Related Research Articles
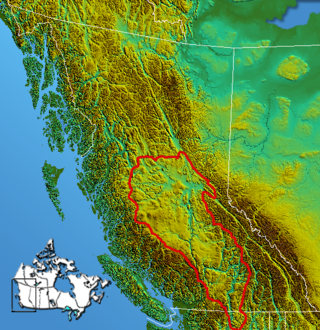
The Interior Plateau comprises a large region of the Interior of British Columbia, and lies between the Cariboo and Monashee Mountains on the east, and the Hazelton Mountains, Coast Mountains and Cascade Range on the west. The continuation of the plateau into the United States is known there as the Columbia Plateau.
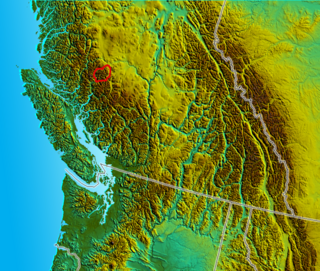
The Niut Range is 3600 km2 in area. It is a subrange of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains of British Columbia, although in some classifications it is considered part of the Chilcotin Ranges. The Niut is located in the angle of the Homathko River and its main west fork, Mosley Creek. It is isolated, island-like, by those rivers from its neighbour ranges, as both streams have their source on the Chilcotin Plateau in behind the range. Razorback Mountain is its highest peak.
Clendinning Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada. It surrounds the drainage of Clendinning Creek, which is a tributary of the Elaho River. Its name is shared by the Clendinning Range, of which Mount Clendinning is the highest summit.
Little Andrews Bay Marine Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada, located on Ootsa Lake in the Nechako Country in that province's Central Interior. It is 102 hectares in size.
Stuart River Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada. It is located in two sections north and northwest of Vanderhoof along the Stuart River southeast of Stuart Lake and the city of Fort St. James. The upper section is located at 54°13′20″N124°00′00″W and comprises c.7391 ha. while the lower, eastern section is centred at 54°03′00″N123°37′00″W and comprises c.3390 ha. and is within the Greater Prince George area. The upper site, which is located around the confluence of the Stuart and Nechako Rivers, includes the site of Chinlac, a Dakelh village whose inhabitants were massacred and enslaved by the Tsilhqot'in of Anahim Lake c. 1745.
The Nechako Plateau is the northernmost subdivision of the Interior Plateau, one of the main geographic regions of the Canadian province of British Columbia. It spans the basin of the Nechako River and its tributaries the Stuart River and Endako Rivers, and is bounded on the south by the West Road River, south of which is the Chilcotin Plateau and on the north by the Nation River and the valleys of Babine and Takla Lakes, beyond which are the Omineca Mountains (N) and Skeena Mountains (NW). To the west, it abuts the various ranges of the Hazelton Mountains while on its east it is bounded by the pass between Prince George, British Columbia and the Parsnip Arm of Williston Lake, beyond which is the McGregor Plateau, which skirts the Northern Rockies. Some classification systems include the plateau area on the east bank of the Fraser River beyond the city of Prince George; this area neighbours the northernmost reaches of the Quesnel Highland and Cariboo Mountains.

Nautley River drains Fraser Lake into the Nechako River in the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada.
The Lytton First Nation, a First Nations band government, has its headquarters at Lytton in the Fraser Canyon region of the Canadian province of British Columbia. While it is the largest of all Nlaka'pamux bands, unlike all other governments of the Nlaka'pamux (Thompson) people, it is not a member of any of the three Nlaka'pamux tribal councils, which are the Nicola Tribal Association, the Fraser Canyon Indian Administration and the Nlaka'pamux Nation Tribal Council.
The Sikanni Range is a subrange of the Omineca Mountains in the Northern Interior of British Columbia, located between the Omineca and Atsika Rivers.
The Hartley Bay Indian Band is also known as the Gitga'at First Nation or the Hartley Bay First Nation. The members of the Gitga'at First nation are often referred to as Gitka'a'ata. The population of Gitk’a’ata peoples living in Hartley Bay ranges from approximately 130-200 people. There are also about 400-500 Gitk’a’ata peoples living in Prince Rupert, British Columbia, Canada, a neighboring territory. The Gitk’a’ata people have lived in Hartley Bay for hundreds of years, if not always. Some notable things regarding the Gitga'at First Nation are their economy, geography, government, sports involvement, COVID-19 regulations, and relations.
The Cadwallader Range, originally named the Cadwallader Mountains, is a sub-range of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains in the Bridge River-Lillooet Country of the South-Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada, located between the south end of Anderson Lake (E) and the Hurley River. According to the provincial basemap, the precise alpine boundaries of the range are McGilliray Pass, at its eastern extremity and beyond which is the Bendor Range, and the pass between Noel and Sockeye Creeks on its west, which is immediately north of the lower end of Birkenhead Lake. The officially unnamed range west of that has been called the Noel Range, after its main peak Mount Noel. At the foot of the range along its northeast flank is Cadwallader Creek, scene of the historic and once-rich Bralorne and Pioneer Mines and the ghost town of Bralorne.
The Sawtooth Range is a subrange of the Shuswap Highland area of the central Monashee Mountains in the Southern Interior of British Columbia, Canada. It is located between Mabel Lake (W) and Sugar Lake (E) and bounded on the south by the upper Shuswap River. Its northern boundary is just south of the Three Valley Gap area of Eagle Pass, which is the route of the Canadian Pacific Railway mainline and the Trans-Canada Highway. To the east, across the uppermost Shuswap River above Sugar Lake, is the Gold Range of the main spine of the Monashees, to which it is connected by the col of Joss Pass. To the west, it is adjoined by the rest of the Shuswap Highland, of which it is a part and is an intermediary mountainous plateau between the Monashees and the northeastern Thompson Plateau.
Joss Pass, 1345 m (4413 ft), is a mountain pass in the central Monashee Mountains of the Southern Interior of British Columbia, Canada. Located just south of the Three Valley Gap area of Eagle Pass, which is the route of the Trans-Canada Highway and the mainline of the Canadian Pacific Railway. It forms the divide between the headwaters of the Shuswap River and those of its eventual tributary Wap Creek, which joins the Shuswap via Mabel Lake. It forms the prominence col for Tsuius Mountain, the highest mountain of the Sawtooth Range, which is part of the Shuswap Highland. It is located just east of Joss Mountain, which is the northernmost peak of the Sawtooths.
The Quaal River is a river in the Kitimat Ranges of the Coast Mountains in British Columbia, Canada, flowing south into Kitkiata Inlet in the North Coast region.
Kitkiata Inlet is an inlet on the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada, off the west side of Douglas Channel. Kitkiata Creek flows into the inlet from the north at 53°38′18″N129°16′20″W. Up it at 53°42′51″N129°17′27″W is Kitkiata Lake.
Lejac is a locality on the Canadian National Railway line in the Nechako Country region of British Columbia, located on the south shore of Fraser Lake between the communities of Fraser Lake (W) and Fort Fraser (E).
The Telegraph Range is a small hill-range located on the Nechako Plateau to the south of Ootsa Lake in the Cariboo Land District of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. It was named by George M. Dawson to commemorate the route of the Collins Overland Telegraph, which lay along the range's northeast flank. The range is approximately 750 km2 in area.
Mount Swannell, 1821 m (5974 ft), prominence 771 m, is a mountain in the Fawnie Range of the Nechako Plateau in the Central Interior region of British Columbia, Canada. It is located to the south of the outlet of the Entiako River into Natalkuz Lake, which is part of the Nechako Reservoir. The northernmost of the summits of the Fawnie Range and is in the northeastern end of Entiako Provincial Park, it is the only named summit of the Fawnie Range within the park.
The Fawnie Range is a small hill-range located to the south of the Ootsa Lake reservoir and to the north of the West Road River in the Nechako Plateau region of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. The northwest part of the park is within Entiako Provincial Park and includes Mount Swannell,, one of the range's main summits, overlooking Natalkuz Lake from the south. Other named summits include Tutial Mountain, Fawnie Dome and Fawnie Nose, the highest summit in the range.
Fawnie Nose is the highest summit of the Fawnie Range of the Nechako Plateau in the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. The range is located north of the West Road River and to the south of the Natalkuz Lake portion of the Ootsa Lake reservoir.