Related Research Articles
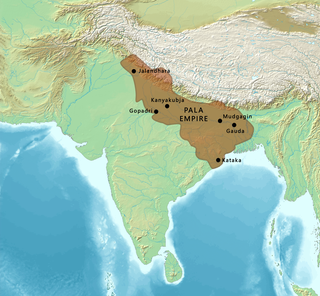
The Pāla Empire was an imperial power during the post-classical period in the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Bengal. It is named after its ruling dynasty, whose rulers bore names ending with the suffix Pāla. The empire was founded with the election of Gopāla as the emperor of Gauda in late eighth century CE. The Pala stronghold was located in Bengal and eastern Bihar, which included the major cities of Gauḍa, Vikramapura, Pāṭaliputra, Monghyr, Somapura, Ramavati (Varendra), Tāmralipta and Jagaddala.

The Kambojas were a southeastern Iranian people who inhabited the northeastern most part of the territory populated by Iranian tribes, which bordered the Indian lands. They only appear in Indo-Aryan inscriptions and literature, being first attested during the later part of the Vedic period.
Pala dynasty may refer to:
Kamboja may refer to:
Ancient Hindu and Buddhist texts use Uttarapatha as the name of the Northern part of Jambudvipa, one of the "continents" in Hindu mythology. In modern times, the Sanskrit word uttarapatha is sometimes used to denote the geographical regions of North India, Western India, Central India, Eastern India, Northeast India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Nepal in just one term. The pronunciation of the word varies depending on the regional language of the speaker.
Dharmapala is a Sanskrit name which means "protector of the Dharma". The Pāli equivalent is Dhammapala. The name is often used by Buddhists to refer to a variety of persons and concepts, including:

The Kamboja-Pala dynasty ruled parts of Bengal in the 10th to 11th centuries CE, after invading the Palas during the reign of Gopala III. The last Kamboja ruler of the Kamboja-Pala Dynasty Dharmapala was defeated by the south Indian Emperor Rajendra Chola I of the Chola dynasty in the 11th century.
Devapala, also known as Devapala the Great, was the emperor of the Pala Empire of Bengal. He was the third king in the line, and had succeeded his father Dharamapala. Devapala expanded the frontiers of the empire by conquering the present-day Assam and Orissa. The Pala inscriptions also credit him with several other victories.
Rajyapala or Kamboja-Vamsa-Tilaka was the founder of the Kamboja Pala dynasty of Bengal. This dynasty had ruled over northern and western Bengal. Four rulers of this dynasty are known who ruled, either over north-west Bengal or parts thereof, from second half of tenth century to the first quarter of the 11th century. The last known king of Kamboja Pala dynasty was Dharmapala, who was the ruler in Dandabhukti division, during the first quarter of the 11th century.
Rajya Pala may refer to:
Dharmapala Kamboja was probably the last ruler of Kamboja Pala dynasty of Bengal. He ruled Dandabhukti-mandala in Vardhamana-bhukti in the first quarter of eleventh century and was contemporary of Rajendra Chola of Chola dynasty of Deccan.
Vigrahapala II was the successor to the Pala king Gopala III in the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent, and tenth ruler of the Pala line reigning for at least 12 years. He was succeeded by the famed Mahipala.
Srichandra was the second and most influential ruler of the Chandra Dynasty in eastern Bengal.
Kalyanachandra was the third ruler of the Chandra dynasty in eastern Bengal. His campaign against the Kamboja dynasty in Varendra allowed the resurgent Pala Emperor Mahipala I to reclaim much of North Bengal.
Dandabhukti was an ancient and medieval territory located between the two rivers, Dwarakeswar and Subarnarekha, and situated in the Rarh region of the ancient Bengal. It covered the present-day districts of Purba Medinipur, Jhargram district and southern part of Paschim Medinipur in West Bengal, and Balasore district in Odisha, India.

The Medieval Chola emperor Rajendra Chola I led an Chola Expedition of the Ganges between 1019 and 1021. The expedition traversed the states of Vengi, Kalinga, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Odisha, Bengal, Bihar and Uttar Pradesh culminating with their arrival at the Ganges river. The Chola victory over the Pala king Mahipala I is considered to be the climax of the expedition. In 1019 CE, Rajendra's forces marched through Kalinga towards the river Ganga. In Kalinga the Chola forces defeated Indraratha the ruler of the Somavamsi dynasty. The Chola army eventually reached the Pala kingdom of Bengal where they defeated Mahipala. The Chola army also defeated the last ruler of the Kamboja Pala dynasty Dharmapala of Dandabhukti. The Chola army went on to raid East Bengal and defeated Govindachandra of the Chandra dynasty and invaded Bastar region.

Indra Pala was ruler of Pala Dynasty (900–1100) of Kamarupa Kingdom.
Dhanga, also known as Dhaṇgadeva in inscriptions, was a king of the Chandela dynasty of India. He ruled in the Jejakabhukti region. Dhanga established the sovereignty of the Chandelas, who had served as vassals to the Pratiharas until his reign. He is also notable for having commissioned magnificent temples at Khajuraho, including the Vishvanatha temple.

The Pahcimbhag copperplate inscription, Srichandra Paschimbhag copperplate inscription or simply Chandrapur inscription is a copperplate inscription issued in 935 by Srichandra, the second king of the Chandra Dynasty of south-east Bengal. The inscription was discovered in the village of Paschimbhag, Moulvibazar district. It is one of 12 known copperplate inscriptions by Chandra Dynasty kings. The inscription is mainly a deed of donation, in which Srichandra grants lands for many Brahmins and for nine monasteries in the Sylhet region, which formed Chandrapur University, named after Srichandra. It includes a detailed description of the Chandra kingdom and the Palas and Kamboja Pala rulers of Bengal and refers to the society of pre-medieval Bengal.
Gopala III previously known as Gopala II, was the successor to the Pala king Rajyapala in the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent, and ninth ruler of the Pala line reigning for 20 years. He was succeeded by Vigrahapala II.