it is separated by a channel about 8 kilometres wide. It lies approximately 150 km south-east of Piraeus. The Municipality of Paros includes numerous uninhabited offshore islets totaling 196.308 square kilometres (75.795 sq mi) of land. Its nearest neighbor is the municipality of Antiparos, which lies to its southwest. In ancient Greece, the city-state of Paros was located on the island.

Andros is the northernmost island of the Greek Cyclades archipelago, about 10 km (6 mi) southeast of Euboea, and about 3 km (2 mi) north of Tinos. It is nearly 40 km (25 mi) long, and its greatest breadth is 16 km (10 mi). It is for the most part mountainous, with many fruitful and well-watered valleys. The municipality, which includes the island Andros and several small, uninhabited islands, has an area of 380 km2 (146.719 sq mi). The largest towns are Andros (town), Gavrio, Batsi, and Ormos Korthiou.

Milos or Melos is a volcanic Greek island in the Aegean Sea, just north of the Sea of Crete. Milos is the southwestern-most island in the Cyclades group.

Syros, also known as Siros or Syra, is a Greek island in the Cyclades, in the Aegean Sea. It is 78 nautical miles (144 km) south-east of Athens. The area of the island is 83.6 km2 (32 sq mi) and at the 2011 census it had 21,507 inhabitants.
Cycladic culture was a Bronze Age culture found throughout the islands of the Cyclades in the Aegean Sea. In chronological terms, it is a relative dating system for artifacts which serves as a roughly contemporary dating system to Helladic chronology and Minoan chronology (Crete) during the same period of time.

The Battle of Lade was a naval battle which occurred during the Ionian Revolt, in 494 BC. It was fought between an alliance of the Ionian cities and the Persian Empire of Darius the Great, and resulted in a decisive victory for the Persians which all but ended the revolt.

The history of Greece encompasses the history of the territory of the modern nation-state of Greece as well as that of the Greek people and the areas they inhabited and ruled historically. The scope of Greek habitation and rule has varied throughout the ages and as a result, the history of Greece is similarly elastic in what it includes. Generally, the history of Greece is divided into the following periods:
Marco Sanudo was the creator and first Duke of the Duchy of the Archipelago, in Italian: "Duca del Mare Egeo e Re di Candia", Barone delle Isole di Nasso, Pario, Milo, Marine ed Andri, duchy granted by the Republic of Venice to him and all his descendants, after the Fourth Crusade his lineage became named Sanudo de Candia.

Kea, also known as Tzia and in antiquity Keos, is a Greek island in the Cyclades archipelago in the Aegean Sea. Kea is part of the Kea-Kythnos regional unit.
Panormos or Panormus, meaning "sheltered harbor", may refer to:

The siege of Naxos was a failed attempt by the Milesian tyrant Aristagoras, operating with support from, and in the name of the Persian Empire of Darius the Great, to conquer the island of Naxos. It was the opening act of the Greco-Persian Wars, which would ultimately last for 50 years.

The siege of Eretria took place in 490 BC, during the first Persian invasion of Greece. The city of Eretria, on Euboea, was besieged by a strong Persian force under the command of Datis and Artaphernes.

Naxos is a city and a former municipality on the island of Naxos, in the Cyclades, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Naxos and Lesser Cyclades, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. The municipal unit has 12,726 inhabitants, and the community 7,374 inhabitants. The Naxos municipal unit covers an area of 126.957 square kilometres (49.018 sq mi). It is located on the west side of Naxos Island in the Cyclades island group in the Aegean. It was the centre of archaic Cycladic culture. It shares the island of Naxos with the municipal unit of Drymalia.
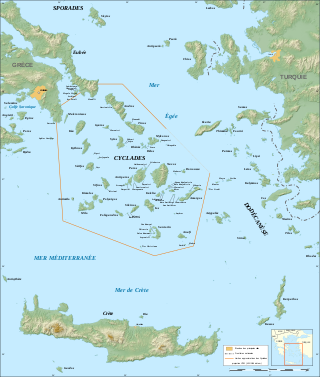
The Cyclades are Greek islands located in the southern part of the Aegean Sea. The archipelago contains some 2,200 islands, islets and rocks; just 33 islands are inhabited. For the ancients, they formed a circle around the sacred island of Delos, hence the name of the archipelago. The best-known are, from north to south and from east to west: Andros, Tinos, Mykonos, Naxos, Amorgos, Syros, Paros and Antiparos, Ios, Santorini, Anafi, Kea, Kythnos, Serifos, Sifnos, Folegandros and Sikinos, Milos and Kimolos; to these can be added the little Cyclades: Irakleia, Schoinoussa, Koufonisi, Keros and Donoussa, as well as Makronisos between Kea and Attica, Gyaros, which lies before Andros, and Polyaigos to the east of Kimolos and Thirassia, before Santorini. At times they were also called by the generic name of Archipelago.

The Wars of the Delian League were a series of campaigns fought between the Delian League of Athens and her allies, and the Achaemenid Empire of Persia. These conflicts represent a continuation of the Greco-Persian Wars, after the Ionian Revolt and the first and second Persian invasions of Greece.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to ancient Greece: